872 Configuring DHCP Server Settings
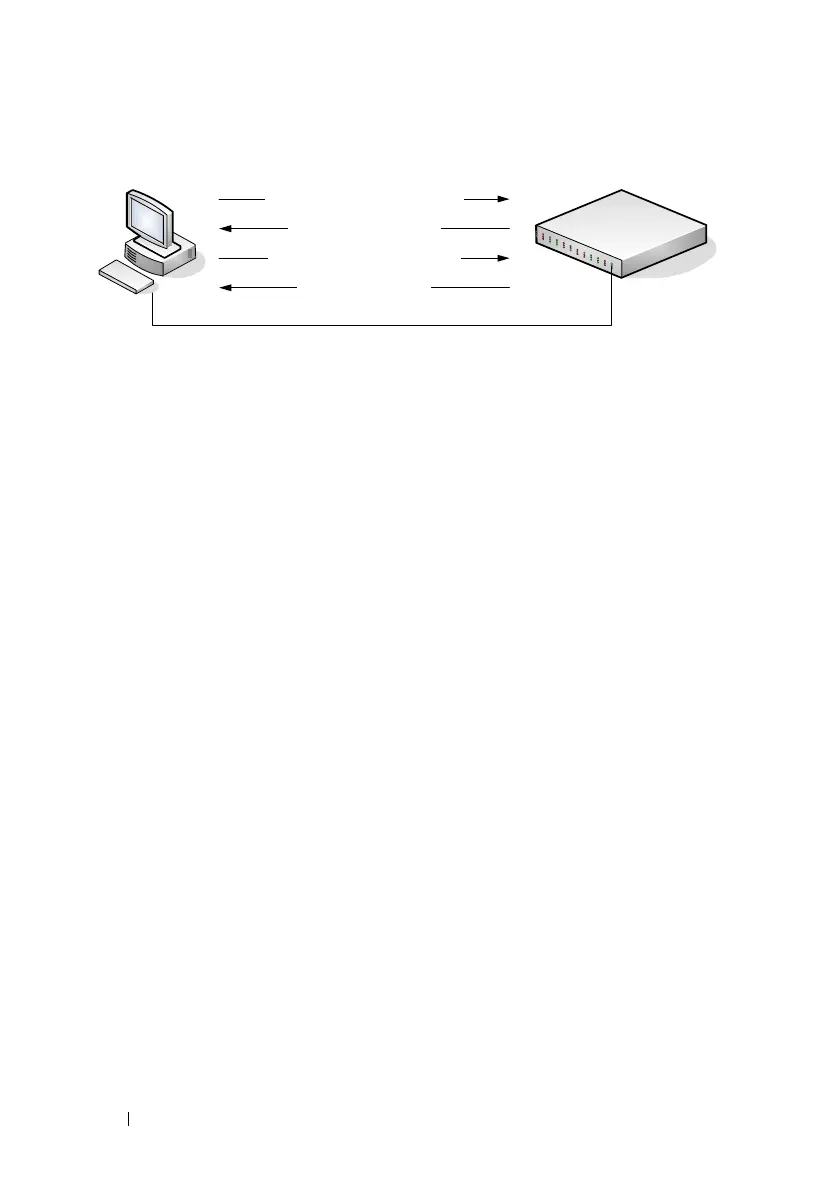
Figure 32-1. Message Exchange Between DHCP Client and Server
The DHCP server maintains one or more set of IP addresses the and other
configuration information available, by request, to DHCP clients. Each set of
information is known as an address pool.
After a client leases an IP address from the DHCP server, the server adds an
entry to its database. The entry is called a binding.
What are DHCP Options?
DHCP options are collections of data with type codes that indicate how the
options should be used. Options can specify information that is required for
the DHCP protocol, IP stack configuration parameters for the client,
information allowing the client to rendezvous with DHCP servers, and so on.
When a client broadcasts a request for information, the request includes the
option codes that correspond to the information the client wants the DHCP
server to supply. The Web pages and CLI commands to configure DHCP
server settings include many predefined options for the information that is
most commonly requested by DHCP clients. For example, DHCP client
discover requests typically include options for the IP address (option 50),
subnet mask (option 1), default gateway (option 3), and DNS server (option
6). These options are predefined.
For options that are not predefined, you can enter the option code and specify
the data type along with the data that the switch should include in DHCP
offers. RFC2132 specifies many of the DHCP options. Additional options are
described in later RFCs.
`
DHCPDISCOVER (broadcast)
DHCPOFFER (unicast)
DHCPREQUEST (broadcast)
DHCPACK (unicast)
DHCP Client DHCP Server
(PowerConnect Switch)

 Loading...
Loading...










