Processor Thermal/Mechanical Information
Thermal and Mechanical Design Guidelines 23
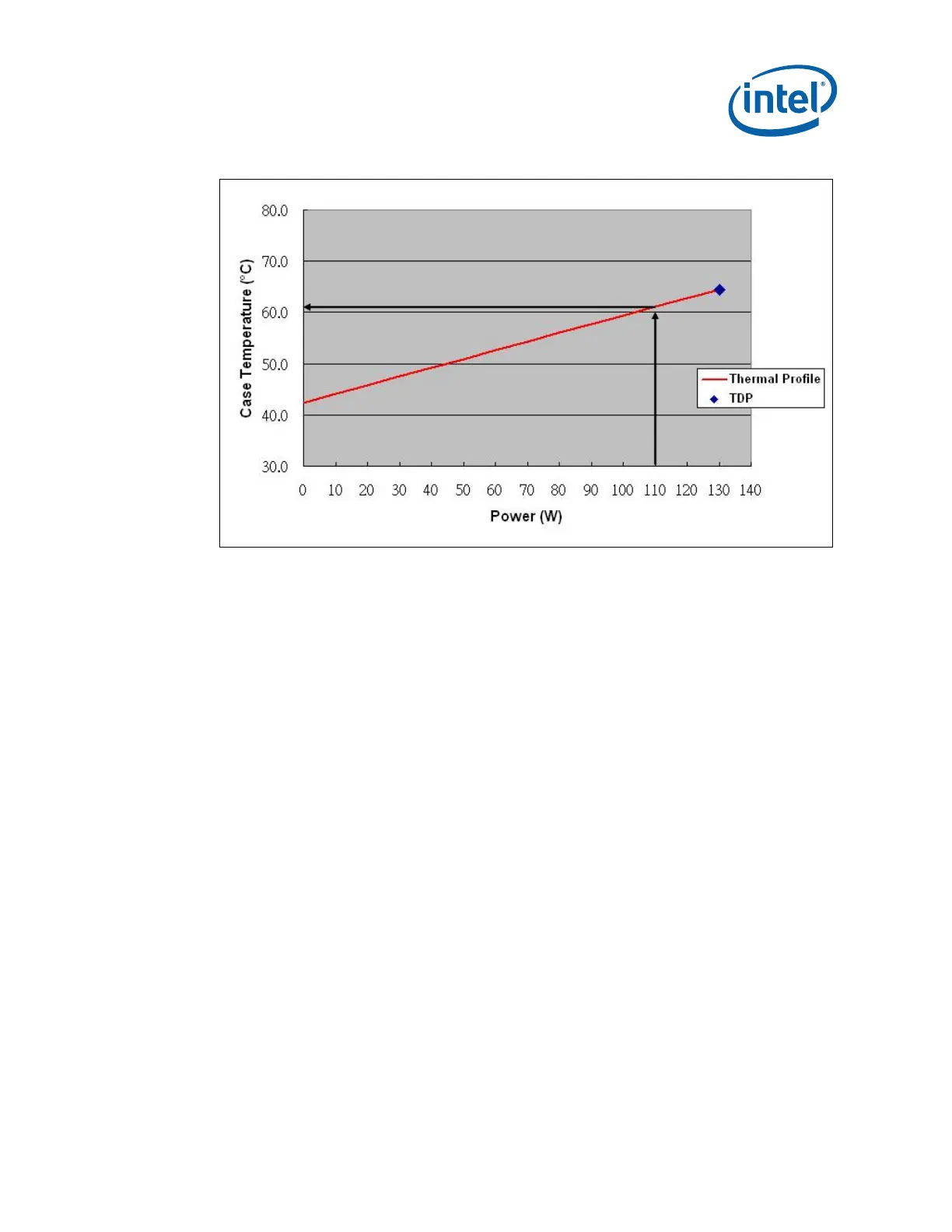
Figure 3. Example Thermal Profile
2.2.3 T
CONTROL
T
CONTROL
defines the maximum operating temperature for the digital thermal sensor
when the thermal solution fan speed is being controlled by the digital thermal sensor.
The T
CONTROL
parameter defines a very specific processor operating region where fan
speed can be reduced. This allows the system integrator a method to reduce the
acoustic noise of the processor cooling solution, while maintaining compliance to the
processor thermal specification.
Note: The T
CONTROL
value for the processor is relative to the Thermal Control Circuit (TCC)
activation set point which will be seen as 0 via the digital thermometer. As a result the
T
CONTROL
value will always be a negative number. See Chapter 4 for the discussion of
the thermal management logic and features and Chapter
6 on Intel
®
Quiet System
Technology (Intel
®
QST).
The value of T
CONTROL
is driven by a number of factors. One of the most significant of
these is the processor idle power. As a result a processor with a high (closer to 0)
T
CONTROL
will dissipate more power than a part with lower value (farther
from 0, e.g., more negative number) of T
CONTROL
when running the same application.
This is achieved in part by using the
CA
vs. RPM and RPM vs. Acoustics (dBA)
performance curves from the Intel enabled thermal solution. A thermal solution
designed to meet the thermal profile would be expected to provide similar acoustic
performance for different parts with potentially different T
CONTROL
values.
The value for T
CONTROL
is calculated by the system BIOS based on values read from a
factory configured processor register. The result can be used to program a fan speed

 Loading...
Loading...











