8 iDirect Satellite Router Installation and Commissioning Guide
iDX Release 3.3
Orientation
2.3 Orientation
The following section describes antenna orientation principles generally applicable to all site
installations, illustrated with a typical VSAT antenna configuration. Magnetic variation and
elevation offset principles are discussed in detail.
Note: The antenna may not be identical to the antenna used in this example. See the
an
tenna manufacturer’s instructions for specific information.
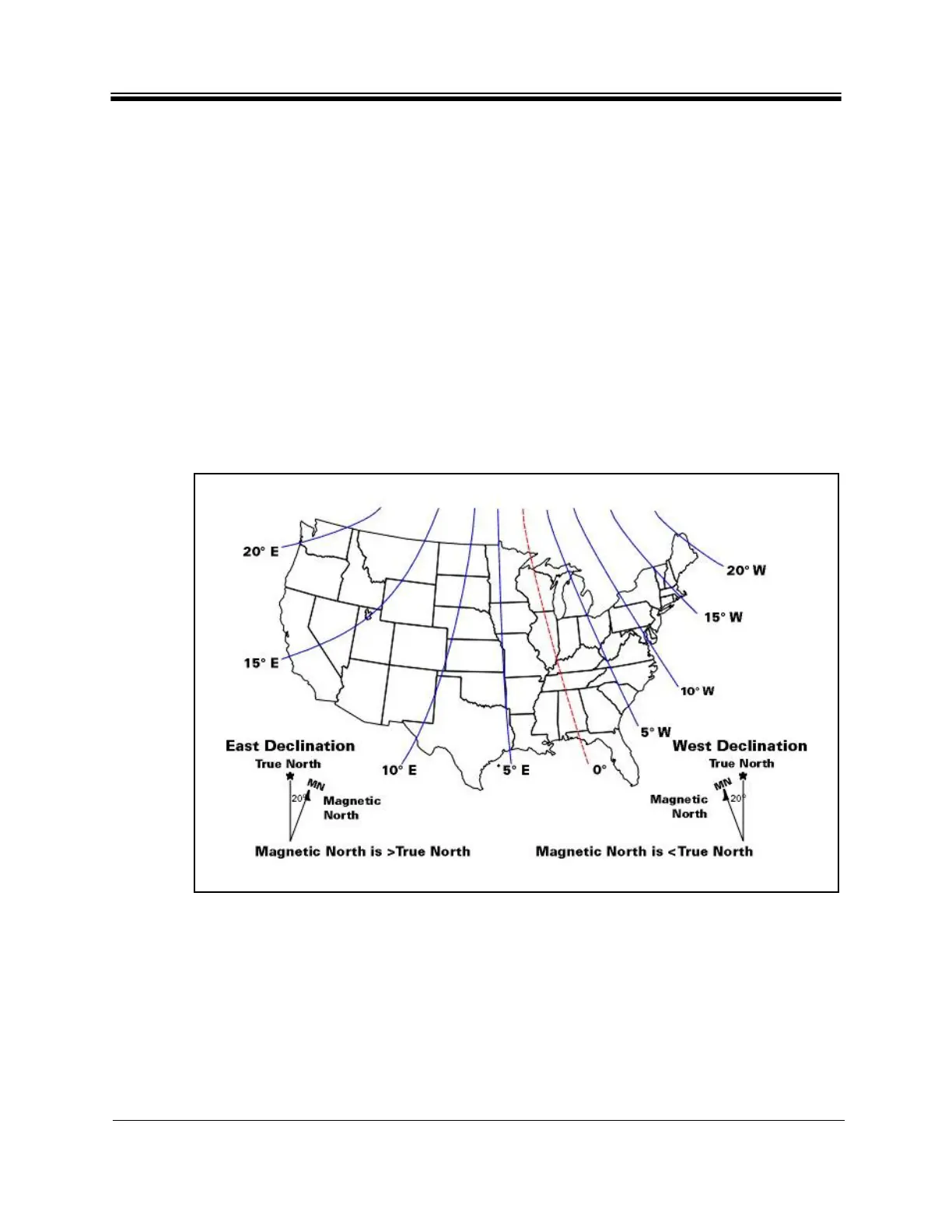
2.3.1 Magnetic Variation
Magnetic variation (also referred to as “declination”) is the difference between the true
heading referenced to the geographic North Pole, and the magnetic heading as registered on a
magnetic compass. The magnitude and direction of magnetic variation differs depending upon
the geographic location. Magnetic variation changes slowly with time.
Figure 2 illustrates magnetic variation in the United States. More detail
ed, up-to-date maps
are available on the Internet, and must be consulted for
the latest data.
Figure 2. Example: Magnetic Declination
Magnetic variation alters the reading of a magnetic
compass with respect to true North. Maps
and map display systems, including the output of the iDirect Look Angle Calculator, are
referenced to true geographic North. Therefore a correction factor must be applied to
readings taken by a magnetic compass to obtain the correct value, referred to as the true
heading.
Magnetic variation is specified in degrees East or W
est of the agonic line (line of zero
variation), shown as a red dotted line in Figure 2. As depicted in the figure, East declination

 Loading...
Loading...