286 Rockwell Automation Publication 1766-UM001O-EN-P - September 2021
Appendix G Connect to Networks via Ethernet Interface
To correct this conflict, use the instructions in this chapter to change the IP
address of the EtherNet/IP device. Then cycle power to the device or reset the
device (such as disconnecting the Ethernet cable and reconnecting the cable).
There is also the possibility that two EtherNet/IP device can detect a conflict
simultaneously. If this occurs, remove the device with the incorrect IP address
or correct its conflict. To get the second device out of conflict mode, cycle
power to the module or disconnect its Ethernet cable and reconnect the cable.
The MicroLogix 1400 checks every 2 minutes for a duplicate IP address on the
network.
Configure the Ethernet
Channel on the
MicroLogix 1400
There are three ways to configure the MicroLogix 1400 Ethernet channel 1.
• via a BOOTP or DHCP request at controller power up
• manually setting the configuration parameters using RSLogix 500/
RSLogix Micro Programming Software
• via LCD display (see Configure the Ethernet Port
on page 103 and
Configure Ethernet Protocol Setup on page 105)
The configuration parameters are shown on the following page, and the configuration
procedures follow.
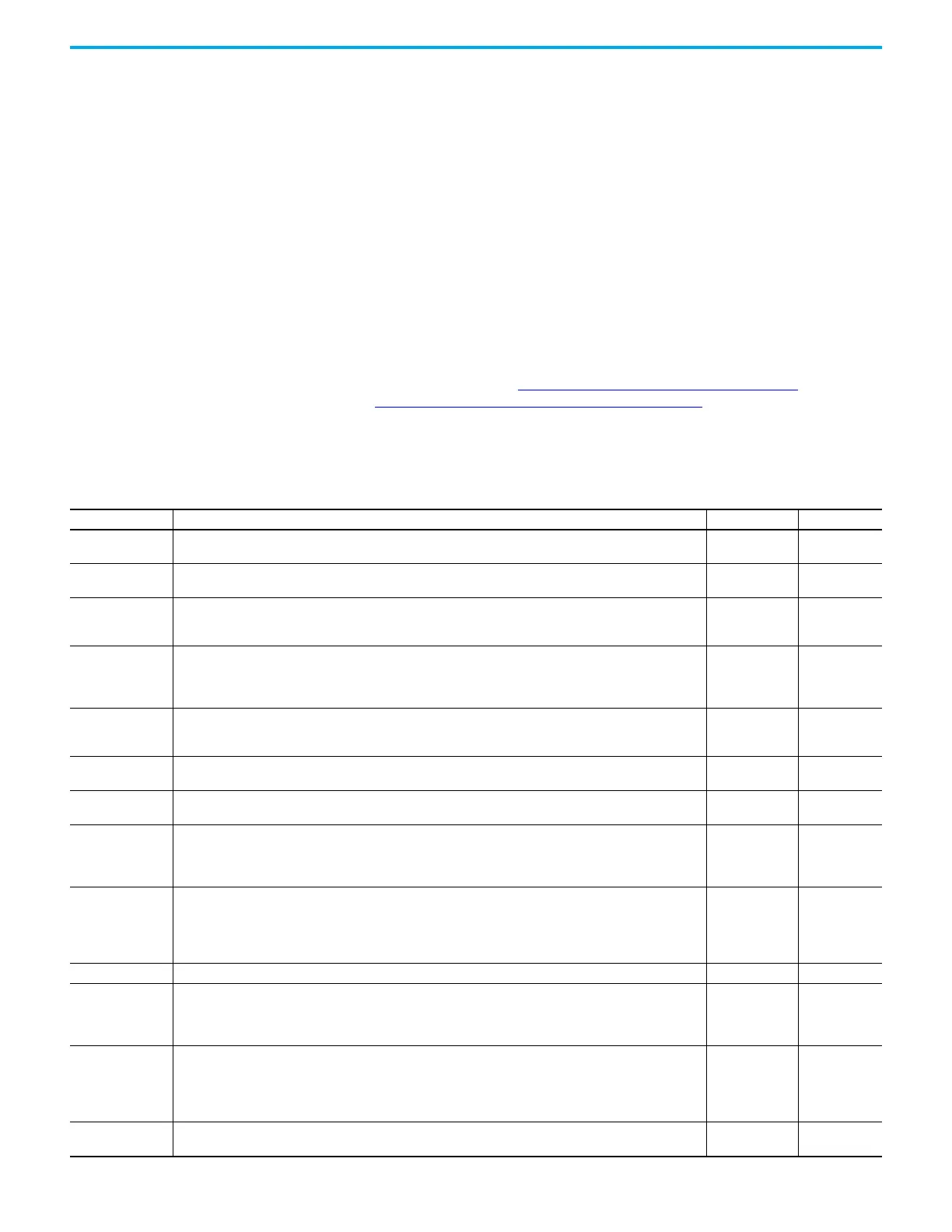
Table 43 - Configuration Parameters
Parameter Description Default Status
Hardware Address The MicroLogix 1400 Ethernet hardware address.
