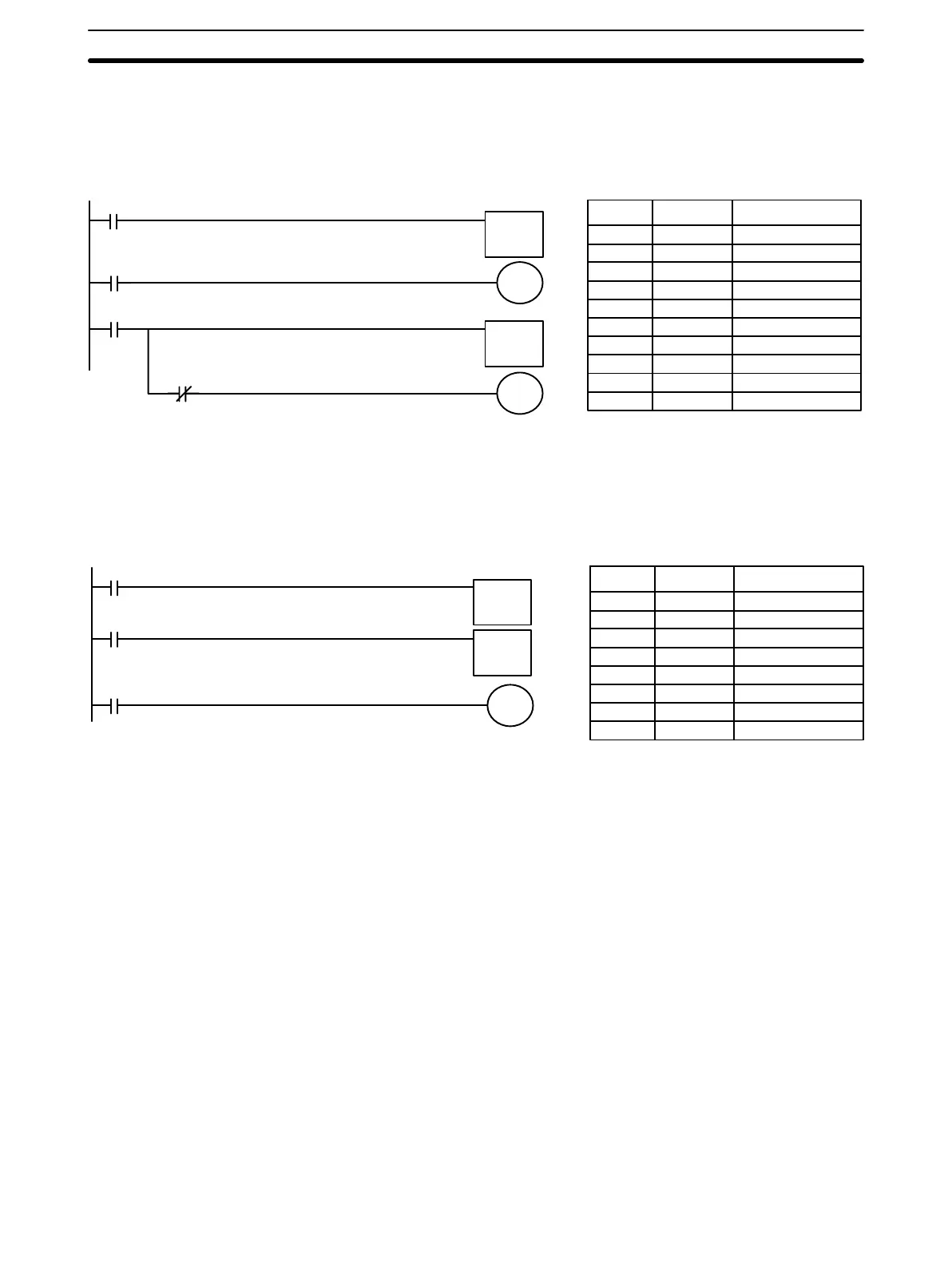
84
OFF, the timer will be reset and 0100 will be turned OFF. When 0001 goes
ON, TIM 01 is started. Bit 0101 is also turned ON when 0001 goes ON.
When 20 seconds have expired, 0101 is turned OFF. This bit will also be
turned OFF when TIM 01 is reset, regardless of whether or not SV has ex-
pired.
0000
TIM 00
0001
TIM 01
0100
0101
Address Instruction Operands
000 LD 0000
001 TIM 00
# 0150
002 LD TIM 00
003 OUT 0100
004 LD 0001
005 TIM 01
# 0200
006 AND NOT TIM 01
007 OUT 0101
TIM 00
#0150
TIM 01
#0200
There are two ways to achieve timers that operate for longer than 999.9 sec-
onds. One method is to program consecutive timers, with the Completion
Flag of each timer used to activate the next timer. A simple example with two
900.0-second (15-minute) timers combined to functionally form a 30-minute
timer.
0000
TIM 01
TIM 02
0100
Address Instruction Operands
000 LD 0000
001 TIM 01
# 9000
002 LD TIM 01
003 TIM 02
# 9000
004 LD TIM 02
005 OUT 0100
TIM 01
#9000
TIM 02
#9000
900.0 s
900.0 s
In this example, bit 0100 will be turned ON 30 minutes after bit 0000 goes
ON.
TIM can also be combined with CNT or CNT can be used to count dedicated
clock pulse bits to produce longer timers. An example is provided in 3-7-18
COUNTER - CNT.
TIM can be combined with KEEP(12) to delay turning a bit ON and OFF in
reference to a desired execution condition. KEEP(12) is described 3-7-9
KEEP - KEEP(12).
To create delays, the Completion Flags for two TIM are used to determine
the execution conditions for setting and reset the bit designated for
KEEP(12). The bit whose manipulation is to be delayed is used in KEEP(12).
Turning ON and OFF the bit designated for KEEP(12) is thus delayed by the
SV for the two TIM. The two SV could naturally be the same if desired.
In the following example, 0100 would be turned ON 5.0 seconds after 0000
goes ON and then turned OFF 3.0 seconds after 0000 goes OFF. It is neces-
sary to use both 0100 and 0000 to determine the execution condition for TIM
02; 0000 in a normally closed condition is necessary to reset TIM 02 when
0000 goes ON and 0100 is necessary to activate TIM 02 (when 0000 is
OFF).
Example 2:
Extended Timers
Example 3:
ON/OFF Delays
Instruction Set Section 3-7
 Loading...
Loading...











