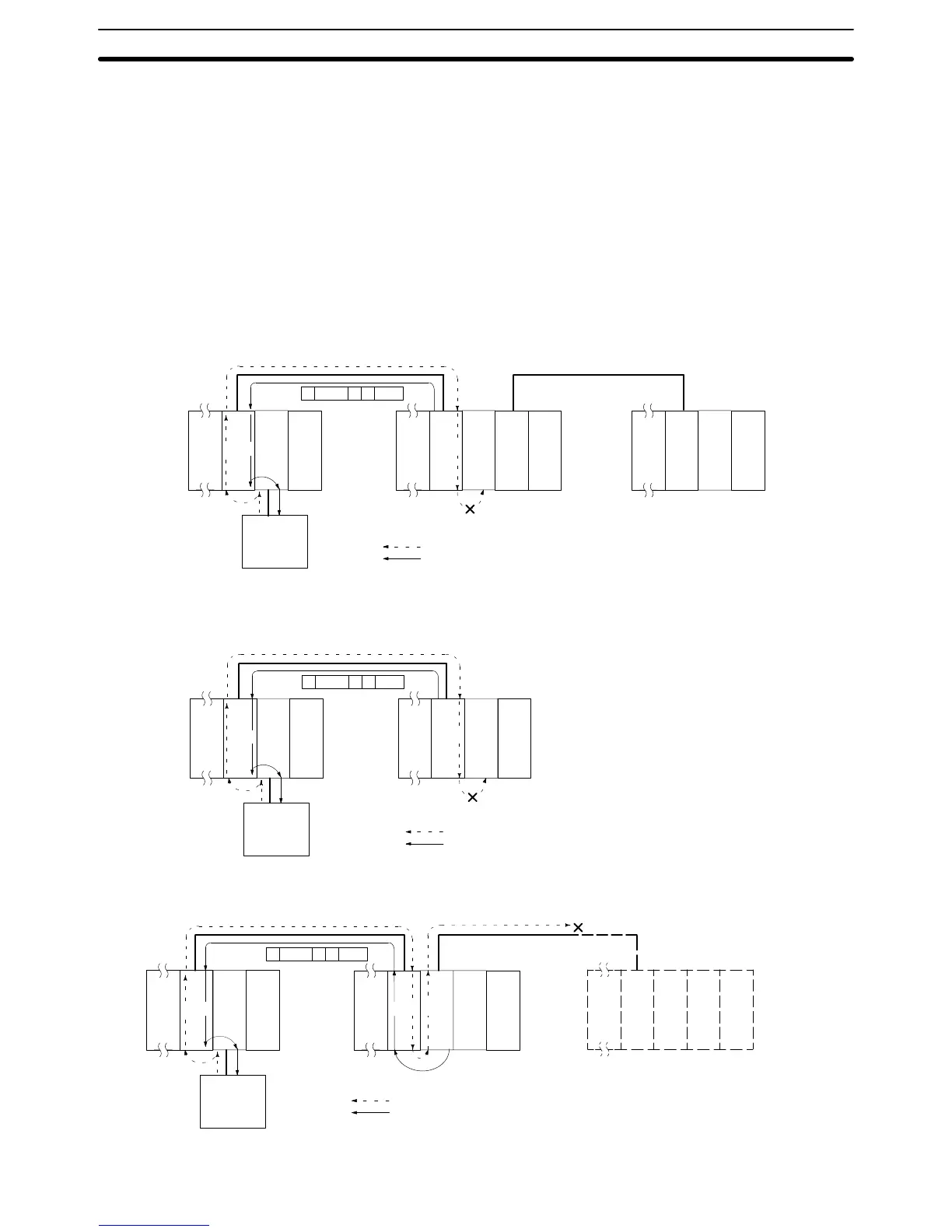
107
Relaying Errors A relaying error occurs when a command from the Host Link Unit is not able to
reach the destination node. There are basically three types of relaying errors:
when data is not passed from one Link Unit to another, when data is not passed
from a Link Unit to another Unit (e.g., a CPU), and when the destination node or
relaying node does not exist. The following graphics show the examples of these
relaying errors.
In the following examples, (1) indicates that transmission data was not relayed,
and (2) indicates that the relaying error data and response code are returned to
the Unit that issued them. MC stands for main code and SC stands for sub-code.
After ascertaining the node where the error occurred, determine the kind of error
from the response code and take necessary steps for correction.
Example 1 In this example, data transmission between two Link Units was not possible,
e.g., due to a routing table error.
SNT
CPU PS
SNT CPU PSCPU PS
Host
computer
Transmission
Response
PS :Power Supply Unit
CPU :Central Processing Unit
SLK :SYSMAC LINK Unit
SNT :SYSMAC NET Link Unit
(1)
SLKSLK
1 MC – – SC
(2)
Example 2 In this example, data transmission from a Link Unit to the CPU was not possible,
e.g., due to no Link Unit servicing
CPU PSCPU PS
Host
computer
(1)
Transmission
Response
SLKSLK
1 MC – – SC
(2)
PS :Power Supply Unit
CPU :Central Processing Unit
SLK :SYSMAC LINK Unit
Example 3 In this example, no destination node or relaying node exists.
CPU PSCPU PS
1 MC – – SC
(2)
Host
computer
SLK
SNT CPU PS
(1)
Transmission
Response
SNT SNT
SLK
PS :Power Supply Unit
CPU :Central Processing Unit
SLK :SYSMAC LINK Unit
SNT :SYSMAC NET Link Unit
CV-mode Response Codes
Section 6-4
 Loading...
Loading...











