0-5492 7-5 TIG (GTAW) Welding
7.03 TIG (GTAW) Basic Welding Technique
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) or TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) as it is commonly referred to, is a weld-
ing process in which fusion is produced by an electric arc that is established between a single tungsten
(non-consumable) electrode and the work piece. Shielding is obtained from a welding grade shielding gas
or welding grade shielding gas mixture which is generally Argon based. A filler metal may also be added
manually in some circumstances depending on the welding application.
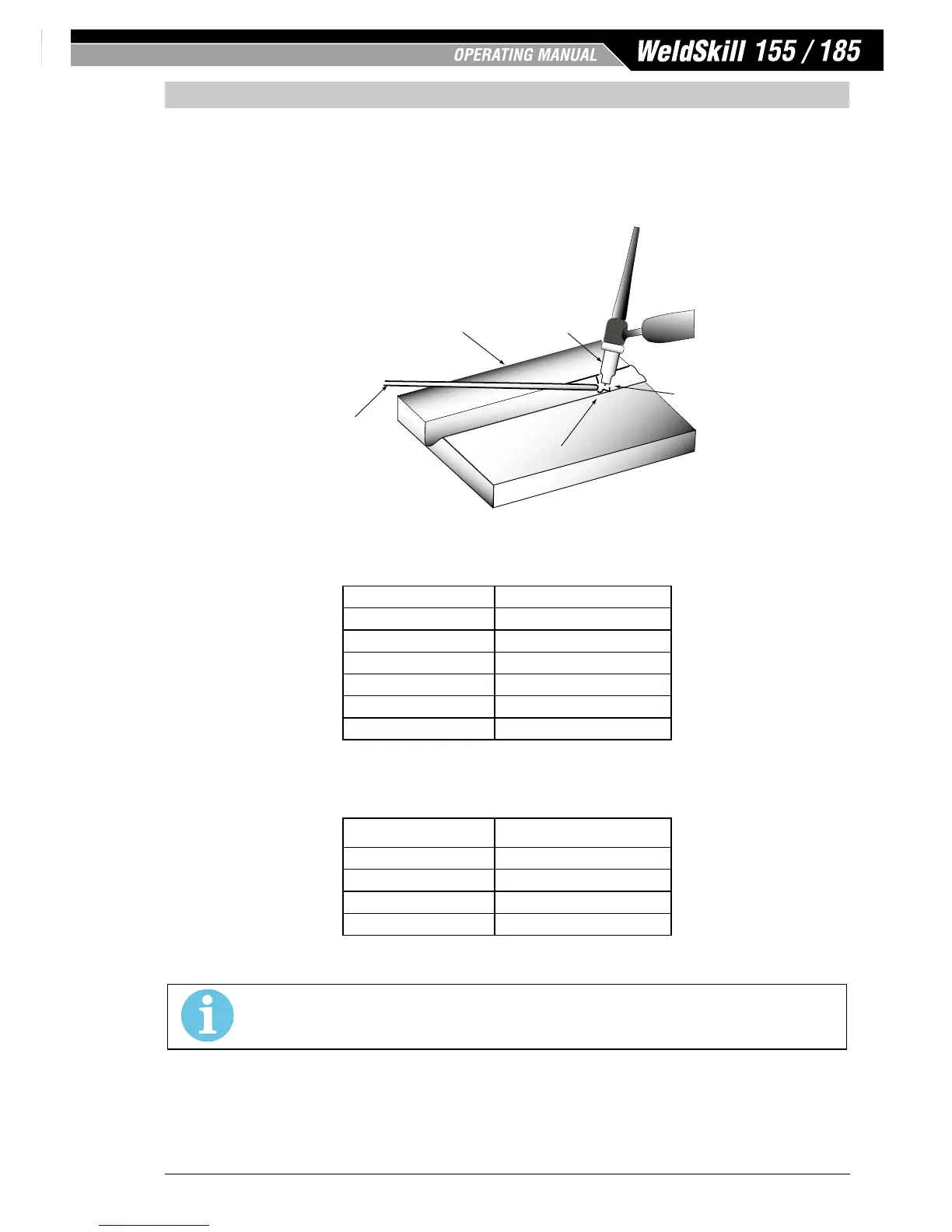
Welds Made With or Without
Addition of Filler Metal
Work Piece
Can Be Any Commercial
Metal
Gas Cup
Either Ceramic,
High-lmpact or
Water Cooled
Metal
Inert Gas
Shields Electrode
and Weld Puddle
Non-Consumable
Art # A-09658_AC
Figure 7-5: TIG Welding Application Shot
Tungsten Electrode Current Ranges
Electrode Diameter DC Current (Amps)
0.040” (1.0mm) 30-60
1/16” (1.6mm) 60-115
3/32” (2.4mm) 100-165
1/8” (3.2mm) 135-200
5/32” (4.0mm) 190-280
3/16” (4.8mm) 250-340
Table 7-1: Current Ranges for Various Tungsten Electrode Sizes
Guide for Selecting Filler Wire Diameter
Filler Wire Diameter DC Current Range (Amps)
1/16” (1.6mm) 20-90
3/32” (2.4mm) 65-115
1/8” (3.2mm) 100-165
3/16” (4.8mm) 200-350
Table 7-2: Filler Wire Selection Guide
NOTE!
The operator should use the welding current range values as a guide only, then nally adjust the current setting to suit
the application.
 Loading...
Loading...











