383
# Enable ARP packet validity check by checking the MAC addresses and IP addresses of ARP
packets.
[SwitchB] arp detection validate dst-mac ip src-mac
After the configurations are completed, ARP packets received on interfaces GigabitEthernet
1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 have their MAC and IP addresses checked first, and then are
checked against the static IP source guard binding entries and finally DHCP snooping entries.
ARP restricted forwarding configuration example
Network requirements
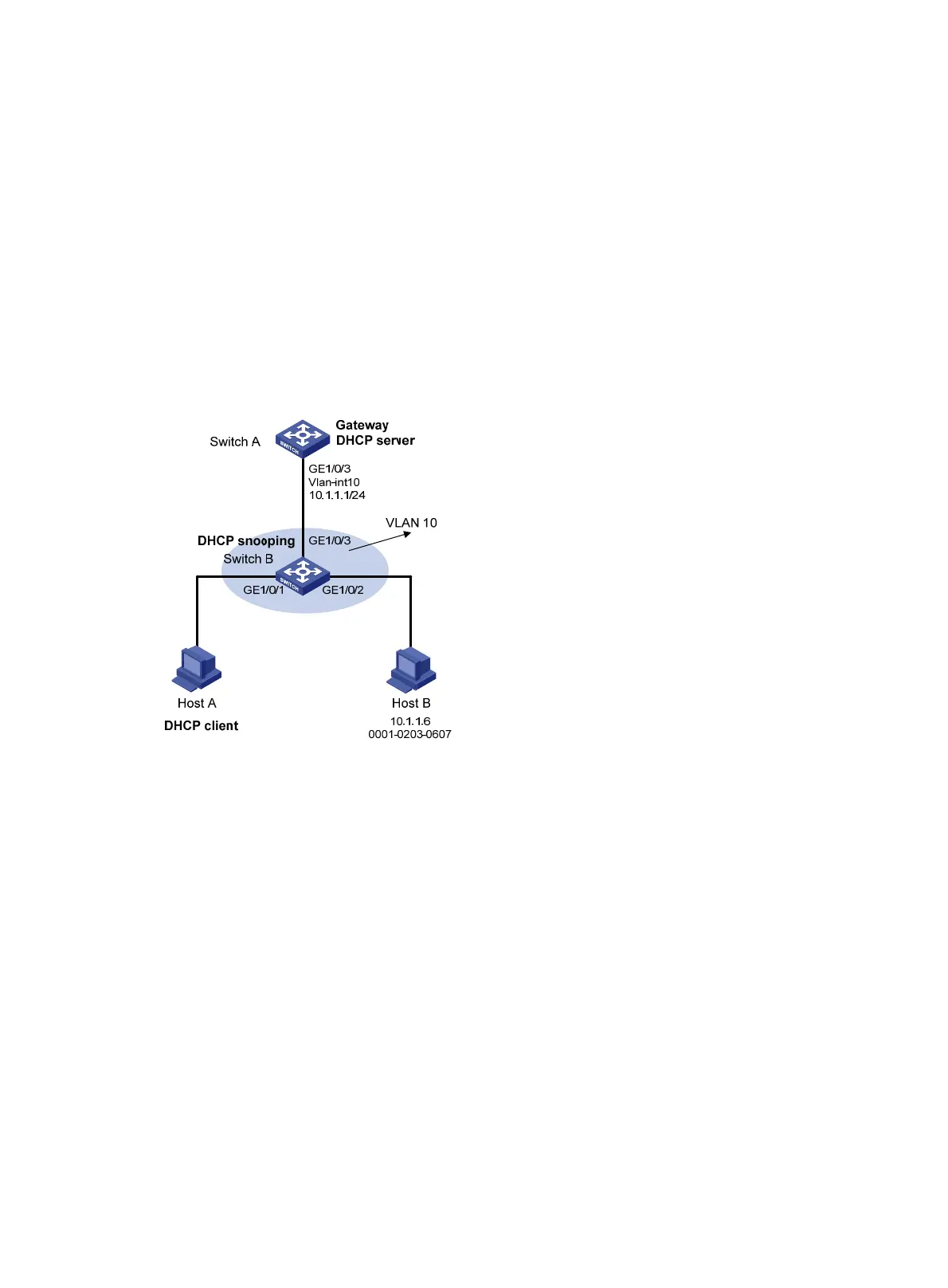
As shown in Figure 121, configure ARP restricted forwarding on Switch B where ARP detection is
configured so that port isolation configured on Switch B can take effect for broadcast ARP requests.
Figure 121 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure VLAN 10, add ports to VLAN 10, and configure the IP address of the VLAN-interface,
as shown in Figure 117. (D
etails not shown.)
2. Configure DHCP address pool 0 on Switch A as a DHCP server.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] dhcp enable
[SwitchA] dhcp server ip-pool 0
[SwitchA-dhcp-pool-0] network 10.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
3. Configure the DHCP client on Hosts A and B. (Details not shown.)
4. Configure Switch B.
# Enable DHCP snooping, and configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 as a DHCP-trusted port.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] dhcp-snooping
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] dhcp-snooping trust
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Enable ARP detection.

 Loading...
Loading...