36
Problem6:BlankLCD
Cause CorrectiveAction
Connection
problem
• Turnoffthecabinet.
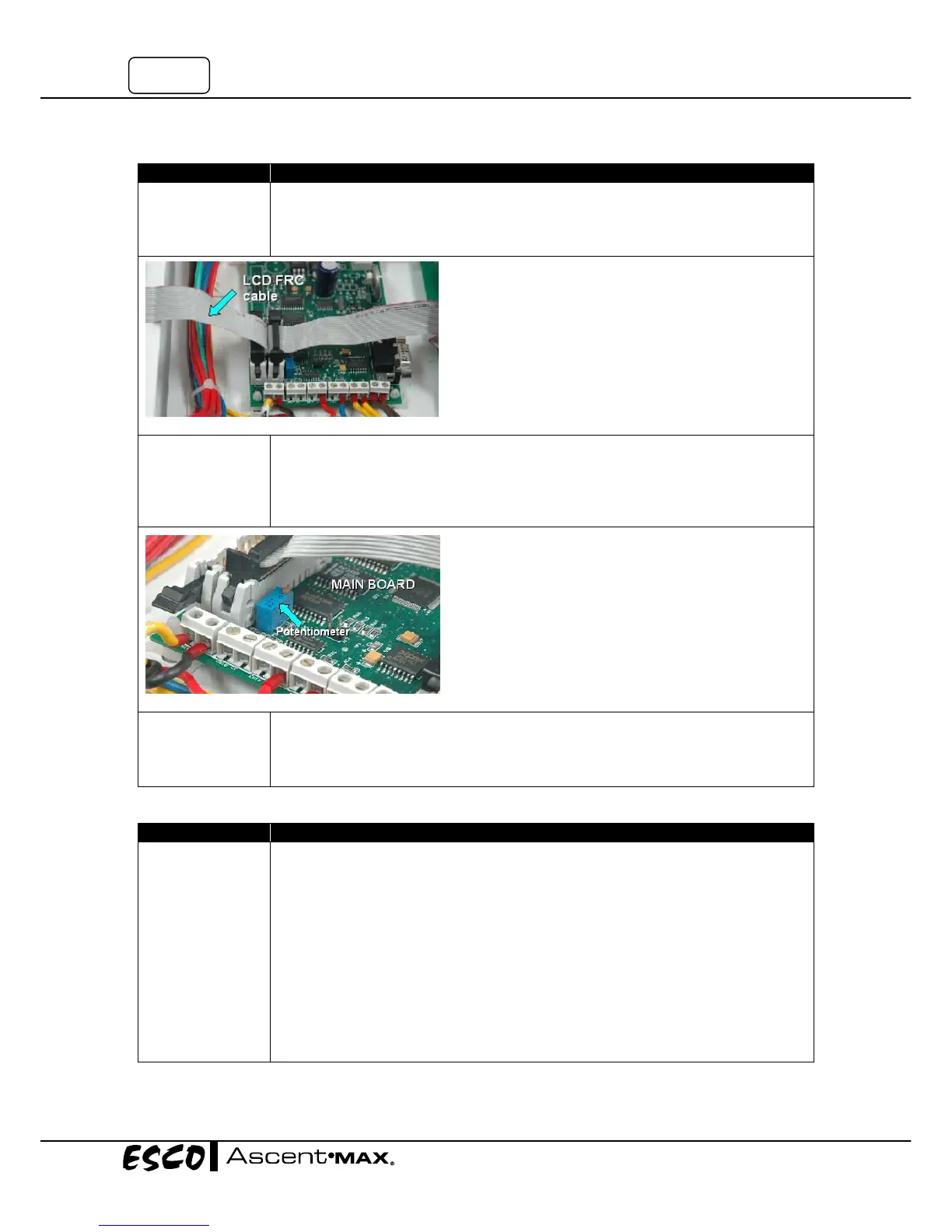
• SeeComponentLayouttolocatethemainboard.
• CheckwhetherLCDFRC(FlatRibbonCable)hasbeeninsertedproperlyintoits
socketonthemainboard.SeeFigure6‐1below.
Contrastproblem
• Turnoffthecabinet.
• Adjustthepotentiometeronmainboardbyrotatingthetopmetalpartusingflat
screwdrivertoachievethebestLCDcontrast.Counterclock‐wisedirectionwill
increasethecontrast.SeeFigure6‐2.
• IftheLCDremainsblank,replaceit.
DefectiveLCD
• ConnectanewLCDtotheLCDportonmainboard(SeeComponentLayout).
• IfthenewLCDfunctionsproperly,meanstheoldoneisDefective.Replaceit.
• IfthenewLCDisnotworking,checkitscableandconnectorinterfacetothemain
board.If
allconnectionsokaybutLCDdoesn'tfunction,replacethemainboard.
Problem7:Inoperativebuttons
Cause CorrectiveAction
Connection
problem
• Turnoffthecabinet.
• SeeComponentLayouttolocatethemainboard.
• Seefigure7‐1andensureFRCcablegoingtointerfaceboardisconnectedproperly.
ThetrianglesignonthefemaleconnectorindicatesPINnumber1.
• Interfaceboardandmembrane/keypadarelocatedbehind
thebluepanel,
underneaththelightmetaldeflector.
• Withthecabinetstillturned‐off,uninstallthefluorescentlightandmetaldeflector
toaccesstheinterfaceboard.SeeFigure7‐3.
• SeeFigure7‐2fortheproperconnectionbetweenmainboard,interfaceboard,and
membrane/keypad.
• Checkif
thegreenplasticcablefromthemembranehasbeeninsertedproperlyinto
theinterfaceboard.FollowFigure7‐4forthecorrectorientationofconnector.
Figure6‐1
Figure6‐2
 Loading...
Loading...