8
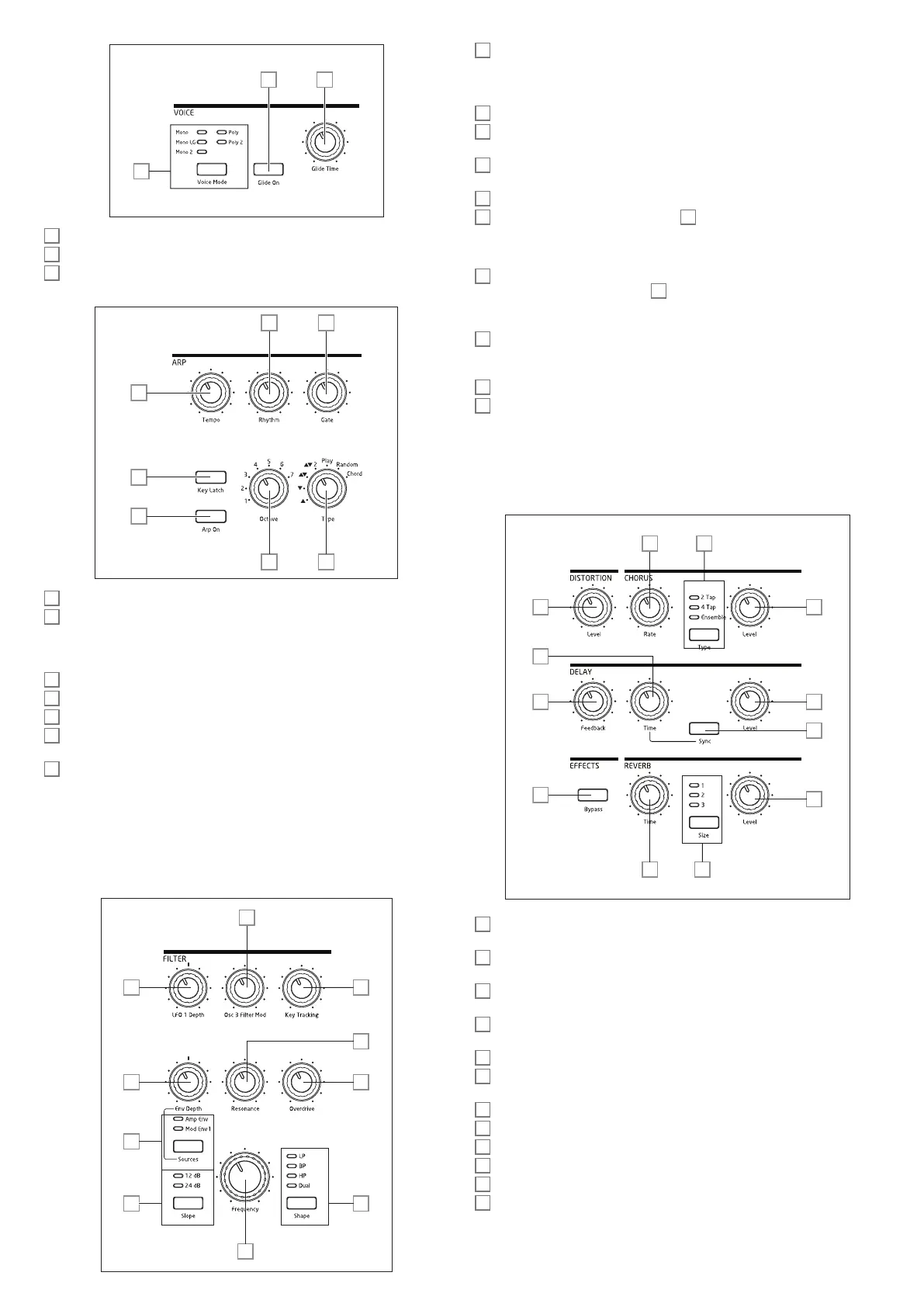
VOICE:
49 50
48
48
Voice Mode – selects one of five voice modes, three monophonic and two polyphonic
49
Glide On – enables/disables the Glide function.
