ESP-SMT Smart Modular Control System
76
How the ESP-SMT Smart Control System Works
Unlike a traditional time-based irrigation controller that
employs xed station run times, start times, and irrigation
days manually set by the user, the Rain Bird ESP-SMT Smart
Control System irrigation schedule automatically changes
daily based on specic weather conditions at the site.
Weather information is collected in real-time by an on-site
SMT Weather Sensor and communicated to the ESP-SMT
Controller. This collected weather information is combined
with 1) historic weather information for the site location
and 2) specic site and individual zone parameters that
are entered into the controller by the user to automatically
create an optimized irrigation schedule that will promote
healthy deep rooted plants while conserving water. Based
on the soil type and slope conditions, the overall irrigation
requirement is split into multiple “cycle and soak” irrigation
events, thereby eliminating the problems from water run-
o.
Automated Management Allowed Depletion (MAD)
Irrigation Scheduling Method
The objective of an automated irrigation system is to
augment rainfall in order to re-supply the (soil) with
enough available water for the plant to make up for the
water lost through Evapotranspiration (ET). The proven
MAD method looks at the soil as a water reservoir that
supplies the plant with water as needed. The soil texture
(class) of the soil reservoir inuences the amount of water
that can be stored in the soil, as well as the potentially
available water (PAW) for the plant material growing in
the soil. The soil texture and the MAD will determine the
amount and frequency of irrigation
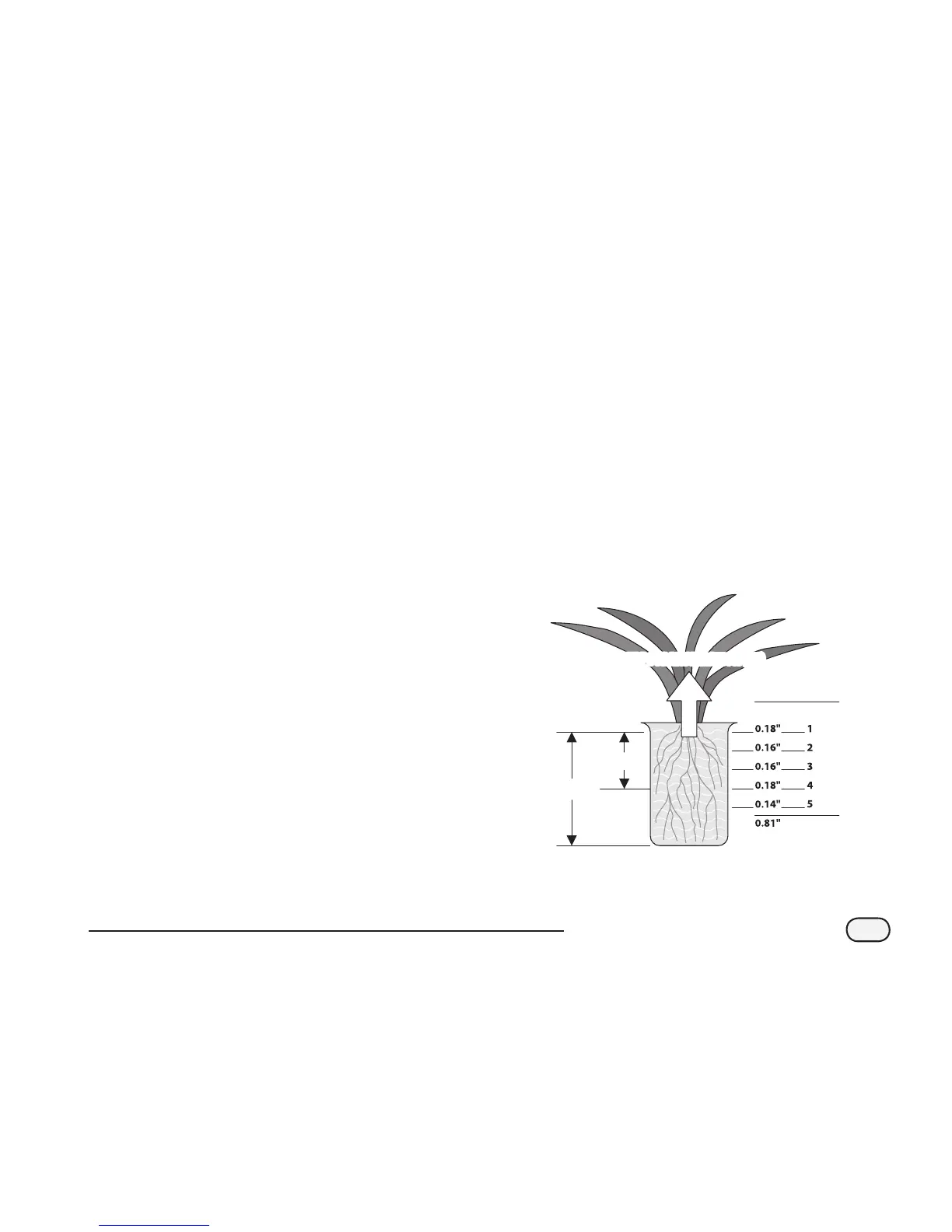
Evapotranspiration
The Evapotranspiration (ET) rate is usually expressed
in inches of water lost over a time period (usually on
a daily basis) due to evaporation from the soil surface
and transpiration from the plant surfaces. The ET rate is
inuenced greatly by the weather conditions at the site.
For example; a hot dry environment would have a much
higher ET rate and require longer, more frequent irrigation
than a cool, humid environment.
EVAPOTRANSPIRATION (ET)
ET
PAW 1"
MAD 0.5"
Day
(50% MAD)
Inches/Day
IRRIGATE:
When? >>>>>
 Loading...
Loading...