22
Basic Concepts Section 2-1
are reset (canceled) at the start of each task, i.e., they are reset when the task
changes.
The following instructions are used in pairs to set and cancel certain instruc-
tion conditions. These paired instructions must be in the same task.
Flags
In this context, a flag is a bit that serves as an interface between instructions.
Operands
Operands specify preset instruction parameters (boxes in ladder diagrams)
that are used to specify I/O memory area contents or constants. An instruction
can be executed entering an address or constant as the operands. Operands
are classified as source, destination, or number operands.
Instruction
condition
Description Setting
instruction
Canceling
instruction
Interlocked An interlock turns OFF part of the program. Special conditions, such as
turning OFF output bits, resetting timers, and holding counters are in
effect.
IL(002) ILC(003)
BREAK(514)
execution
Ends a FOR(512) - NEXT(513) loop during execution. (Prevents execu-
tion of all instructions until to the NEXT(513) instruction.)
BREAK(514) NEXT(513)
Executes a JMP0(515) to JME0(516) jump. JMP0(515) JME0(516)
Block program
execution
Executes a program block from BPRG(096) to BEND(801). BPRG(096) BEND(801)
Input flags Output flags
• Differentiation Flags
Differentiation result flags. The status of these
flags are input automatically to the instruction for
all differentiated up/down output instructions and
the DIFU(013)/DIFD(014) instructions.
• Carry (CY) Flag
The Carry Flag is used as an unspecified operand
in data shift instructions and addition/subtraction
instructions.
• Flags for Special Instructions
These include teaching flags for FPD(269) instruc-
tions and network communications enabled flags
• Differentiation Flags
Differentiation result flags. The status of these flags are output
automatically from the instruction for all differentiated up/down
output instructions and the UP(521)/DOWN(522) instruction.
• Condition Flags
Condition Flags include the Always ON/OFF Flags, as well as
flags that are updated by results of instruction execution. In user
programs, these flags can be specified by labels, such as ER,
CY, >, =, A1, A0, rather than by addresses.
• Flags for Special Instructions
These include memory card instruction flags and MSG(046)
execution completed flags.
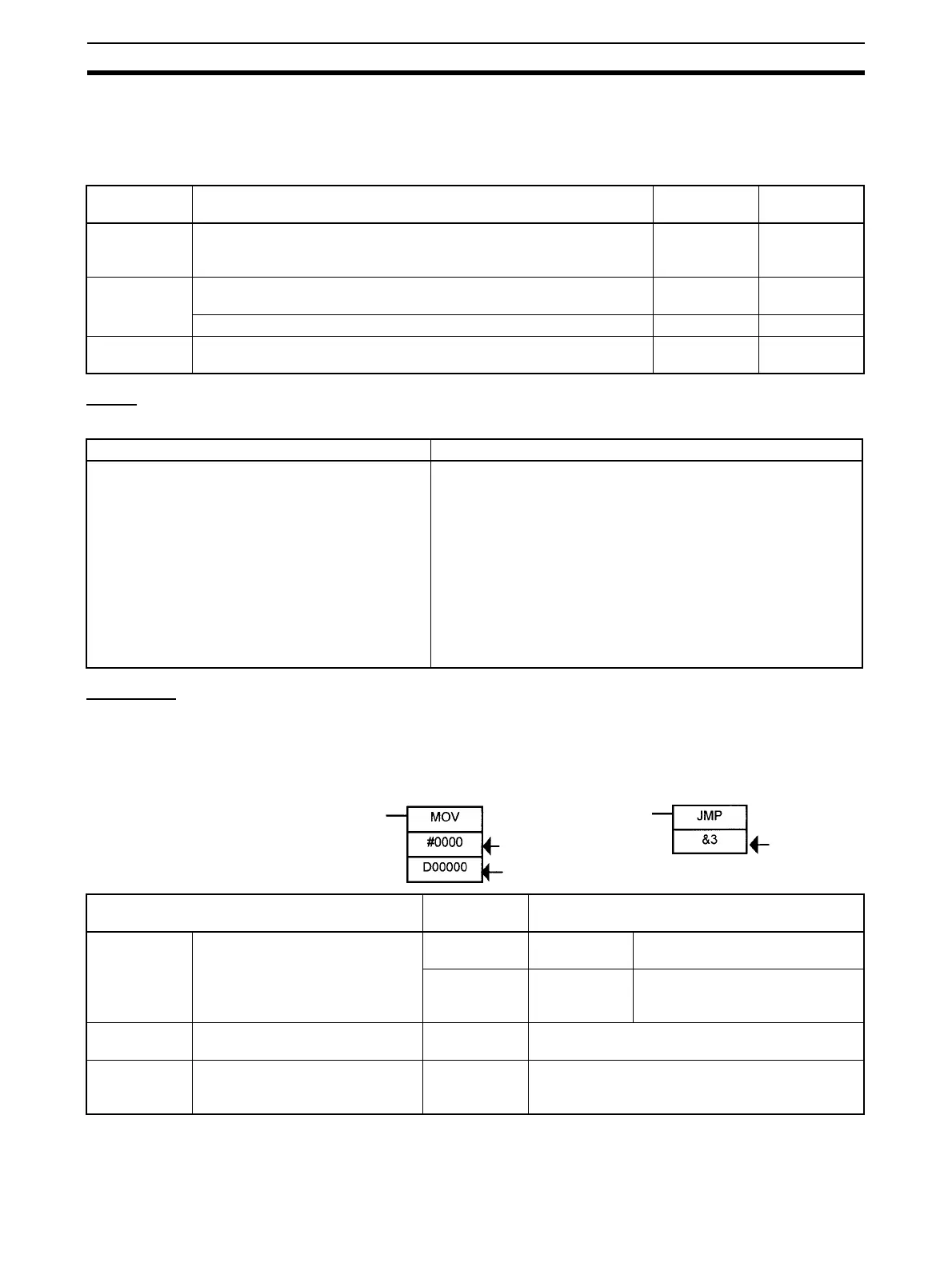
Example
S (source)
D (destination)
N (number)
Operand types Operand
symbol
Description
Source Specifies the address of the data
to be read or a constant.
S Source Oper-
and
Source operand other than control
data (C)
C Control data Compound data in a source oper-
and that has different meanings
depending bit status.
Destination
(Results)
Specifies the address where data
will be written.
D (R) ---
Number Specifies a particular number used
in the instruction, such as a jump
number or subroutine number.
N---
 Loading...
Loading...











