Chapter 2 Standard specifications
9
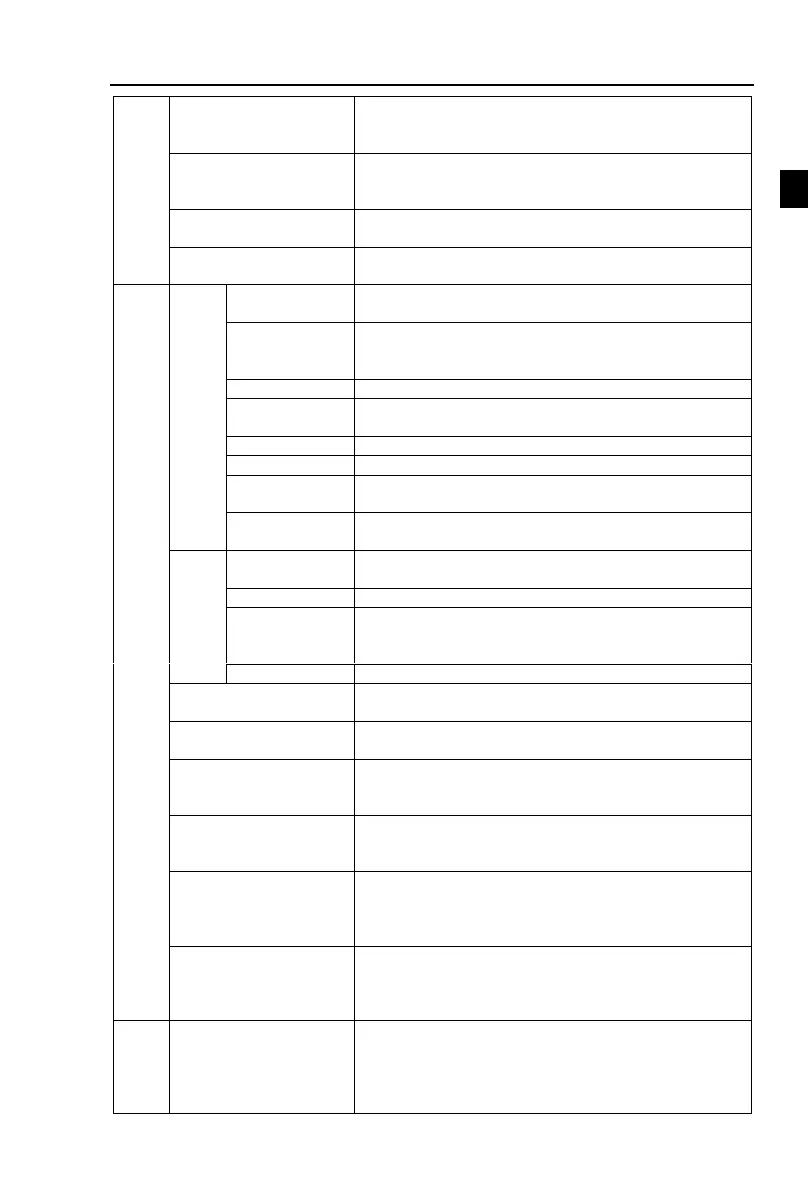
Self-inspection of
peripherals after power-
on
After powering on, peripheral equipment will perform
safety testing, such as ground, short circuit, etc.
The current limiting algorithm is used to reduce the
inverter overcurrent probability, and improve whole unit
anti-interference capability.
Timing control function: Time setting range(0m to
6500m)
On line cutting machine operation mode, using a terminal
to control the motor forward and reverse operation.
Keyboard/terminal/communication
8 frequency settings available, including adjustable DC(0
to 10V), adjustable DC(0 to 20mA), panel potentiometer,
etc.
At most 16-speed can be set(run by using the multi-
function terminals or program)
Interrupt controller output
When the protection function is active, you can
automatically or manually reset the fault condition.
Including DC(0 to 10V), DC(0 to 20mA)
Motor status display, stop, ac/deceleration, constant speed,
program running status.
Contact capacity :normally closed contact AC 250V/7A
one-way analog output, 16 signals can be selected such as
frequency, current, voltage and other, output signal range
(0 to 10V / 0 to 20mA).
one-way output signal, there are 40 signals each way
Limit frequency, jump frequency, frequency
compensation, auto-tuning, PID control
Built-in PID regulates braking current to ensure sufficient
braking torque under no overcurrent condition.
Three channels: Operation panel, control terminals and
serial communication port. They can be switched through
a variety of ways.
Total 5 frequency sources: Digital, analog voltage, analog
current, multi-speed and serial port. They can be switched
through a variety of ways.
7digital input terminals, compatible with active PNP or
NPN input mode, one of them can be for high-speed pulse
input(0 to 100 kHz square wave); 1 analog input terminal
0-10v or 0-20mA
1 digital output terminal, one relay output terminal; 1
analog output terminals respectively for optional range (0
to 20mA or 0 to 10V), they can be used to set frequency,
output frequency, speed and other physical parameters.
Overvoltage protection, undervoltage protection,
overcurrent protection, overload protection, overheat
protection, overcurrent stall protection, overvoltage stall
protection, losting-phase protection (optional),
communication error, PID feedback signal abnormalities,

 Loading...
Loading...