5–90 745 TRANSFORMER PROTECTION SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
S4 ELEMENTS CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS
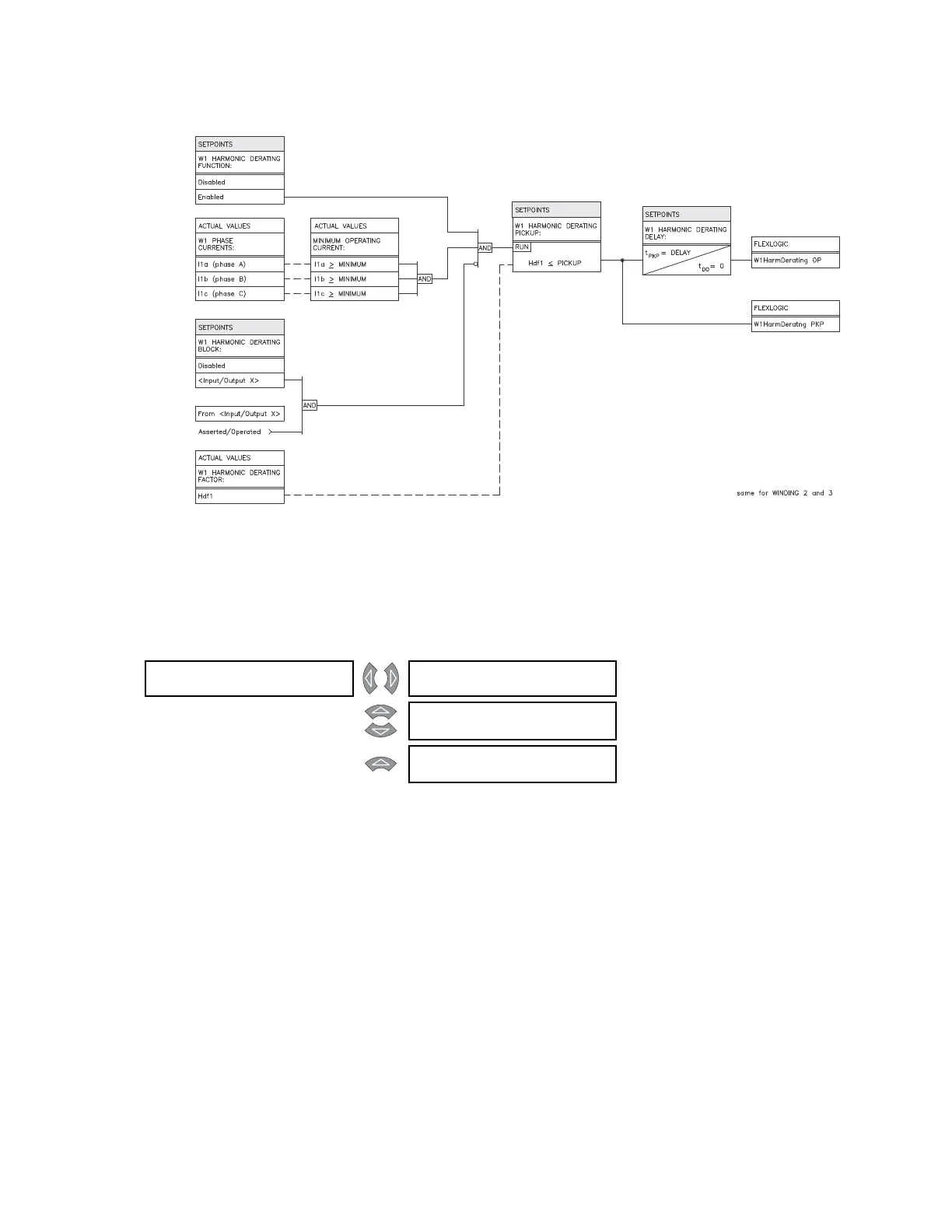
FIGURE 5–39: Harmonic derating scheme logic
5.6.13 Insulation Aging
5.6.13.1 Main Menu
PATH: SETPOINTS S4 ELEMENTS INSULATION AGING
The 745 insulation aging / loss of life feature is based on the computational methods
presented in IEEE standards C57.91–1995, IEEE Guide for Loading Mineral-Oil-Immersed
Transformers, and C57.96–1989, IEEE Guide for Loading Dry-Type Distribution and Power
Transformers. These standards present a method of computing the top oil temperature,
the hottest spot inside the transformer, the aging factor, and the total accumulated loss of
life. The computations are based on the loading of the transformer, the ambient
temperature, and the transformer data entered. The computations assume that the
transformer cooling system is fully operational and able to maintain transformer
temperatures within the specified limits under normal load conditions.
The computation results are a guide only. The transformer industry has not yet been able
to define, with any degree of precision, the exact end of life of a transformer. Many
transformers are still in service today, though they have long surpassed their theoretical
end of life, some of them by a factor of three of four times.
INSULATION []
AGING
HOTTEST-SPOT []
LIMIT
See page 5–91
MESSAGE
AGING FACTOR []
LIMIT
See page 5–92
MESSAGE
LOSS OF LIFE []
LIMIT
See page 5–93
 Loading...
Loading...