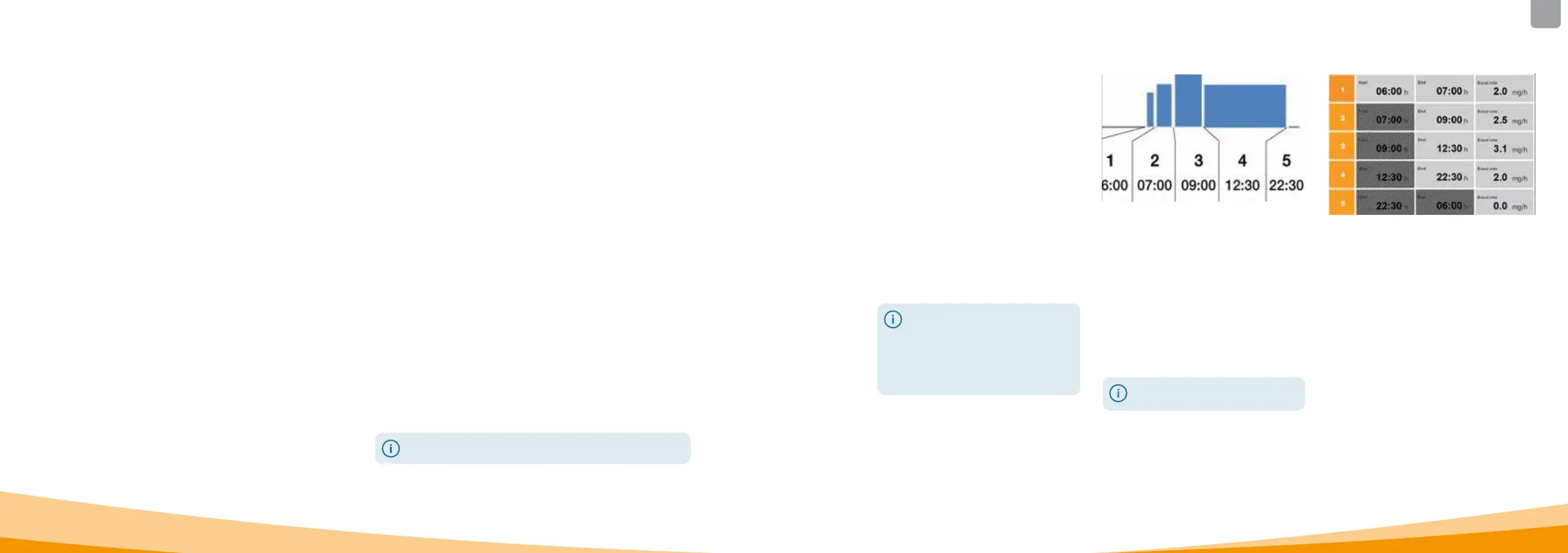94
95
6
You can program the daily course of drug delivery
(basal rate) in up to five freely selectable time periods
(basal periods). The following is applicable here:
• A basal period is a time period for which you set a
certain basal rate, e.g. 6:00 AM to 9:00 AM.
• The basal rate is entered in mg per hour. Example:
1.5mg/h for 24h = 36mg per day.
• Basal period 1 is always the first period in the
course of the day. For this basal period, you can
set both the beginning and the end.
• All other basal periods automatically start as soon
as the preceding period ends. You set the end for
each of these periods.
• The last defined time period lasts to the start
of ba
sal period 1 in each case. No further basal
periods can be entered once five time periods have
been defined.
In order to program the basal rate, review your daily course
from morning to evening and consecutively set the new
periods and delivery amounts. Any previous values will be
overwritten.
Sections 6.1.1to 6.1.4guide you step by step through the
programming process.
The basal rate can only be set if delivery has been stopped.
6.1
PROGRAMMING THE BASAL
RATE
6.1.1 PREPARING FOR
PROGRAMMING
Gather the necessary information
before you start programming a
basal rate profile.
The information presented in this
table has been randomly selected
and is intended only as an ex‑
ample. Use the values applicable
to you when programming your
profile.
Define profile
Define the basal rate profile for an
entire day. Divide the day into
between one and five basal periods
according to the treatment plan
and define the corresponding basal
rate in mg/h for each basal period.
A reservoir has a volume of 20ml
which equals 100mg of drug.
Table
It is recommended to enter the data
in a table for better overview. You can
then simply refer to the table when
entering the values. The appendix to
these instructions includes a patient
form with this table.
The information in the hatched fields
is automatically completed by the
system and does not need to be
entered.
 Loading...
Loading...