7-410
• When the target module is a CPU module in multiple CPU systems
Specify the value obtained by dividing the start I/O number of the target CPU module by
16.
Or, the model name can be read by specifying the start I/O number of a module controlled
by another CPU.
(3) +0 and +1 to +9 store the execution result of the instruction and module model
name, respectively.
A value stored in is as follows:
(a) When the model name has been written to the target module (example: QJ71GP21-SX)
The following table shows the examples of model names stored in +1 to +9.
Target module Stored model name
CPU module Q06UDEHCPU
Intelligent function module QJ71GP21-SX
GOT GOT1000
Power
supply
module
CPU
module
Q20UDH
CPU
Q20UDH
CPU
Q20UDH
CPU
QY41
P
Q68
ADV
QY41
P
QY10 QY10
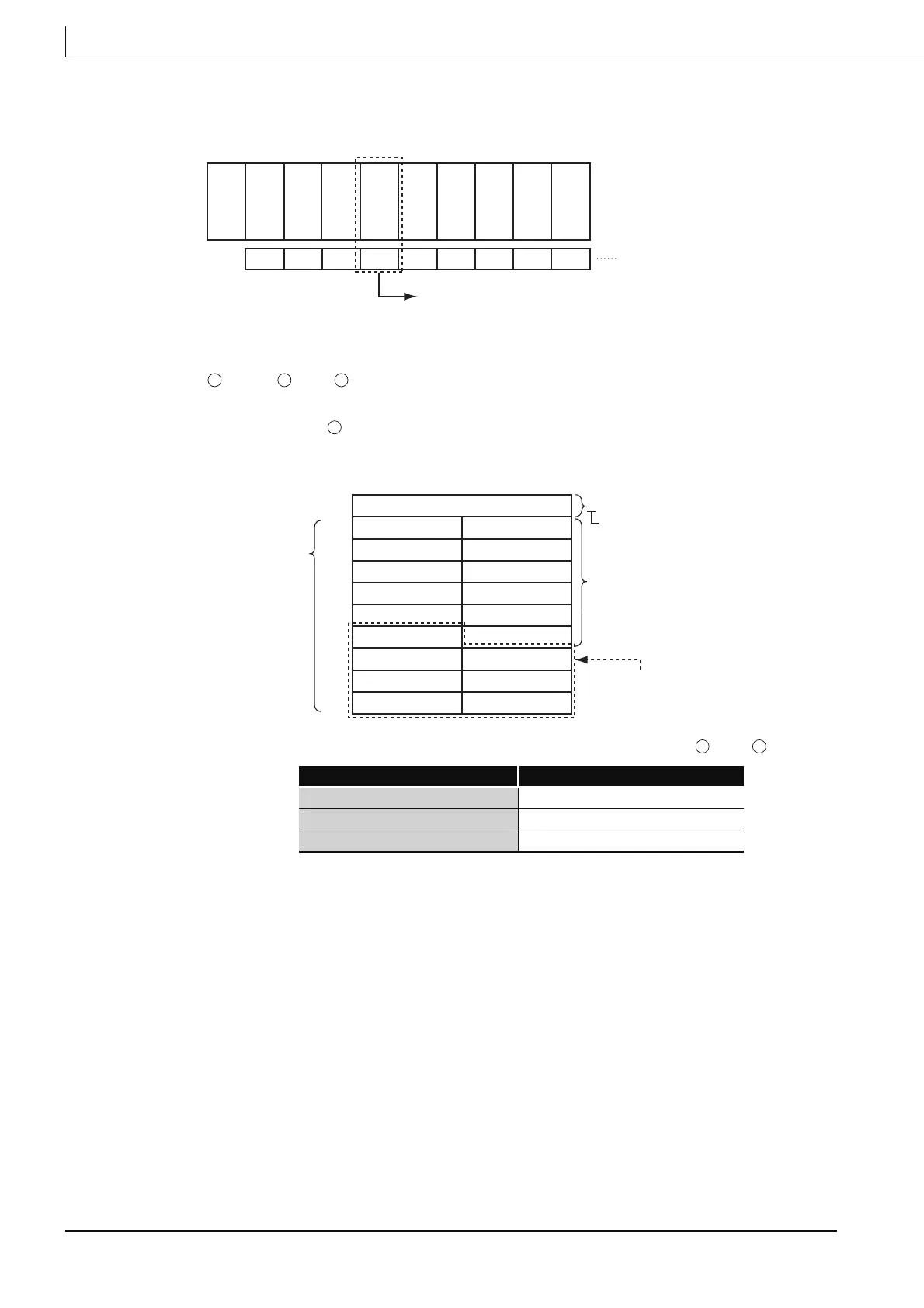
3E00
H 3E10H 3E20H 3E30H 0000H 0010H 0020H 0030H 0040H Start I/O number configured in
the I/O assignment setting
Specify the start I/O number by H3E3.
D D D
D
4AH (J)
D
0
b15 to b8 b7 to b0
31
H (1)
50
H (P)
31
H (1)
53
H (S)
00
H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
51H (Q)
Stores 0.
Stores the model name that has been
written to the target module
(stored in ASC II).
Stores the remaining model name and
00
H to the 12th to 17th devices and
the 18th device, respectively.
Indicates that the model name
that has been written to
the target module is stored.
37
H (7)
47
H (G)
32
H (2)
2D
H (-)
58
H (X)
○
+0
D
○
+1
D
○
+2
D
○
+3
D
○
+4
D
○
+5
D
○
+6
D
○
+7
D
○
+8
D
○
+9
Nine words are used.
D D

 Loading...
Loading...











