Network
E220 Series Cellular Router User Guide 149
Parameters Description
Static IPv4 Routes
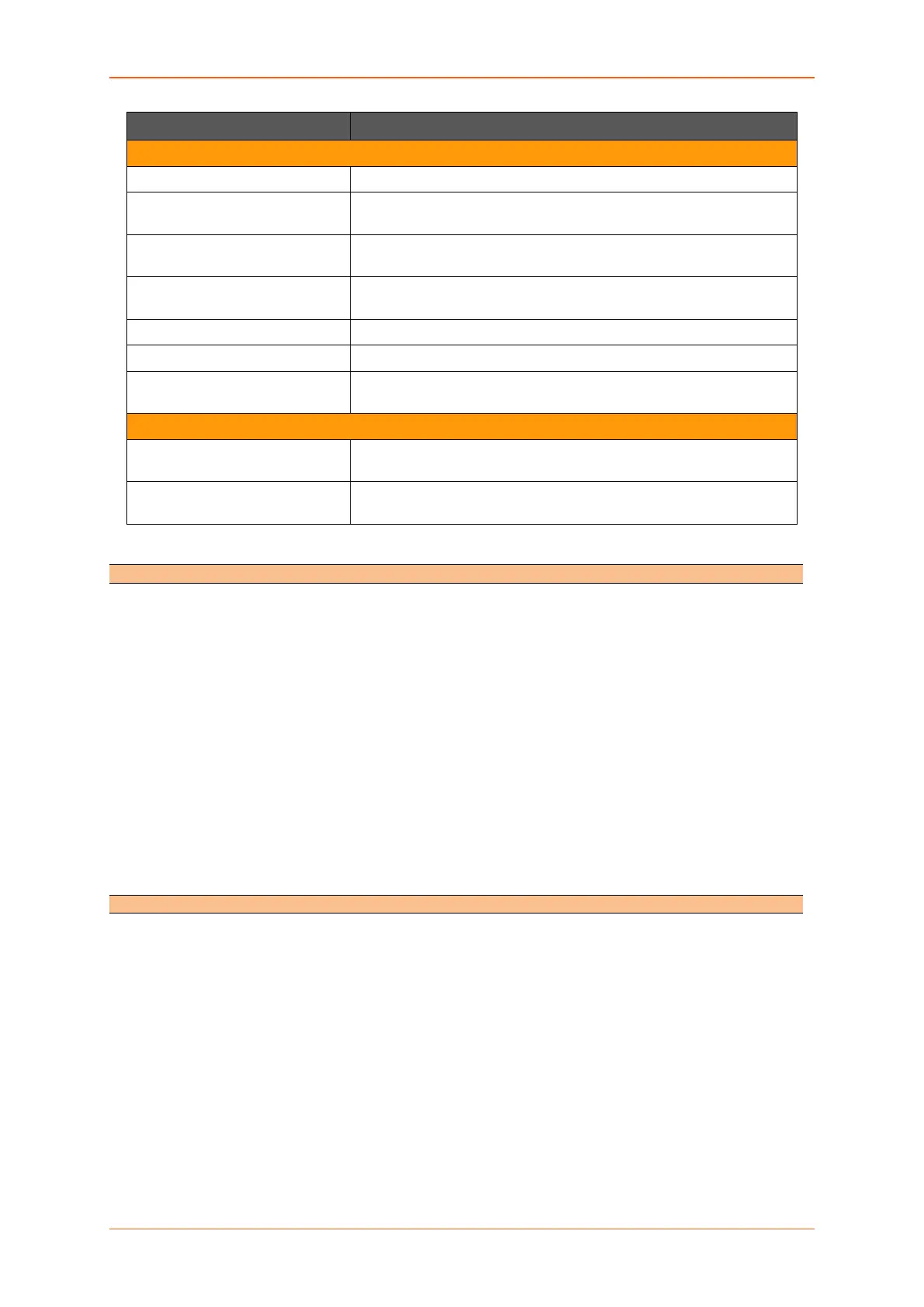
Name Enter the name of the zone.
Input Select to accept or reject the inbound traffic to all the configured
zones.
Output Select to accept or reject the outbound traffic from all the configured
zones.
Forward Select to accept or reject the forwarded traffic from all the configured
zones.
Masquerading Check to allow IP Masquerading.
MSS clamping Check to allow MSS clamping.
Covered network Select the network interfaces that must be included in the zone
configuration.
Inter-Zone Forwarding
Allow forward to destination
zones
Select to allow or deny forwarding traffic to the configured
destination zone.
Allowed forward from source
zones
Select to allow or deny forwarding traffic from the configured source
zone.
Table 10.9-2: General Configuration for Firewall Zone (LAN)
Concept of zone based Firewall
A zone section groups one or more interfaces and serves as source or destination for forwarding,
rules, and redirects. Masquerading (NAT) of outgoing traffic is controlled on a per zone basis. Note
that masquerading is defined in the outgoing interface.
• INPUT rules for a zone describe what happens to traffic trying to reach the router itself through
an interface in that zone.
• OUTPUT rules for a zone describe what happens to traffic originating from the router itself going
through an interface in that zone.
• FORWARD rules for a zone describe what happens to traffic passing between different
interfaces in that zone.
By default, there are 2 zones which are already created in the Router, Viz LAN Zone and WAN Zone.
All traffic from LAN to WAN has no restrictions but all incoming traffic on WAN side is blocked unless a
port forwarding rule is set or unless a particular port is opened.
Drop vs Reject
DROP
• less information is exposed
• less attack surface
• client software may not cope well with it (hangs until connection times out)
• may complicate network debugging (where was traffic dropped and why)
REJECT
• may expose information (like the ip at which traffic was actually blocked)
• client software can recover faster from rejected connection attempts
• network debugging easier (routing and firewall issues clearly distinguishable)

 Loading...
Loading...