Configuring Modular QoS Congestion Avoidance on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers
Information About Configuring Modular QoS Congestion Avoidance on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers
QC-75
Cisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Router Modular Quality of Service Configuration Guide
OL-23108-02
WRED makes early detection of congestion possible and provides for multiple classes of traffic. It also
protects against global synchronization. For these reasons, WRED is useful on any output interface in
which you expect congestion to occur.
However, WRED is usually used in the core routers of a network, rather than at the edge of the network.
Edge routers assign IP precedences to packets as they enter the network. WRED uses these precedences
to determine how to treat different types of traffic.
WRED provides separate drop thresholds (minimum and maximum) for different classification criteria
(such as IP precedences, MPLS EXP values), allowing you to provide different qualities of service in
regard to packet dropping for different traffic types. Standard traffic may be dropped more frequently
than premium traffic during periods of congestion.
WRED treats non-IP traffic as precedence 0, the lowest precedence. Therefore, non-IP traffic, in general,
is more likely to be dropped than IP traffic.
WRED is useful only when the bulk of the traffic is TCP/IP traffic. With TCP, dropped packets indicate
congestion, so the packet source reduces its transmission rate. With other protocols, packet sources may
not respond or may resend dropped packets at the same rate. Thus, dropping packets does not decrease
congestion.
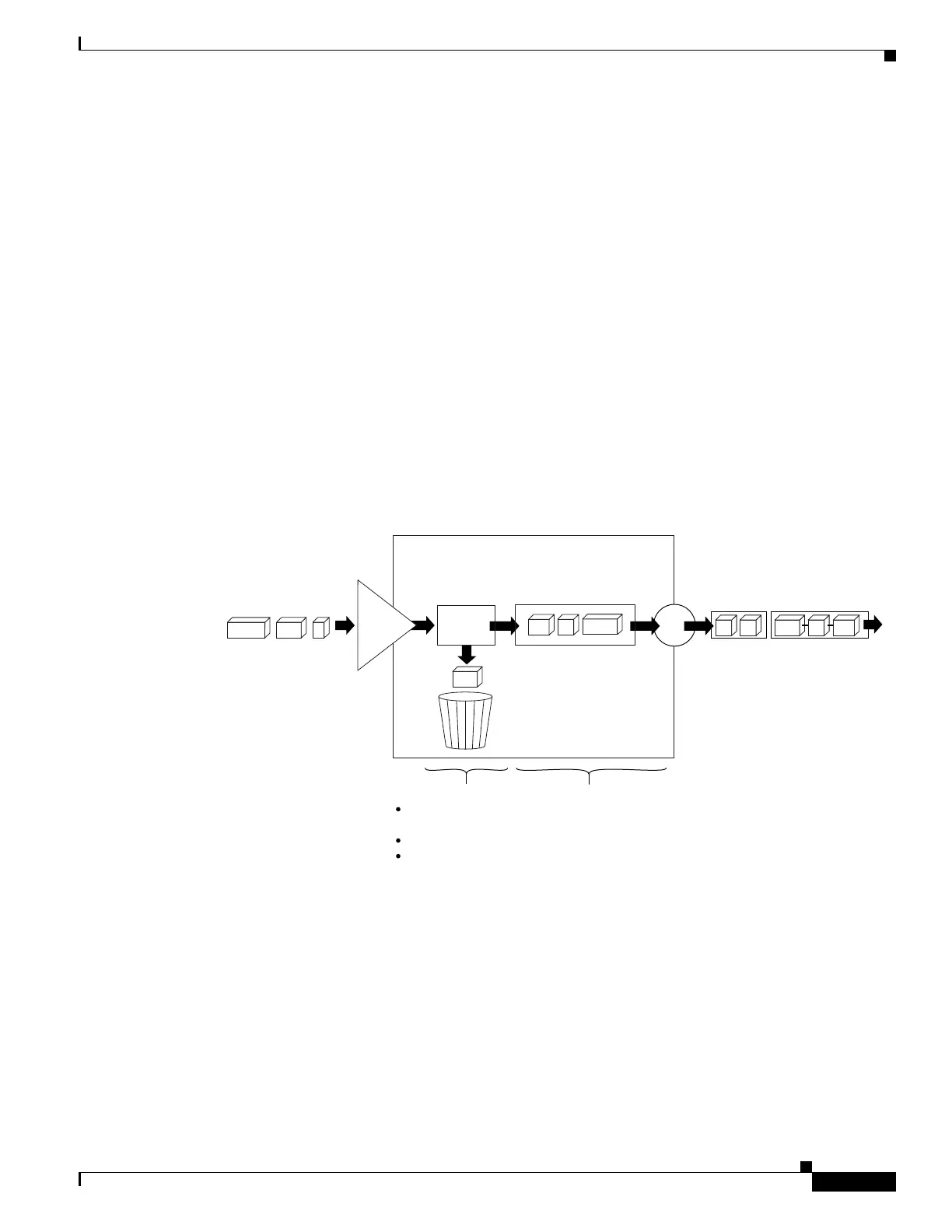
Figure 1 illustrates how WRED works.
Figure 1 Weighted Random Early Detection
Queue-limit for WRED
Queue-limit is used to fine-tune the number of buffers available for each queue. It can only be used on
a queuing class. Default queue limit is 100 ms of the service rate for the given queue. The service rate
is the sum of minimum guaranteed bandwidth and bandwidth remaining assigned to a given class either
implicitly or explicitly.
The queue-limit is rounded up to one of the following values: 8 KB, 16 KB, 24 KB, 32 KB, 48 KB, 64
KB, 96 KB, 128 KB, 192 KB, 256 KB, 384 KB, 512 KB, 768 KB, 1024 KB, 1536 KB, 2048 KB, 3072
KB, 4196 KB, 8192 KB, 16394 KB, 32768 KB, 65536 KB, 131072 KB, or 262144 KB.
Incoming packets
Transmit
queue
Outgoing
packets
FIFO scheduling
Queueing
buffer
resources
16759
Discard test based on:
Buffer queue
depth
IP Precedence
RSVP session
Classify
Discard test

 Loading...
Loading...











