Configuring Username and Password Security
Saving Security Credentials in a Config File
SNMP Security Credentials
SNMPv1 community names and write-access settings, and SNMPv3
usernames continue to be saved in the running configuration file even when
you enter the include-credentials command.
In addition, the following SNMPv3 security parameters are also saved:
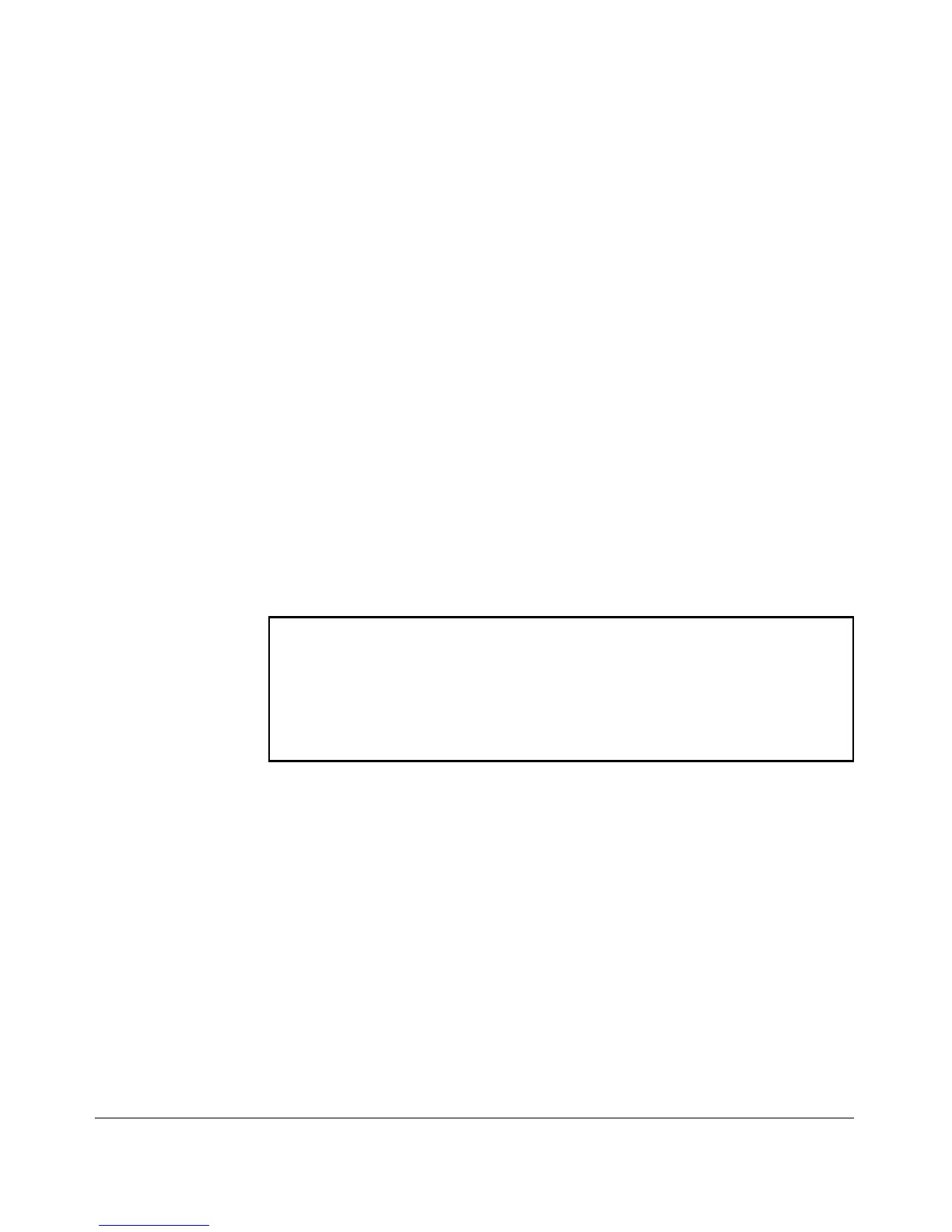
snmpv3 user “<name>" [auth <md5|sha> “<auth-pass>”]
[priv “<priv-pass>"]
where:
<name> is the name of an SNMPv3 management station.
[auth <md5 | sha>] is the (optional) authentication method used for the
management station.
<auth-pass> is the hashed authentication password used with the
configured authentication method.
[priv <priv-pass>] is the (optional) hashed privacy password used by a
privacy protocol to encrypt SNMPv3 messages between the switch and the
station.
The following example shows the additional security credentials for SNMPv3
users that can be saved in a running-config file:
snmpv3 user boris \
auth md5 “9e4cfef901f21cf9d21079debeca453” \
priv “82ca4dc99e782db1a1e914f5d8f16824”
snmpv3 user alan \
auth sha “8db06202b8f293e9bc0c00ac98cf91099708ecdf” \
priv “5bc4313e9fd7c2953aaea9406764fe8bb629a538”
Figure 2-4. Example of Security Credentials Saved in the Running-Config
Although you can enter an SNMPv3 authentication or privacy password in
either clear ASCII text or the SHA-1 hash of the password, the password is
displayed and saved in a configuration file only in hashed format, as shown in
the preceding example.
802.1X Port-Access Credentials
802.1X authenticator (port-access) credentials can be stored in a
configuration file. 802.1X authenticator credentials are used by a port to
authenticate supplicants requesting a point-to-point connection to the switch.
802.1X supplicant credentials are used by the switch to establish a point-to-
point connection to a port on another 802.1X-aware switch. Only 802.1X
authenticator credentials are stored in a configuration file. For information
2-14
 Loading...
Loading...