Commissioning
7.3 Checking the insulation resistance
Synchronous/induction motors 1PH813
Operating Instructions, 04/2009, 610.48000.22
55
Limits
The table below specifies the measuring circuit voltage as well as the limit values for the
minimum insulation resistance and the critical insulation resistance with a rated motor
voltage of U
N
< 2 kV:
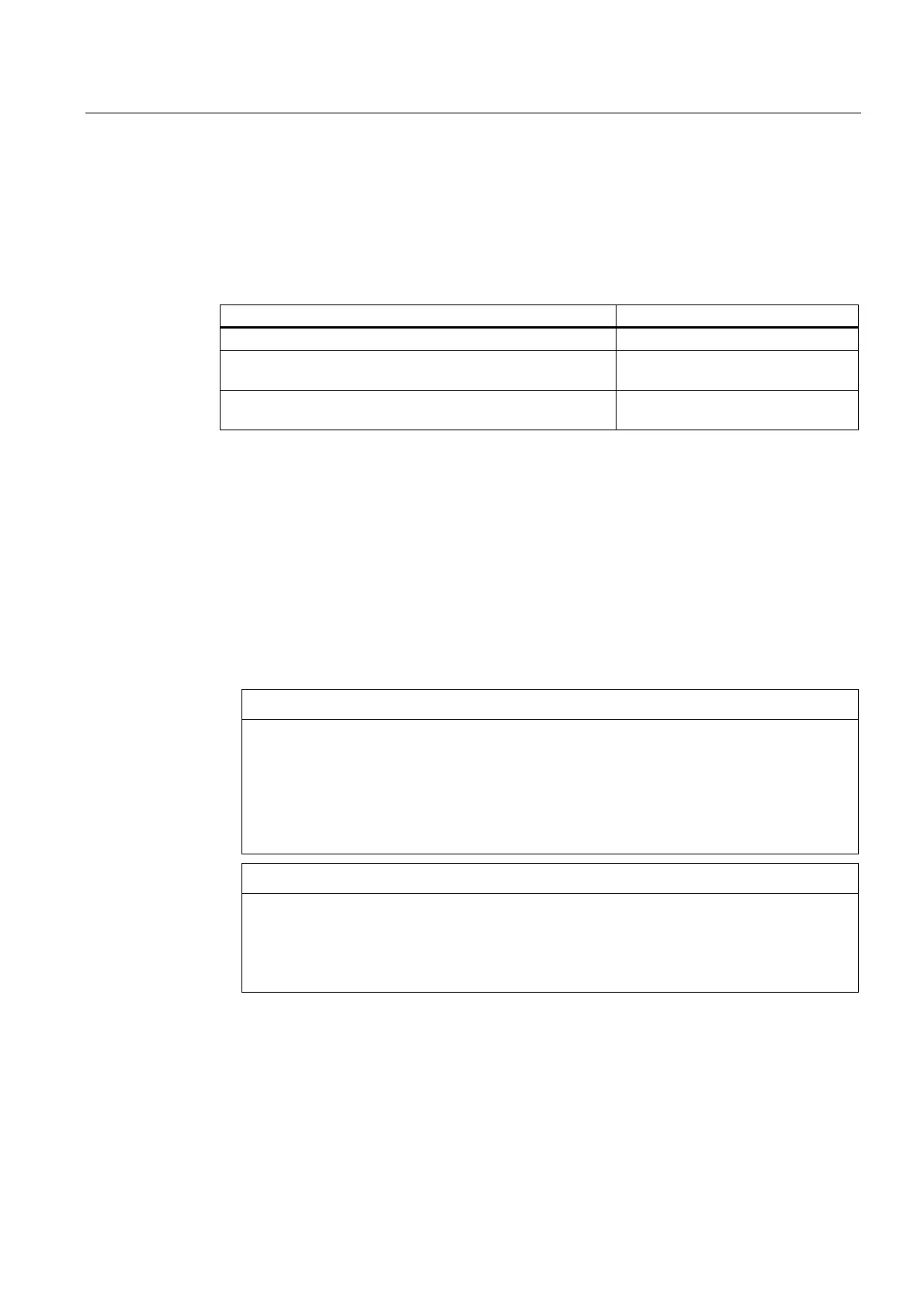
Table 7- 1 Stator winding insulation resistance at 25 °C
Rated voltage U
N
< 2 kV
Measurement voltage 500 V (at least 100 V)
Minimum insulation resistance with new, cleaned, or repaired
windings
10 MΩ
Critical specific insulation resistance after a long operating
time
5 MΩ/kV
Note the following:
● Dry, new windings have an insulation resistance of between 100 and 2000 MΩ
(sometimes higher).
If the insulation resistance is close to the minimum value, this could be due to humidity
and/or an accumulation of dirt.
● The insulation resistance of the motor winding can drop during the course of its service
life can drop due to ambient and operational influences. The critical insulation resistance
for a temperature of 25°C on the winding can be calculated by multiplying the rated
voltage (kV) by the specific critical resistance value (5 MΩ/kV);
Example: Critical resistance for a rated voltage (U
N
) of 500 V:
500 V x 5 MΩ/kV = 2.5 MΩ
NOTICE
Cleaning and/or drying the windings when reaching critical insulation resistance
If the critical insulation resistance is less than or equal to this value, the windings must
be dried or, if the fan is removed, cleaned thoroughly and dried.
Note that the insulation resistance of dried, clean windings is lower than that of warm
windings. The insulation resistance can only be evaluated accurately when measured
on a winding that has been cooled down to room temperature (approx. 20 to 30°C).
NOTICE
Measured value close to critical value
If the measured value is close to the critical value, the insulation resistance should be
subsequently checked at suitably regular intervals.
Values apply for measurement at a winding temperature of 25 °C.
 Loading...
Loading...











