42
Curtis PMC 1204/1205 Manual
APPENDIX B
APPENDIX B
PULSE WIDTH MODULATION
B-1
+
–
+
THROTTLE
POTBOX
FILTER
CAPS
POWER
MOSFETS
MOTOR
FIELD
PLUG
DIODE
FREEWHEEL
DIODE
ARM
TIME
MOTOR CURRENT
CURRENT PATH DURING
TRANSISTOR
ON
TIME
CURRENT PATH DURING
TRANSISTOR
OFF
TIME
BATTERY
CONTROL
CIRCUITRY
(SHADED AREA REPRESENTS CONTROLLER)
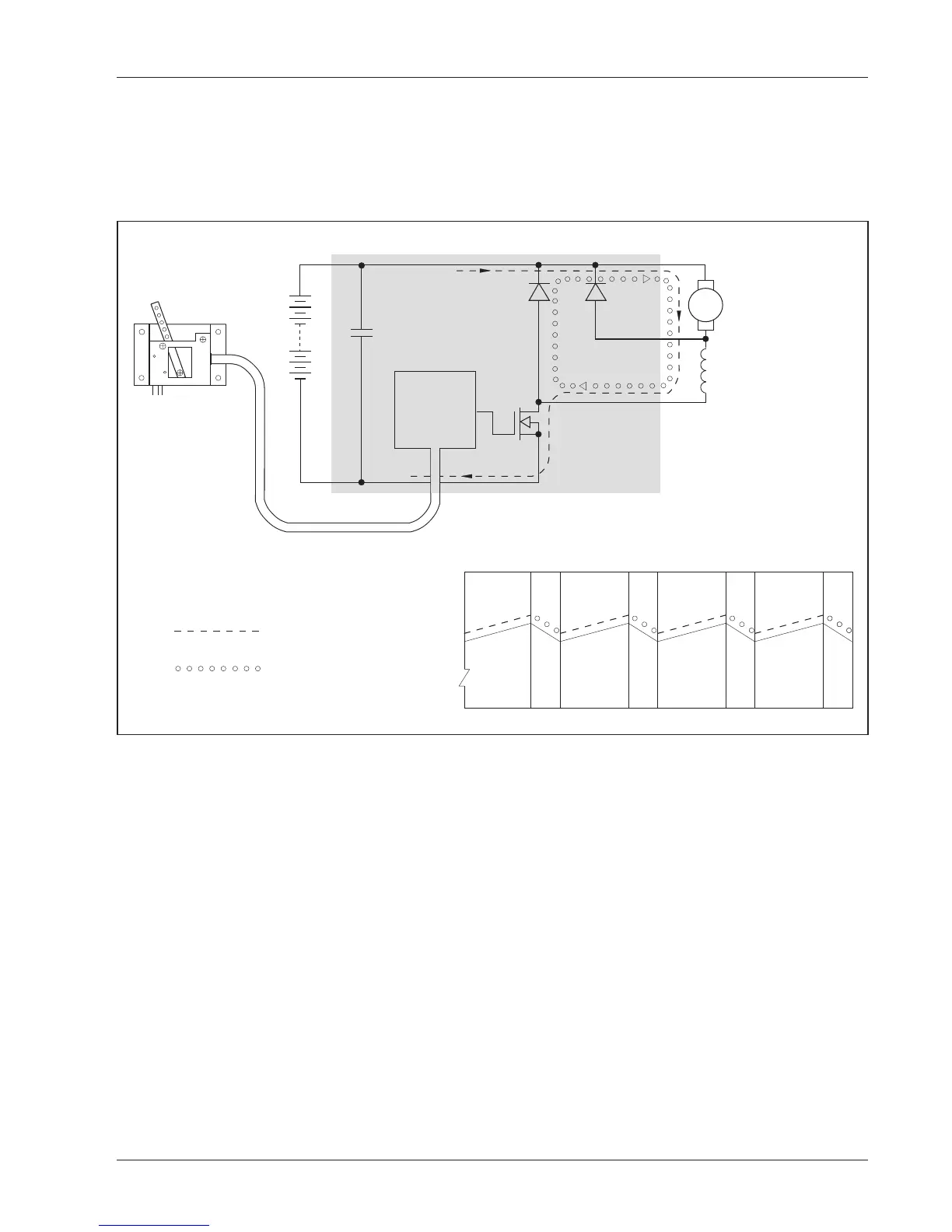
Fig. B-1 Pulse width modulation.
A high power semiconductor switch, consisting of an array of parallel power MOSFET transistors,
controls the current in the motor windings. The transistors are connected in series with the battery
and the motor. The transistors are turned on and off 15,000 times per second by the controller
circuitry, while the ratio of the on/off times is varied in response to the input demanded by the
accelerator.
When the transistors are on, the current through the motor builds up, storing energy in the motor’s
magnetic field. When the transistors are off, the stored energy causes the motor current to continue
to flow through the freewheel diode. The control current ramps up and down as the switch turns
on and off. Average current, which determines motor torque, is controlled by the ratio of on/off
times. Smooth, stepless control of the power delivered to the motor is achieved with almost no
power loss in the control components.

 Loading...
Loading...