English (US)
24
15.2 Current
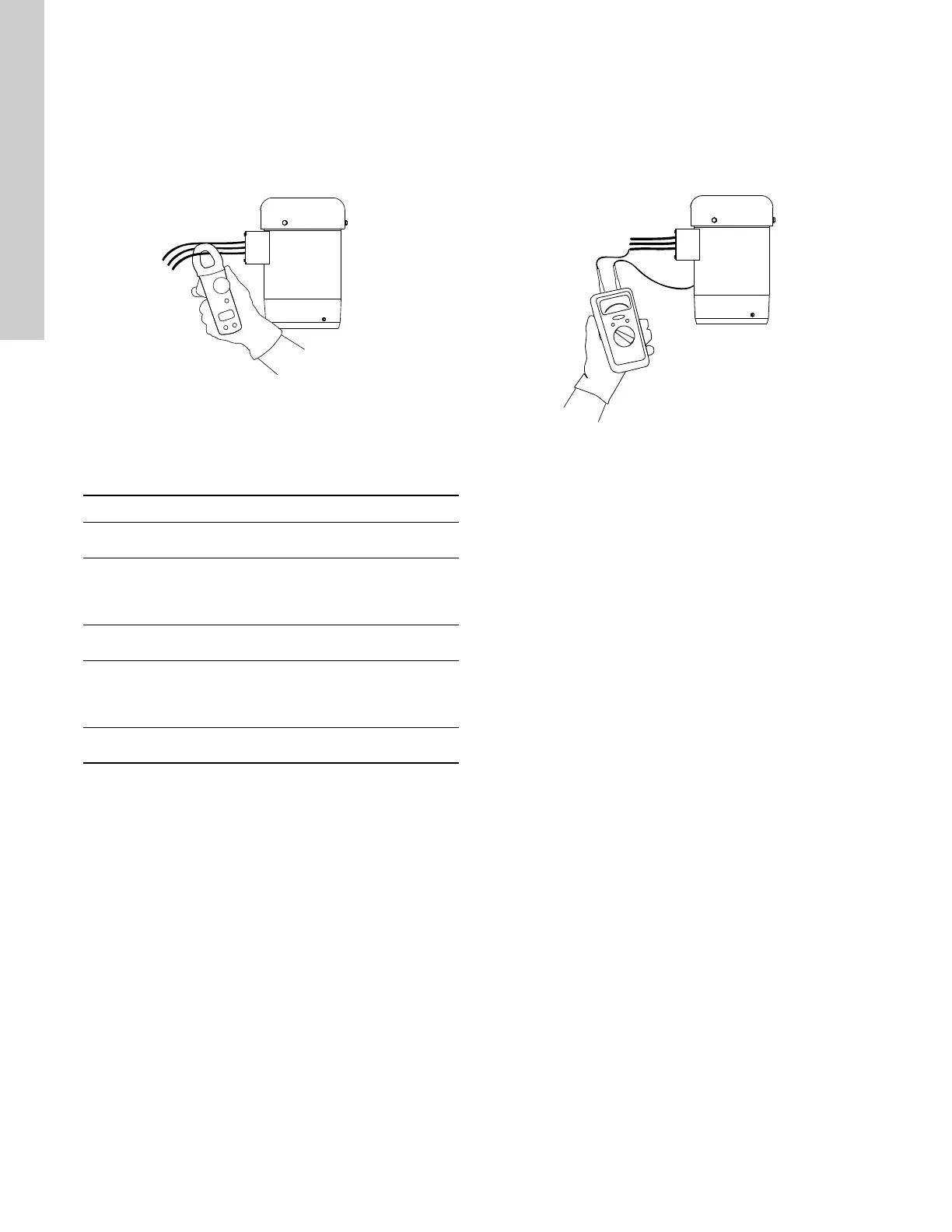
15.2.1 How to measure the current
Use an ammeter (set on the proper scale) to measure the current
on each power lead at the terminal box or starter. See the motor
nameplate for amp draw information. Current should be
measured when the pump is operating at constant discharge
pressure.
Fig. 25 Measuring current
15.2.2 Meaning of current measurement
If the amp draw exceeds the listed service factor amps (SFA) or if
the current unbalance is greater than 5 % between each leg on
three-phase units, check for the following faults:
15.3 Insulation resistance
15.3.1 How to measure the insulation resistance
Turn off power and disconnect the supply power leads in the
pump terminal box. Using an ohmmeter or megohmmeter, set the
scale selector to R x 100K and zero-adjust the meter.
Measure and record the resistance between each of the terminals
and ground.
Fig. 26 Measuring insulation resistance
15.3.2 Meaning of insulation resistance measurement
Motors of all hp, voltage, phase and cycle duties have the same
value of insulation resistance. Resistance values for new motors
must exceed 1,000,000 ohms. If they do not, the motor should be
repaired or replaced.
TM04 3908 2609
Fault Remedy
Burned contacts in the motor-
protective circuit breaker.
Replace contacts.
Loose terminals in motor-
protective circuit breaker or
terminal box or possibly
defective lead.
Tighten terminals or replace
lead.
Too high or too low supply
voltage.
Reestablish correct supply
voltage.
Motor windings are short-
circuited or grounded. (Check
winding and insulation
resistances).
Remove cause of short circuit
or grounding.
Pump is damaged causing
motor overload.
Replace defective pump parts.
TM04 3907 2609

 Loading...
Loading...