EPSON Stylus C50/C60/C61/C62 Revision C
Operating Principles Overview 27
2.1.2 Printhead
The Printhead uses the same U-CHIPS type as the previous printer (Stylus COLOR
680), and makes it possible to perform multiple shot printing and variable dot printing.
The Printhead nozzle configuration is as follows.
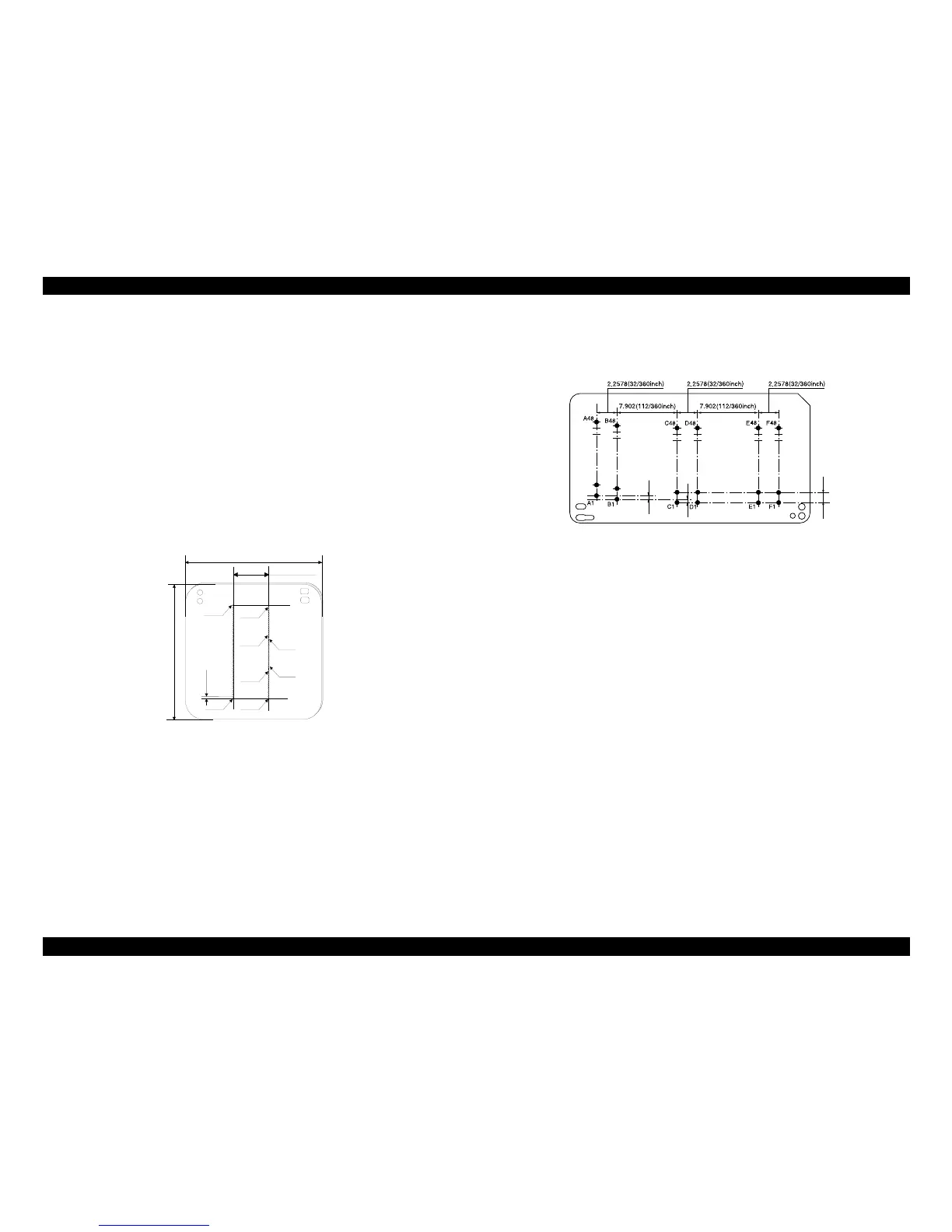
Nozzle layout
The nozzle layout when viewed from the back surface of the Printhead is shown
below.
Stylus C50
Black: 48 nozzles x 1 row (nozzle pitch of row: 1/120 inch)
Color : 45 nozzles x 1 row (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow : 15 nozzles is assigned
for each 3colors in one row45 nozzles x 1 row/col. (nozzle pitch of row: 1/120
inch)
Figure 2-2. Nozzle layout (Stylus C50)
Stylus C60/C61/C62
Black: 48 nozzles x 3 staggered (nozzle pitch of row: 1/360 inch)
Color: 48 nozzles x 1 row/col. (nozzle pitch of row: 1/120 inch)
Figure 2-3. Nozzle layout (Stylus C60/C61/C62)
The Printhead has the electric poles to store the ink consumption amount data into the
CSIC chip mounted on the ink cartridge. By storing the ink consumption amount data,
these printers can detect the ink consumption status, such as ink low/end condition.
The basic operating principles of the Printhead, which plays a major role in printing,
are the same as the previous printer (Stylus COLOR 680); on-demand method which
uses PZT (Piezo Electric Element). In order to uniform the ejected ink amount, the
Printhead has its own Head ID (6 digits for
the
Stylus C50 printhead
, 11 digits code
for
the Stylus C60/C61/C62 printhead
) which adjusts PZT voltage drive features.
So, you are required to store the Head ID pasted on the Printhead into the EEPROM by
using the Adjustment program when replacing the Printhead, the Main board, the
Printer mechanism with new one. (Note : there are no resistor arrays to determine the
Head ID on the Main board.) And then, based on the stored Head ID into the
EEPROM, the Main board generates appropriate PZT drive voltage.
0.21117 (1/120")
#M 15
#M 1
#C 1
#C 15
#Y1
#Y15
#B1
#B48
2.2578(32/360")
16.5
17
 Loading...
Loading...











