How to Read the Diagrams
This chapter contains circuit diagrams and component layout
information.
Signals
The signal designations reflect the functions. ADCDATA0,
for insta nce, means DATA BIT 0 from the ADC (Analog/Dig
-
ital Converter).
Three different types of graphic symbols are used to m ark ref
-
erences for continued connection somewhere else in the dia
-
gram.
This arrow is u sed if the reference to a supply
voltage is directed to a point located on the same
sheet. The example means that the supply voltage
-2.1V can also be found elsewhere on the same sheet.
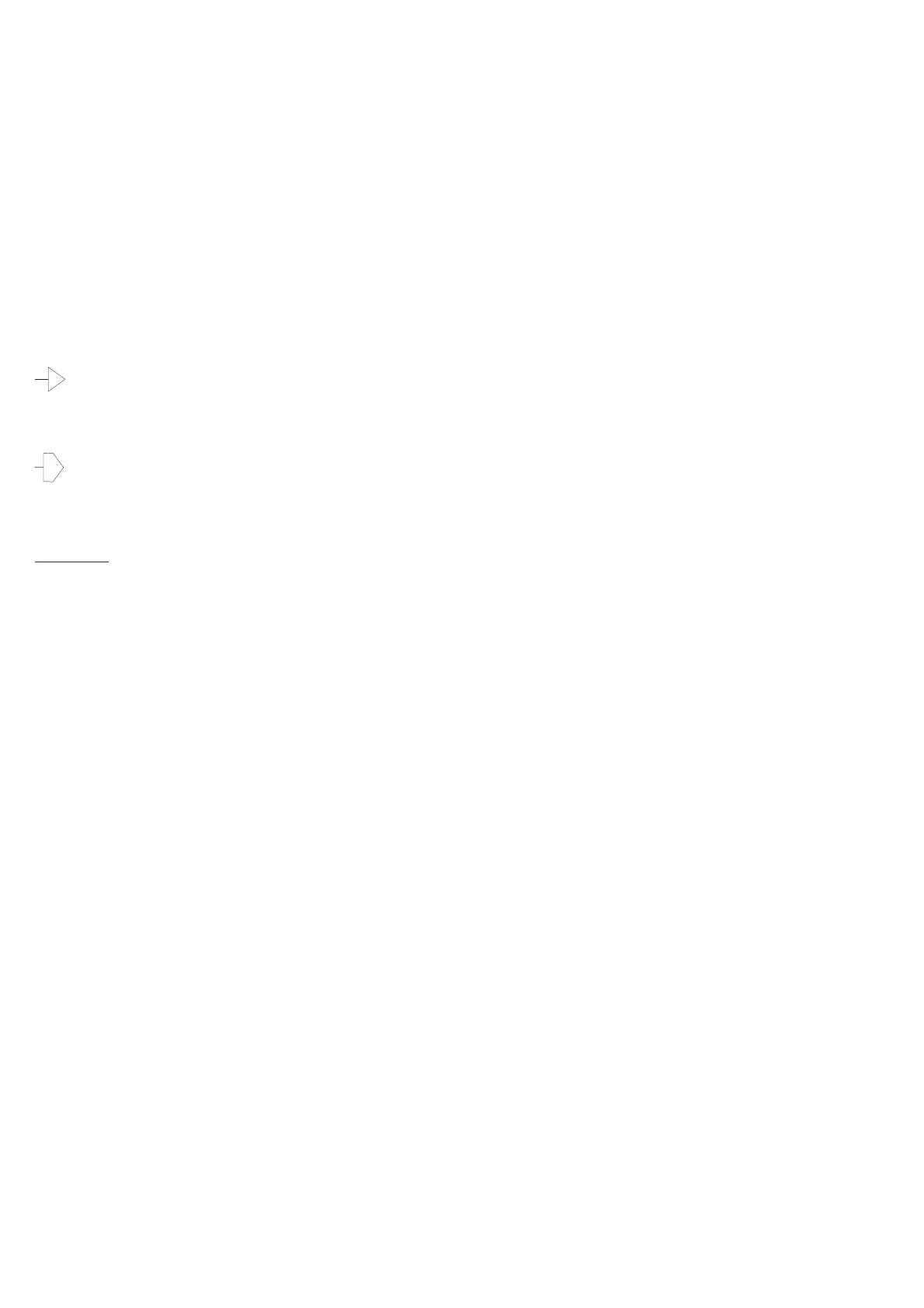
This arrow is used if the reference to a supply
voltage or a signal is directed to a point located
on another sheet. The example means that the
supply voltage +3.3VD goes to sheet 1, 2, 5, 7 and 8.
A broken line with a signal designation label
means that this p articular signal can also be
found elsewhere on the same sheet.
Circuit Symbols
The diagrams are computer-drawn. The symbols conform to
IEC standards. These symbols are designed to be logical and
easy to read.
The component number is written above the symbol. The type
number is written below the symbol
Inside the symbol there is sometimes an abbreviated descrip
-
tion of the circuit’s function.
Pin numbers are written outside the symbol and, if the circuit
is complex, the pin functions are written inside.
A small circle on a pin indicates that the input/output inverts
the signal.
The signal flow through the circuit is normally from left to
right.
Resistors, Capacitors, Diodes,
Transistors and Other Components.
These components are similar to the old-fashioned,
hand-drawn symbols. They have their component numbers
above or beside the symbol and their value or type number be
-
low the component number.
Component Numbers
Letters Components
B Crystals and crystal filters
C Capacitors
D Diodes
F Fuses
J Jumpers and connectors
K Relays
L Coils
P Connectors
Q Transistors
R Resistors
U ICs
X Test points
The numbers that follow are sequential and serve as sche-
matic diagram and layout identifiers together with the leading
character.
9-2 Schematic Diagrams
-2.1
+3.3VD 1,2,5,7,
PLL LOCK
 Loading...
Loading...