Ethernet hardware
address
read only
IP Address
The MicroLogix 1400 Internet address (in network byte order). The Internet address must be specified to connect to
the TCP/IP network.
0 (undefined) read/write
Subnet Mask
The MicroLogix 1400 subnet mask (in network byte order). The Subnet Mask is used to interpret IP addresses when
the internet is divided into subnets. A Subnet Mask of all zeros indicates that no subnet mask has been configured.
In this case, the controller assumes a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0.
0 (undefined) read/write
Gateway Address
The address of a gateway (in network byte order) that provides connection to another IP network. A Gateway Address
of all zeros indicates that no gateway has been configured.
In this case, the controller assumes a Gateway Address of aaa.bbb.ccc.001, where aaa.bbb.ccc are the first three
octets of the configured IP Address.
0 (undefined) read/write
Default Domain
Name
The default domain name can have the following formats:
’a.b.c’, ’a.b’ or ’a’, where a, b, c must start with a letter, end with a letter or digit, and have as interior characters only
letters, digits or hyphens. Maximum length is 63 characters.
NULL
(undefined)
read/write
Primary Name Server
This is the IP address of the computer acting as the local Ethernet network Primary Domain Name System (DNS)
server.
0 (undefined) read/write
Secondary Name
Server
This is the IP address of the computer acting as the local Ethernet network Secondary Domain Name System (DNS)
server.
0 (undefined) read/write
BOOTP Enable
The BOOTP enable switch. When BOOTP is enabled, the MicroLogix 1400 attempts to learn its network related
parameters at powerup via a BOOTP request. There must be a BOOTP server on the network capable of responding to
this BOOTP request. When both BOOTP and DHCP are disabled, the MicroLogix 1400 uses the locally configured
network related parameters (IP Address, Subnet Mask, Broadcast Address, etc.).
1 (enabled) read/write
DHCP Enable
The DHCP auto configuration enable switch. When DHCP is enabled, a DHCP server automatically assigns network
related parameters to the MicroLogix 1400 when it logs into a TCP/IP network. There must be a DHCP server on the
network capable of allocating network addresses and configuring parameters to newly attached device. When both
BOOTP and DHCP are disabled, the MicroLogix 1400 uses the locally configured network related parameters (IP
Address, Subnet Mask, Broadcast Address, etc.).
0 (disabled) read/write
SNMP Server Enable SNMP enable switch. Check this to enable SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol). 1 (enabled) read/write
SMTP Client Enable
The SMTP Client service enable switch. When SMTP is enabled, MicroLogix 1400 is capable of transmitting e-mail
messages generated by a 485CIF write message with a string element. There must be a SMTP server on the network
capable of processing e-mail service. This provides an extremely versatile mechanism to report alarms, status, and
other data-related functions.
0 (disabled) read/write
Auto Negotiate and
Port Setting
When Auto Negotiate is disabled (unchecked), the Ethernet speed/duplex is forced to either 10 Mbps/Half-duplex, 10
Mbps/Full-duplex, 100 Mbps/Half-duplex, or 100 Mbps/Full-duplex, as selected in the Port Setting field.
When Auto Negotiate is enabled (checked), the Port Setting Field allows you to select the range of speed/duplex
settings that the MicroLogix 1400 will negotiate.
Auto Negotiate
enabled and Port
Setting. 10/100
Mbps Full Duplex/
Half Duplex
read/write
MSG Connection
Timeout
The amount of time (in ms) allowed for a MSG instruction to establish a connection with the destination node. The MSG
Connection Timeout has 250 ms resolution and a range from 250…65,500.
15,000 ms read/write

 Loading...
Loading...











