PARAMETERS
139
(3) Pr. 502 "error-time stop mode selection"
You can choose inverter operation to be performed if a communication line fault or CC-
Link microcomputer fault occurs.
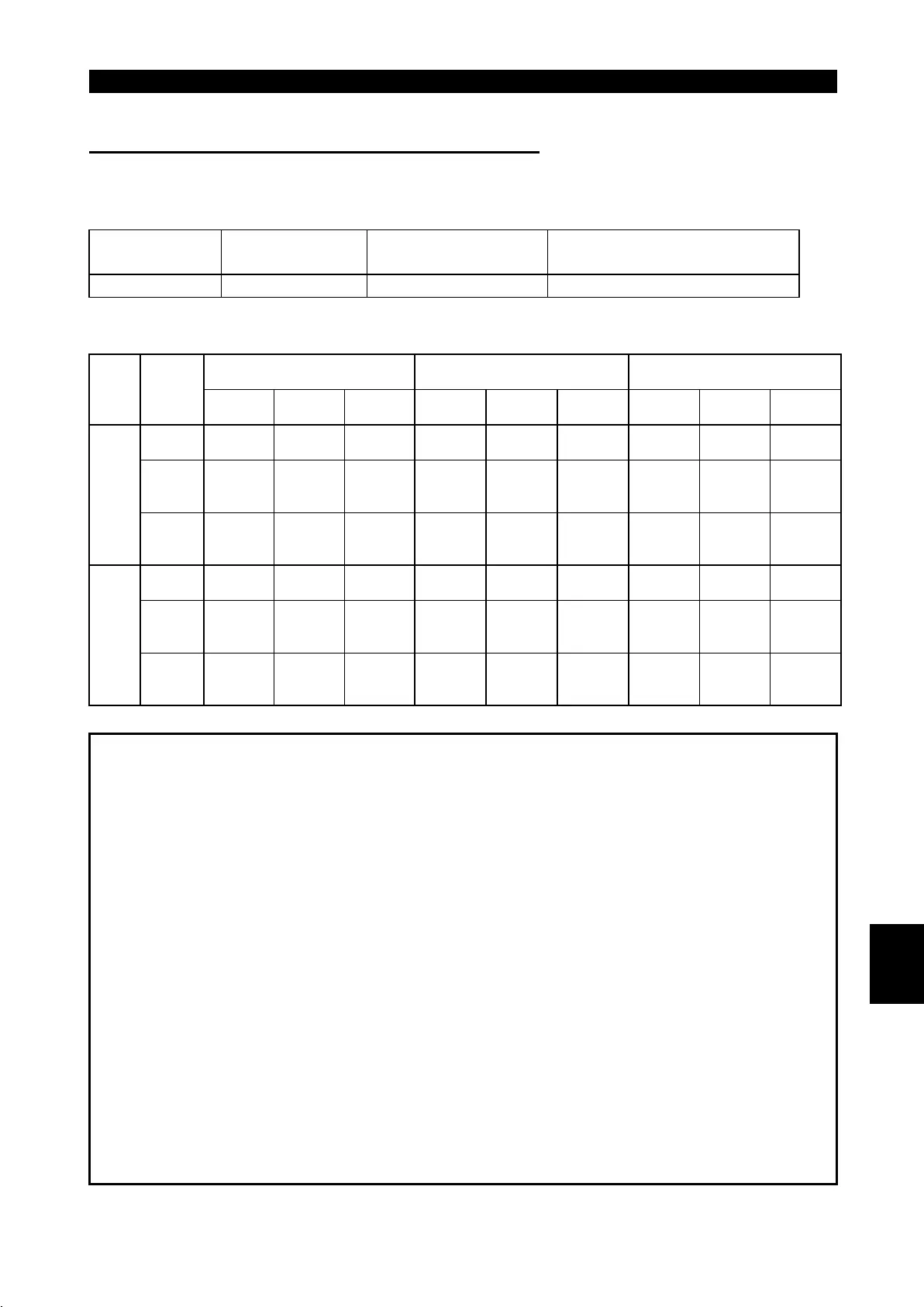
Parameter
Number
Setting Range
Minimum Setting
Increment
Factory Setting
502 0, 1, 2 1 0
(About the settings)
At Occurrence of Fault
Error Recognition after
Pr. 500 Time
At Resolution of Fault
Fault
Pr. 502
Setting
Operating
status
Indi-
cation
Alarm
output
Operating
status
Indi-
cation
Alarm
output
Operating
status
Indi-
cation
Alarm
output
0 Continued No
Not
provided
Coasting
to stop
E.OPT lit Provided
Stop
held
E.OPT
kept lit
Provided
1 Continued No
Not
provided
Decele-
ration to
stop
E.OPT lit
after
stop
Provided
after
stop
Stop
held
E.OPT
kept lit
Provided
Communication
line
2 Continued No
Not
provided
Decele-
ration to
stop
E.OPT lit
after
stop
Not
provided
Restart
E.OPT
kept lit
Not
provided
0
Coasting
to stop
E.3 lit
Provided
Coasting
to stop
E.3 lit Provided
Stop
held
E.3 kept
lit
Provided
1
Decele-
ration to
stop
E.3 lit
after
stop
Provided
after
stop
Decele-
ration to
stop
E.3 lit
after
stop
Provided
after
stop
Stop
held
E.3 kept
lit
Provided
CC-Link
microcomputer
2
Decele-
ration to
stop
E.3 lit
after
stop
Provided
after
stop
Decele-
ration to
stop
E.3 lit
after
stop
Provided
after
stop
Stop
held
E.3 kept
lit
Provided
Note: 1. A communication error [E.OPT (fault data: A0
H
)] is a fault on the communication
line, and a communication error [E.3 (fault data: F3
H
)] is a communication error
inside the inverter.
2. The alarm output is the ABC contact output or alarm bit output.
3. If the Pr. 502 setting is 1 or 2, the deceleration time is the ordinary
deceleration time setting (Pr. 8, Pr. 44, Pr. 45).
4. The acceleration time at restart is the ordinary acceleration time setting (Pr. 7,
Pr. 44).
5. If the Pr. 502 setting is 2, the operation command/speed command at restart
follows the command before occurrence of a fault.
6. For the setting of alarm output, the fault definition is stored in the alarm history.
(Write to the alarm history is performed when the alarm output is provided.)
If the alarm output is not provided, the fault definition overwrites the alarm
indication of the alarm history temporarily but is not stored.
After the fault is cleared, the alarm indication is reset and returns to the
ordinary monitor and the alarm history returns to the original alarm history.
7. When a communication line fault, which occurred at the Pr. 502 setting of 2, is
cleared during deceleration, acceleration restarts at that point. (Acceleration
does not restart at occurrence of a CC-Link microcomputer fault.)
4

 Loading...
Loading...











