495
FX3G/FX3U/FX3GC/FX3UC Series
Programming Manual - Basic & Applied Instruction Edition
18 Floating Point – FNC110 to FNC139
18.6 FNC118 – EBCD / Floating Point to Scientific Notation Conversion
11
FNC30-FNC39
Rotation and
Shift
12
FNC40-FNC49
Data Operation
13
FNC50-FNC59
High-Speed
Processing
14
FMC60-FNC69
Handy
Instruction
15
FNC70-FNC79
External FX I/O
Device
16
FNC80-FNC89
External FX
Device
17
FNC100-FNC109
Data
Transfer 2
18
FNC110-FNC139
Floating Point
19
FNC140-FNC149
Data
Operation 2
20
FNC150-FNC159
Positioning
Control
18.6 FNC118 – EBCD / Floating Point to Scientific Notation Conversion
Outline
This instruction converts binary floating point into scientific notation.
→ For handling of floating point, refer to Subsection 5.1.3.
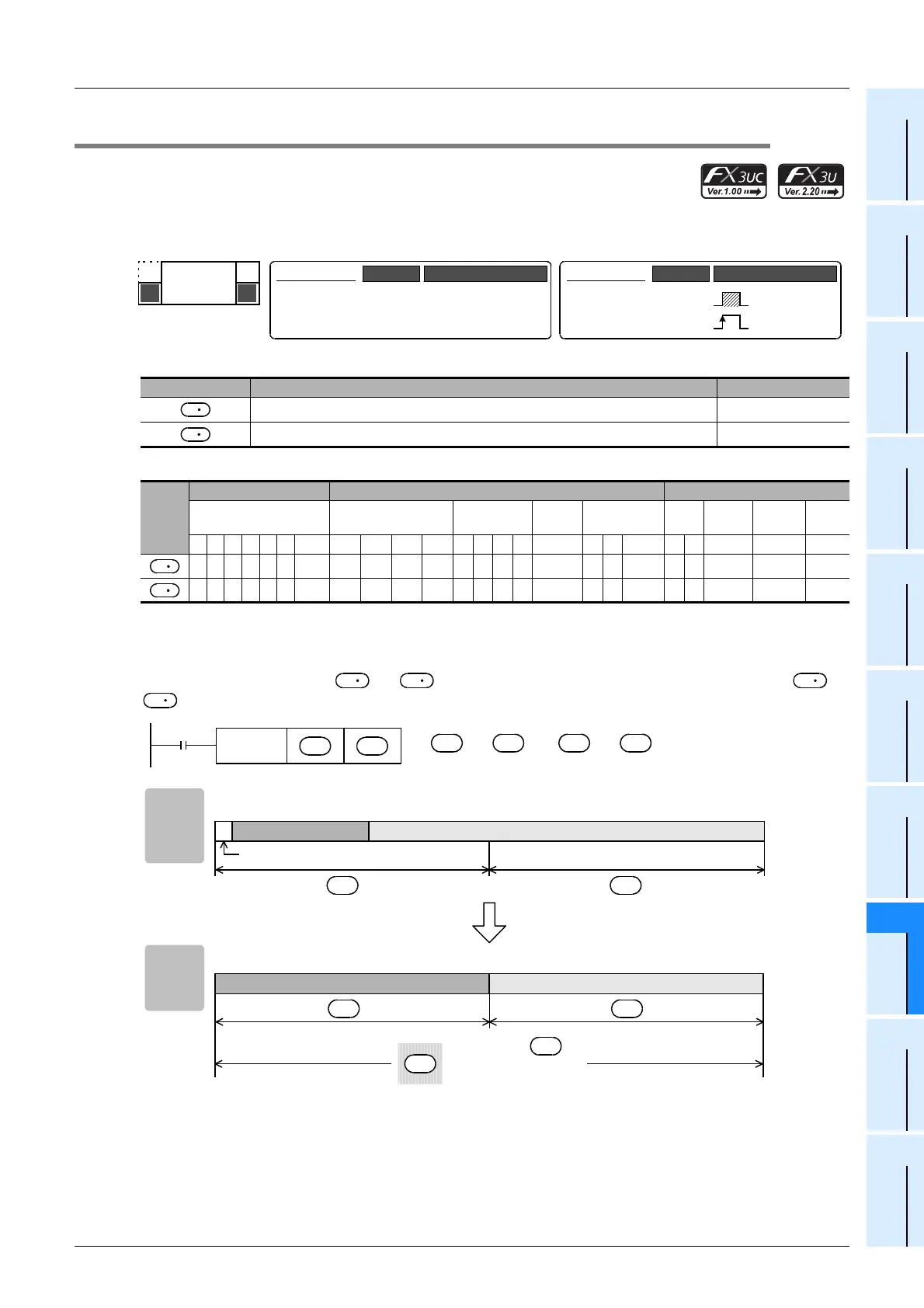
1. Instruction format
2. Set data
3. Applicable devices
Explanation of function and operation
1. 32-bit operation (DEBCD and DEBCDP)
Binary floating point stored in [ +1, ] is converted into scientific notation, and transferred to [ +1,
].
Caution
1. Handling of floating point
In floating point operations, all data is handled in binary floating point.
Because binary floating point is difficult to understand (requiring a dedicated monitoring method), it is converted into
scientific notation so that monitoring can be easily executed by peripheral equipment.
GX Developer and GOT have the function to directly monitor and display binary floating point.
Operand Type Description Data Type
Data register number storing binary floating point Real number (binary)
Data register number storing converted scientific notation Real number (decimal)
Oper-
and
Type
Bit Devices Word Devices Others
System User Digit Specification System User
Special
Unit
Index
Con-
stant
Real
Number
Charac-
ter String
Pointer
XYMTCSD.b KnX KnY KnM KnS T C D R U\G VZModifyKH E ""P
33 3 3
33 3 3
P
FNC 118
EBCD
D
−
Mnemonic Operation Condition
16-bit Instruction
DEBCD
DEBCDP
Mnemonic Operation Condition
32-bit Instruction
9 steps
Continuous
Operation
Pulse (Single)
Operation
S
D
S
D
S
S
D
D
Command
input
FNC118
DEBCD
Binary floating point Scientific notation
S
D
[ +1, ]
→
[ +1, ]
S
S
D
D
After execution
High order Low order
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0b31 b30 b29 b28 b27 b26 b25 b24 b23 b22 b21 b20 b19 b18 b17 b16
Before
execution
Mantissa part (23 bits)
+1
Low order
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
High order
b31 b30 b29 b28 b27 b26 b25 b24 b23 b22 b21 b20 b19 b18 b17 b16
After
execution
Mantissa partExponent part
+1
×
10
+1
Exponent part (8 bits)
Sign (1 bit)
S
D
S
D
D
D

 Loading...
Loading...