50
Glide Time – sets the portamento glide time.
ARP:
54 55
56 57
53
52
51
51
Arp On – turns the Arpeggiator on and off.
52
Key Latch – if Key Latch is selected while holding keys down, Summit will play the
held notes continuously until it is deselected. This can be used to automatically maintain an
arp sequence, but Key Latch can be used independently of the Arpeggiator to hold played
notes for any length of time.
53
Tempo – sets the speed of the arp pattern.
54
Rhythm – selects one of 33 different patterns based on the notes played.
55
Gate – sets the duration of the notes played by the Arpeggiator.
56
Octave – sets the number of octaves over which the arp pattern extends; increasing
the octave range increases the pattern length.
57
Type – further variations of the arp pattern are possible by varying Type. This allows
the user to choose the direction and/or order of the notes making up the pattern, such as
up or down, random or chord formation.
The Arpeggiator has further parameters available for adjustment via the Arp Menu; these
include basic settings such as clock source, sync rate and swing. These are described in
detail later in the User Guide. Most of the panel controls are duplicated in the Arp/Clock
menu.
FILTER :
66
60
65 67
62
61
58
64
59
63
58
Shape – steps through the three basic types of filter: low-pass (LP), band-pass (BP)
or high-pass (HP); selecting Dual opens a menu page (Voice Menu Page 4), where
nine more options, based on series or parallel combinations of two filter types operating
simultaneously may be selected.
59
Slope – sets the slope of the filter to either 12dB or 24dB per octave.
60
Frequency – large rotary knob controlling the filter’s cut-off frequency (LP or HP), or
its centre frequency (BP).
61
Resonance – adds resonance (an increased response at the filter frequency) to the
filter characteristic.
62
Overdrive – adds a degree of pre-filter distortion to the mixer output.
63
Source – assigns the Env Depth control
64
to one of two sources which can
modulate the filter frequency. The options are modulation by the amplitude envelope
(Amp Env) or one of the mod envelopes (Mod Env 1). The two sources are additive: and
may be used simultaneously.
64
Env Depth – controls the amount by which the filter frequency is modified by the
envelope currently selected by Source
63
. The two sources may have different values of
depth. Env Depth is a centre-zero control and thus both positive and negative variations
may be imposed on the filter frequency by each modulating source.
65
LFO 1 depth – controls the amount by which the filter frequency is modified by
LFO 1. LFO 1 Depth is a centre-zero control and thus the filter frequency can be made to
vary both positively and negatively.
66
Osc 3 Filter Mod – allows the filter frequency to be modulated directly by Oscillator 3.
67
Key Tracking – controls the amount by which the keyboard position of the note being
played varies the filter frequency between 0 and 100%.
EFFECTS:
The Effects section for each of Summit’s two Parts comprises three different DSP-based
processors producing time-domain effects, plus an analogue distortion generator.
76 77
73 74
68 78
72
75
70
69
71
79
68
DISTORTION: Level – controls the amount of analogue distortion applied to the sum
of all active voices for each Part.
69
DE LAY: Time – sets the timing of the delayed signal (echo) added to the original.
Maximum delay is approx. 1.4 seconds.
70
DE LAY: Sync – electing Sync allows the delay time to be synchronised to the internal
clock or an incoming MIDI clock.
71
DELAY: Feedback – allows the delayed signal to be fed back to the input of the delay
processor, creating multiple echoes.
72
DE LAY: Level – controls the volume of the delayed signal.
73
REVERB: Time – adjusts reverberation decay time. (The maximum time is longer than
anything you’ll ever likely to need!)
74
REVERB: Size – emulates spaces of three different sizes: 3 is the largest.
75
REVERB: Level – controls the “amount” of reverberation.
76
CHORUS: Rate – adjusts the rate of chorus modulation.
77
CHORUS: Type – lets you select one of three different chorus algorithms.
78
CHORUS: Level – controls the degree of chorus effect.
79
EFFECTS: Bypass – the three time-domain effects (delay, reverb and chorus) may be
switched in or out with this button. Bypass does not affect analogue distortion.
 Loading...
Loading...