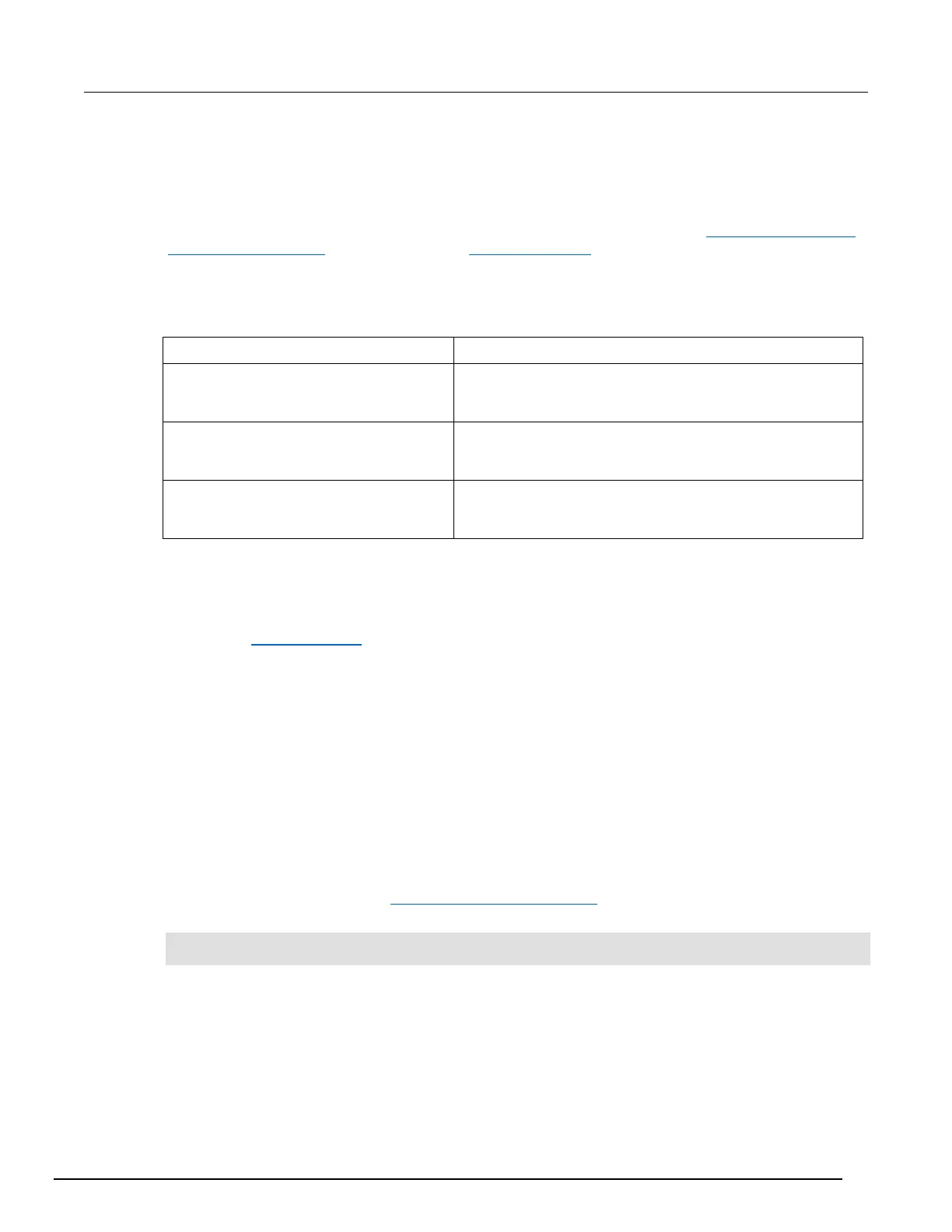
Status byte and service request commands
The commands to program and read the Status Byte Register and Service Request Enable Register
are listed in the table below. Note that the table includes both common commands and their script
command equivalents. For details on programming and reading registers, see Programming enable
and transition registers (on page C-14) and Reading registers (on page C-15).
To reset the bits of the Service Request Enable Register to 0, use 0 as the parameter value for the
command (for example, *SRE 0 or status.request_enable = 0).
Enable and transition registers
In general, there are three types of user-writable registers that are used to configure which bits feed
the register summary bit and when it occurs. The registers are identified in each applicable command
(as listed in TSP commands (on page 11-8)) as follows:
• Enable register (identified as .enable in each attribute's command listing): Allows various
associated events to be included in the summary bit for the register.
• Negative-transition register (identified as .ntr in each attributes command listing): A particular
bit in the event register will be set when the corresponding bit in the NTR is set, and the
corresponding bit in the condition register transitions from 1 to 0.
• Positive-transition register (identified as .ptr in each attributes command listing): A particular
bit in the event register will be set when the corresponding bit in the PTR is set, and the
corresponding bit in the condition register transitions from 0 to 1.
Controlling node and SRQ enable registers
Attributes to control system node and service request (SRQ) enable bits and read associated
registers are summarized in the Status Byte Register overview (on page C-3). For example, either of
the following will set the system node QSB enable bit:
status.node_enable = status.QSB
status.node_enable = 8

 Loading...
Loading...