Chapter 12 Descriptions of Parameter SettingsC2000 Plus
12.1-07-18
Use this function when Pr.07-21 = 1. If the power factor angle is larger than Pr.07-43, the drive
continuously adjusts the energy-saving until it is smaller than Pr.07-43.
Pr.07-43 is the angle θ between active power and reactive power. The smaller COSθ, the lower
the reactive power, and the lower the loss.
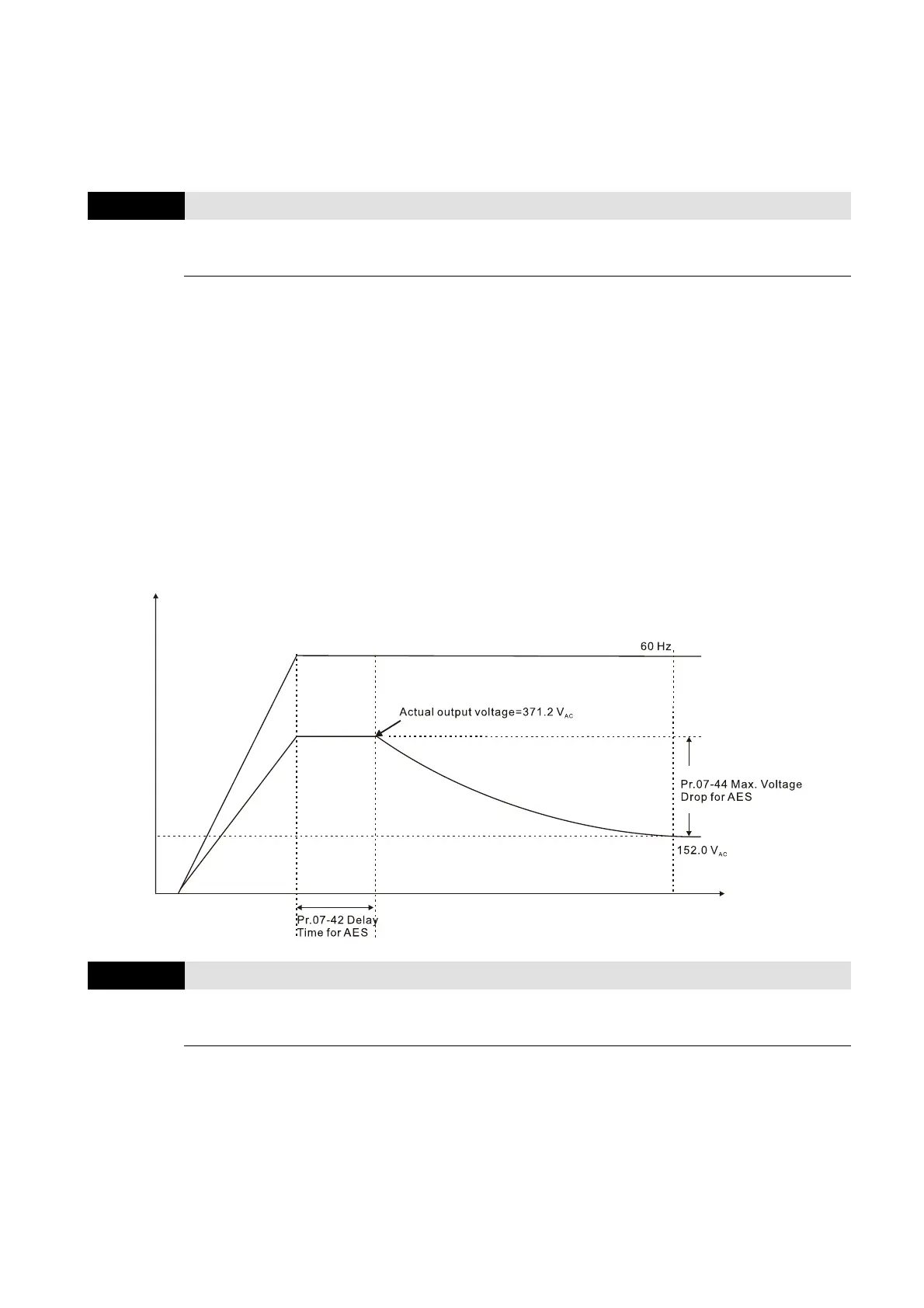
07-44
Maximum Voltage Drop for AES
Default: 60.00
Settings 0.00–70.00%
Define the maximum allowed voltage drop when the drive is in energy-saving mode.
The drive has bigger energy-saving efficiency when running in no-load or light-load. But the output
voltage drop is not unlimited. Use Pr.07-44 to limit the maximum ratio (%) of the output voltage
drop.
Example:
(1) If Pr.01-01 = 60 Hz, Pr.01-02 = 380 V
AC
, the frequency command is 60Hz and the actual
voltage output is 371.2 V
AC
, and Pr.07-44 = 60%, then the
maximum voltage drop = 380V (the voltage command corresponding to the frequency
command in the VF table: 60 Hz corresponds to 380V) × 60% = 228 V
AC
.
(2) If the frequency command is 30 Hz, the corresponding voltage is 200 V
AC
in the VF table, and
Pr.07-44 = 60%, then the maximum voltage drop = 200V × 60% = 120 V
AC
.
07-45
AES Coefficient
Default: 100
Settings 0–10000%
Define the motor power loss constant. Default 100% corresponds to the drive’s iron loss constant
that is calculated by motor parameter auto-tuning or motor nameplate information.
Pr.07-45 affects the final steady-state output voltage value for the energy-saving control. The
larger the Pr.07-45 setting value, the higher the steady-state output voltage (smaller voltage drop).
The smaller the Pr.07-45 setting value, the lower the steady-state output voltage (larger voltage
drop).

 Loading...
Loading...











