i02177969
Starting Motor - Inspect
Perkins recommends a scheduled inspection of the
starting motor. If the starting motor fails, the engine
may not start in an emergency situation.
Check the starting motor for correct operation. Check
the electrical connections and clean the electrical
connections. Refer to the Systems Operation, Testing
and Adjusting Manual, “Electric Starting System -
Test” for more information on the checking procedure
and for specifications or consult your Perkins dealer
or your Perkins distributor for assistance.
i04922217
Turbocharger - Inspect
Hot engine components can cause injury from
burns. Before performing maintenance on the en-
gine, allow the engine and the components to
cool.
NOTICE
Turbocharger bearing failures can cause large quanti-
ties of oil to enter the air intake and exhaust systems.
Loss of engine lubricant can result in serious engine
damage.
Minor leakage of oil into a turbocharger under ex-
tended low idle operation should not cause problems
as long as a turbocharger bearing failure has not
occured.
When a turbocharger bearing failure is accompanied
by a significant engine performance loss (exhaust
smoke or engine rpm up at no load), do not continue
engine operation until the turbocharger is renewed.
A visual inspection of the turbocharger or
turbochargers can minimize unscheduled downtime.
A visual inspection of the turbocharger or
turbochargers can also reduce the chance for
potential damage to other engine parts. Do not
inspect the engine with the engine in operation.
Engine Installed with Single
Turbocharger
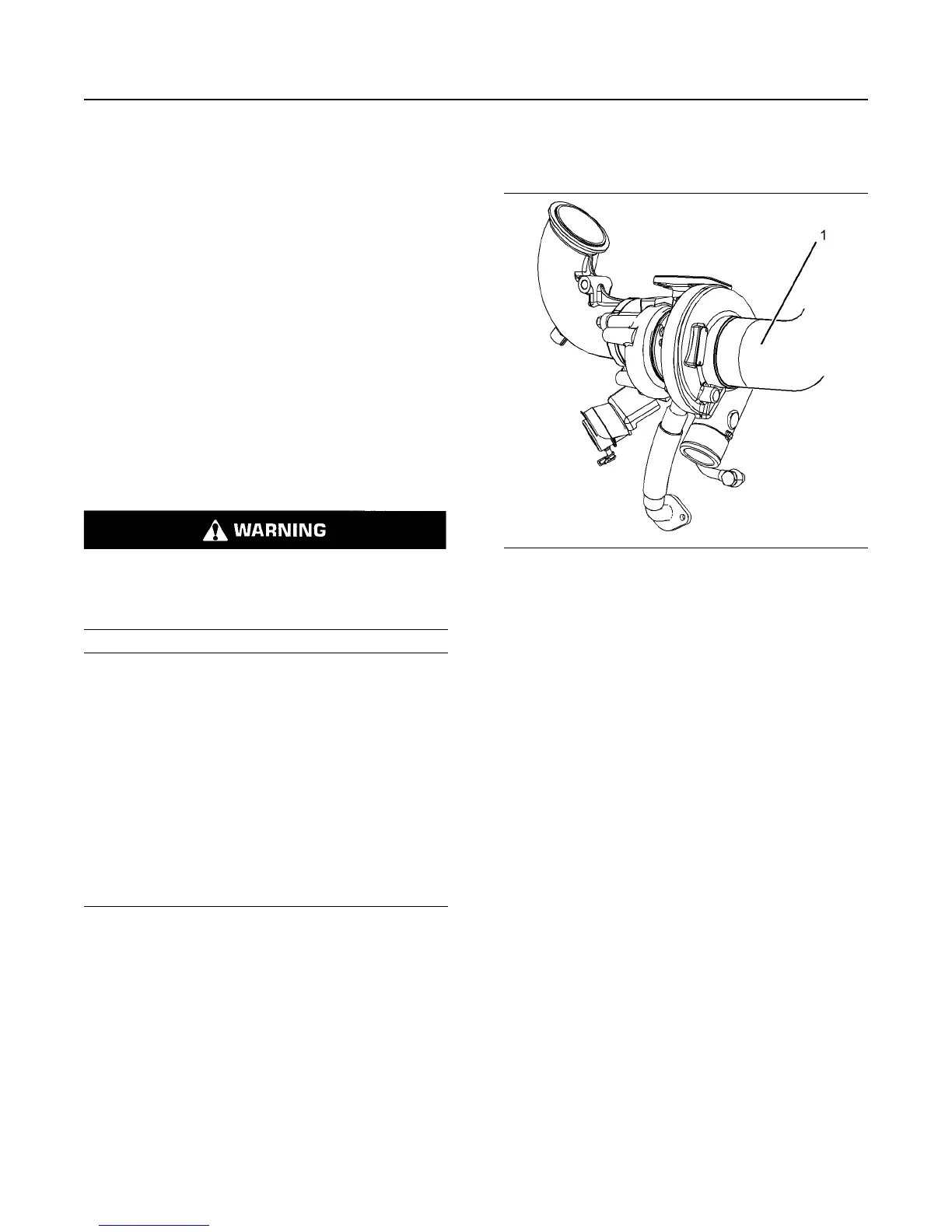
Illustration 101 g03089297
1. Ensure that the turbocharger is clean and free from
dirt before removing components for inspection.
2. Remove the pipe from the turbocharger exhaust
outlet and remove the air intake pipe (1). Visually
inspect the piping for the presence of oil. Clean the
interior of the pipes in order to prevent dirt from
entering during reassembly.
3. Check for obvious heat discoloration of the
turbocharger. Check for any loose bolts or any
missing bolts. Check for damage to the oil supply
line and the oil drain line. Check for cracks in the
housing of the turbocharger. Ensure that the
compressor wheel can rotate freely.
4. Check for the presence of oil. If oil is leaking from
the back side of the compressor wheel, there is a
possibility of a failed turbocharger oil seal.
The presence of oil may be the result of extended
engine operation at low idle. The presence of oil
may also be the result of a restriction of the line for
the intake air (clogged air filters), which causes the
turbocharger to slobber.
5. Install the air intake pipe and the exhaust outlet
pipe to the turbocharger housing. Ensure that all
clamps are installed correctly and that all clamps
are tightened securely. For more information, refer
to Systems Operation, Testing, and Adjusting,
“Turbocharger - Inspect”.
SEBU8732 123
Maintenance Recommendations
Starting Motor - Inspect

 Loading...
Loading...