25-17
Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide
OL-10088-01
Chapter 25 Configuring Application Layer Protocol Inspection
DNS Inspection
Step 4 If DNS inspection is disabled or if you want to change the maximum DNS packet length, configure DNS
inspection. DNS application inspection is enabled by default with a maximum DNS packet length of 512
bytes. For configuration instructions, see the “Configuring Application Inspection” section on
page 25-5.
Step 5 On the public DNS server, add an A-record for the web server, such as:
domain-qualified-hostname. IN A mapped-address
where domain-qualified-hostname is the hostname with a domain suffix, as in server.example.com. The
period after the hostname is important. mapped-address is the translated IP address of the web server.
The following example configures the security appliance for the scenario shown in Figure 25-1. It
assumes DNS inspection is already enabled.
hostname(config)# static (inside,outside) 209.165.200.225 192.168.100.1 netmask
255.255.255.255 dns
hostname(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp any host 209.165.200.225 eq www
hostname(config)# access-group 101 in interface outside
This configuration requires the following A-record on the DNS server:
server.example.com. IN A 209.165.200.225
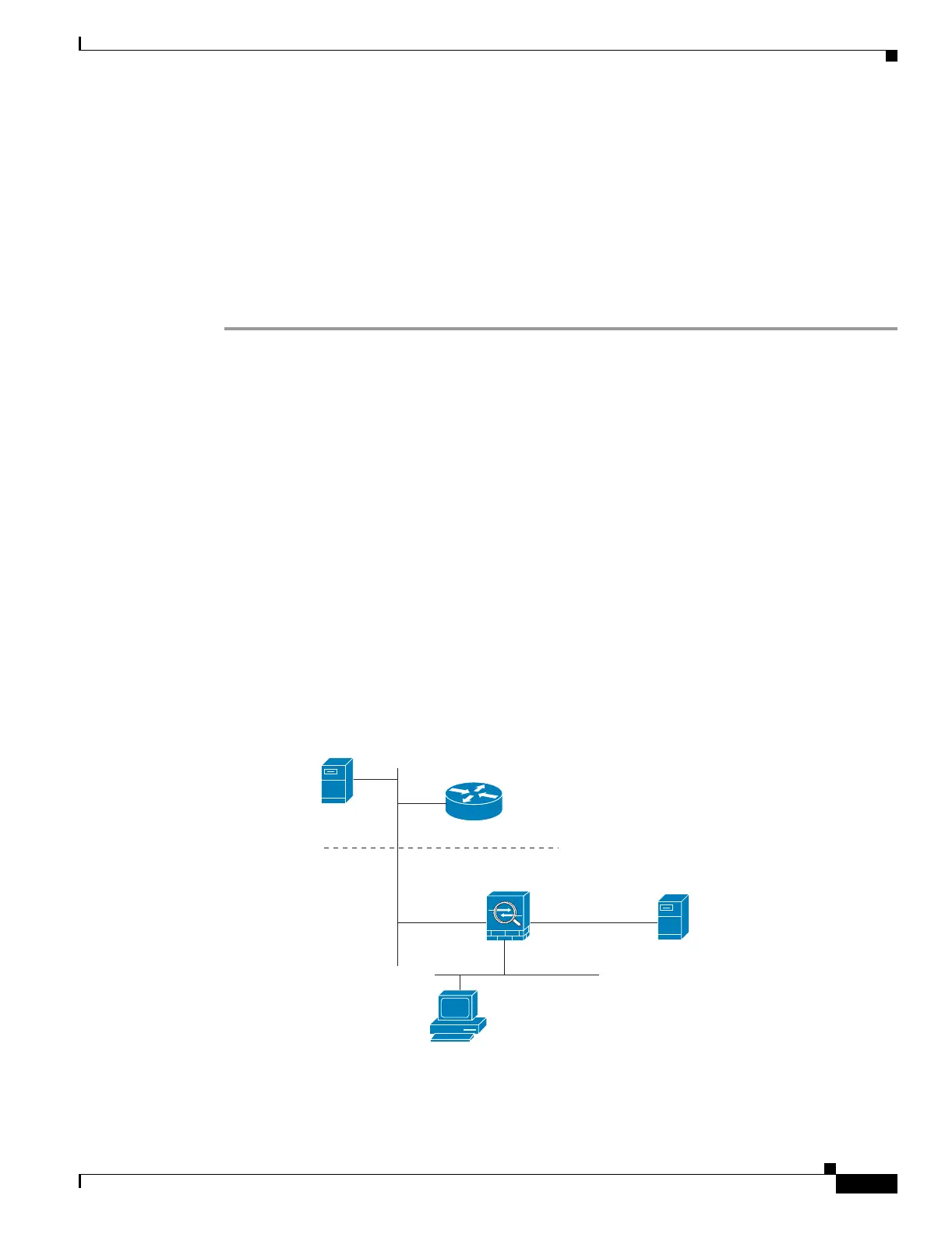
DNS Rewrite with Three NAT Zones
Figure 25-2 provides a more complex scenario to illustrate how DNS inspection allows NAT to operate
transparently with a DNS server with minimal configuration. For configuration instructions for scenarios
like this one, see the “Configuring DNS Rewrite with Three NAT Zones” section on page 25-19.
Figure 25-2 DNS Rewrite with Three NAT Zones
132407
Web client
10.10.10.25
Web server
192.168.100.10
DNS server
rver.example.com IN A 209.165.200.5
Security
appliance
Outside
DMZ
192.168.100.1
10.10.10.1
Inside
99.99.99.2

 Loading...
Loading...











