15
PMEN0654 rev.0 - 12/2023
5
FLARED PIPES
REFRIGERANT PIPING AND REFRIGERANT CHARGE
Therefore, all work carried out on the copper pipes for refrigerant must follow the three principles
described below:
Principle Cause of the fault Possible fault Prevenve measure
Absence of
humidity
Water inltraon due to
insucient protecon on the
ends of the pipes.
Condensaon on the inside of
the pipes.
Insucient vacuum.
Ice on the inside of the pipe,
on the expansion valve (water
obstrucon)
+
Absorpon of oil humidity and
oxidaon
↓
Filter clogging, insulaon and
compressor fault
Seal the ends of the pipes.
Protect and insulate the ends of
the pipes.
↓
Wash
↓
Vacuum dry (*)
Cleaning
Dust or other elements
entering the ends of the pipes.
Film of rust formed during
brazing without nitrogen
injecon.
Insucient nitrogen wash aer
brazing.
Expansion valve, Capillary tube
and lter clogging, Oil oxidaon
↓
Compressor fault, insucient
cooling or heang
Fit caps to the ends of the pipes.
Protect and insulate the ends of
the pipes.
↓
Wash
Absence of
leaks
Brazing fault.
Flaring fault and insucient
torque.
Insucient torque on
compressor connectors.
Lack of refrigerant, Drop in
performance, Compressor fault,
Oil oxidaon
↓
Compressor overheang
Carry out basic brazing →
Flaring → Connecon work
carefully
↓
Airght test
↓
Preserving of vacuum
(*) One gram of water becomes approximately 1000 l of steam at 1 Torr. (1 Torr = 1 mmHg = 133.32 Pa). Therefore, a
long me must be spent on vacuum work using a small pump.
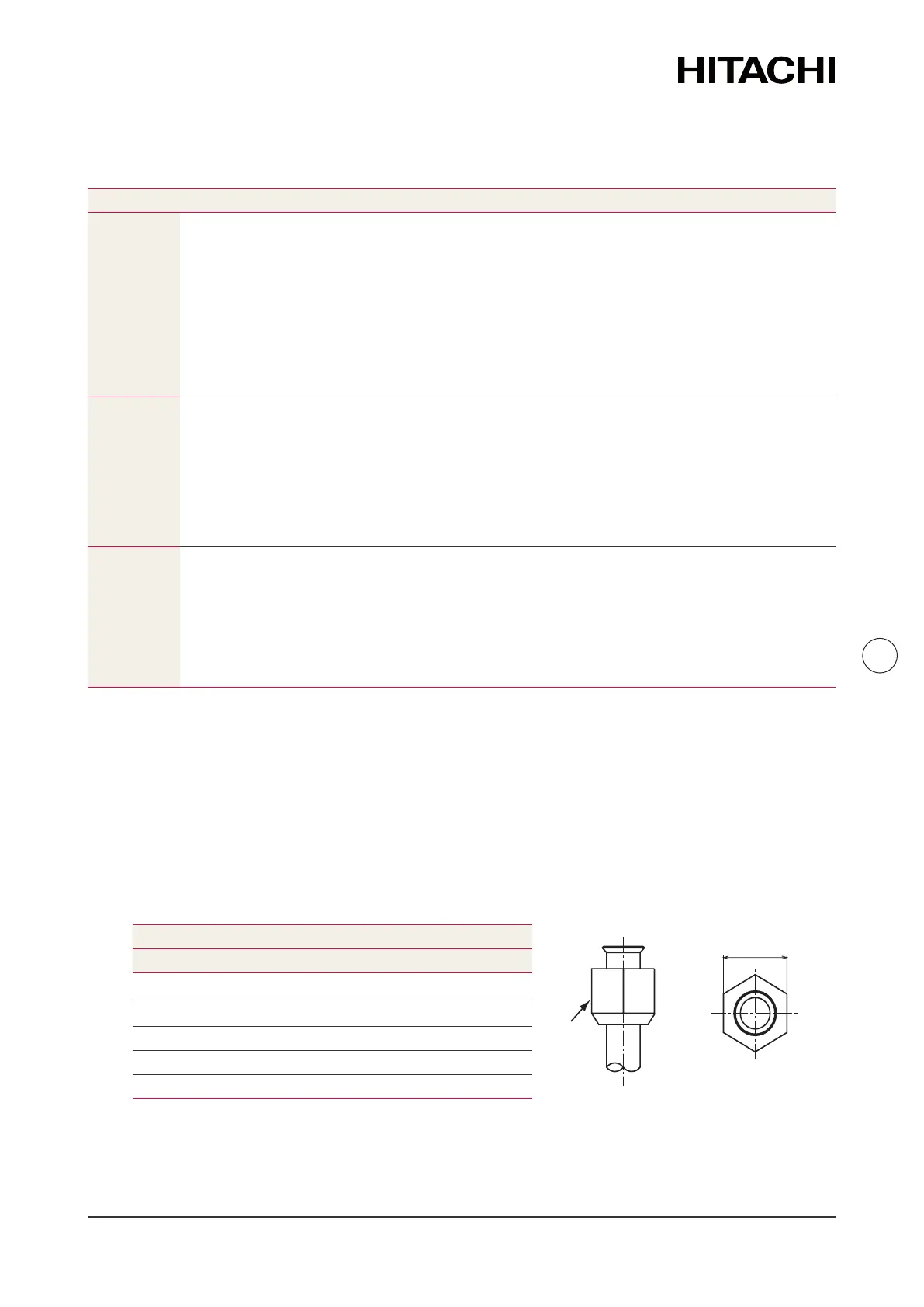
5.3 Flared pipes
5.3.1 Selecon of the connecon with are ng
If it is not possible to perform the widening operaon, use a connecon with are ng.
Distance between sides -B- of the nut -A-
Diameters (mm) -B- (mm)
Ø6.35 17
Ø9.52 22
Ø12.7 26
Ø19.05 36
Check that there are no scratches, adhered grinding swarf, deformaon or surface unevenness at
the aring part.

 Loading...
Loading...











