MIG (GMAW) WELDING 5-12 Manual 0-5492
5.12 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Basic Welding Technique
Two different welding processes are covered in this section (GMAW and FCAW), with the intention of providing
the very basic concepts in using the Mig mode of welding, where a welding gun is hand held, and the electrode
(welding wire) is fed into a weld puddle, and the arc is shielded by an inert welding grade shielding gas or inert
welding grade shielding gas mixture.
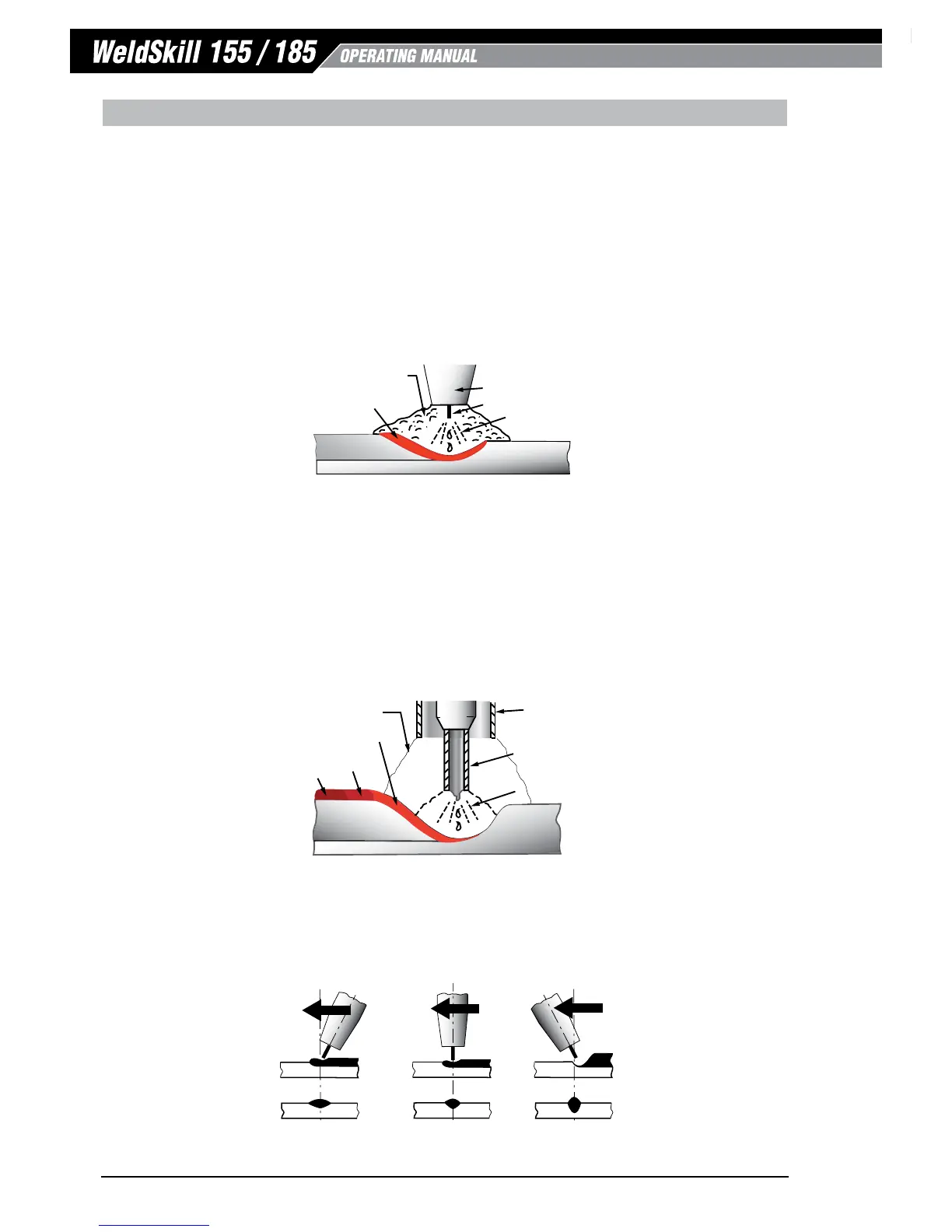
GAS METAL ARC WELDING (GMAW): This process, also known as MIG welding, CO
2
welding, Micro Wire
Welding, short arc welding, dip transfer welding, wire welding etc., is an electric arc welding process which
fuses together the parts to be welded by heating them with an arc between a solid continuous, consumable
electrode and the work. Shielding is obtained from an externally supplied welding grade shielding gas or welding
grade shielding gas mixture. The process is normally applied semi automatically; however the process may
be operated automatically and can be machine operated. The process can be used to weld thin and fairly thick
steels, and some non-ferrous metals in all positions.
Art # A-8991_AB
Shielding Gas
eld Metal
Solidified
Weld Metal
Nozzle
Electrode
Arc
Base Metal
GMAW Process
Figure 5-14
FLUX CORED ARC WELDING (FCAW): This is an electric arc welding process which fuses together the parts to
be welded by heating them with an arc between a continuous flux filled electrode wire and the work. Shielding
is obtained through decomposition of the flux within the tubular wire. Additional shielding may or may not be
obtained from an externally supplied gas or gas mixture. The process is normally applied semi automatically;
however the process may be applied automatically or by machine. It is commonly used to weld large diameter
electrodes in the flat and horizontal position and small electrode diameters in all positions. The process is used
to a lesser degree for welding stainless steel and for overlay work.
Art # A-08992_AB
Molten
Slag
Nozzle
(Optional)
 Loading...
Loading...











