D6F-series MEMS Flaw Sensor User’s Manual (A286) 16
6.4.3 The influence of pressure and temperature
OMRON’s flow sensors can measure a mass flow rate. In order to comply with the
combined gas law, even in the same gas volume flow, the mass flow rate becomes low when
the pressure is low or the temperature is high. On the other hand, the mass flow rate
becomes high when the pressure is high or the temperature is low. For example, when
measuring the same volumetric flow rate at a high altitude (or high temperature) and a low
altitude (or low temperature), the mass flow rate at a high altitude (high temperature) is
smaller than that at a low altitude (or low temperature).
Equation of state of ideal gas
Boyle-Charle's law
Fig.19 Influence of pressure and temperature
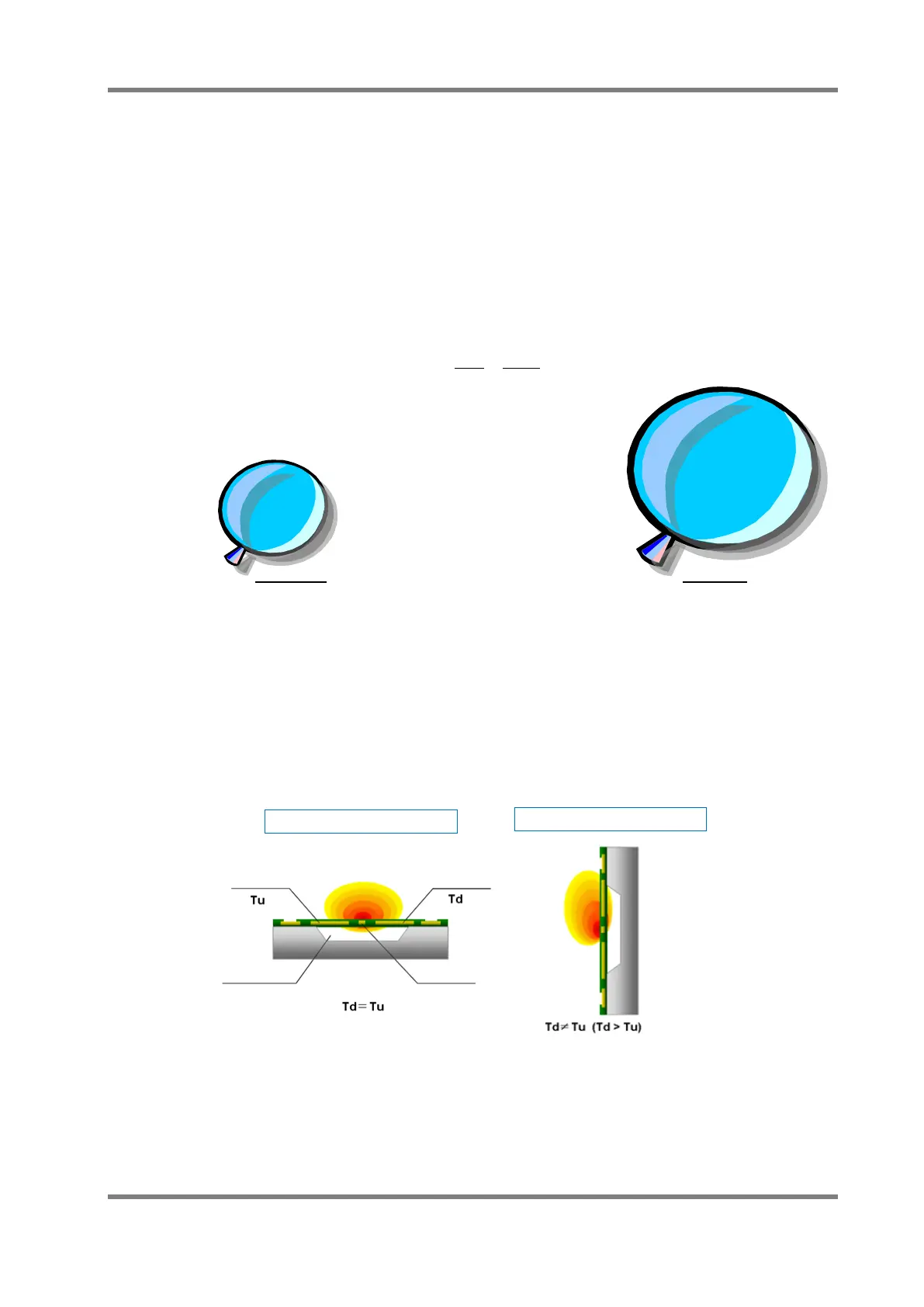
6.4.4 The influence of the mounting direction
The mounting direction can influence the output characteristics of a flow sensor. These
characteristics can vary slightly due to the heat distribution of the flow sensor chip, as shown
in Fig.20. The variation will be about 0.4%FS in actual measurement. OMRON recommends
a horizontal installation in product specifications for this reason. It should be considered that
there are some characteristics variations with vertical installation.
Horizontal mounting
Thermopile A Thermopile B
Space
Heater
Vertical mounting
Symmetry of the temperature
distribution is broken in the natural
convection heat
Horizontal mounting
Thermopile A Thermopile B
Space
Heater
Horizontal mounting
Thermopile A Thermopile B
Space
Heater
Vertical mounting
Symmetry of the temperature
distribution is broken in the natural
convection heat
Fig.20 Influence of mounting direction of the sensor chip
Pressure is high / Temperature is low
The volume is different.
But, the mass is same.
Pressure is low / Temperature is high
=

 Loading...
Loading...