Motion synchronous actions
10.4 Actions in synchronized actions
Job planning
10-34 Programming Manual, 03/2006 Edition, 6FC5398-2BP10-1BA0
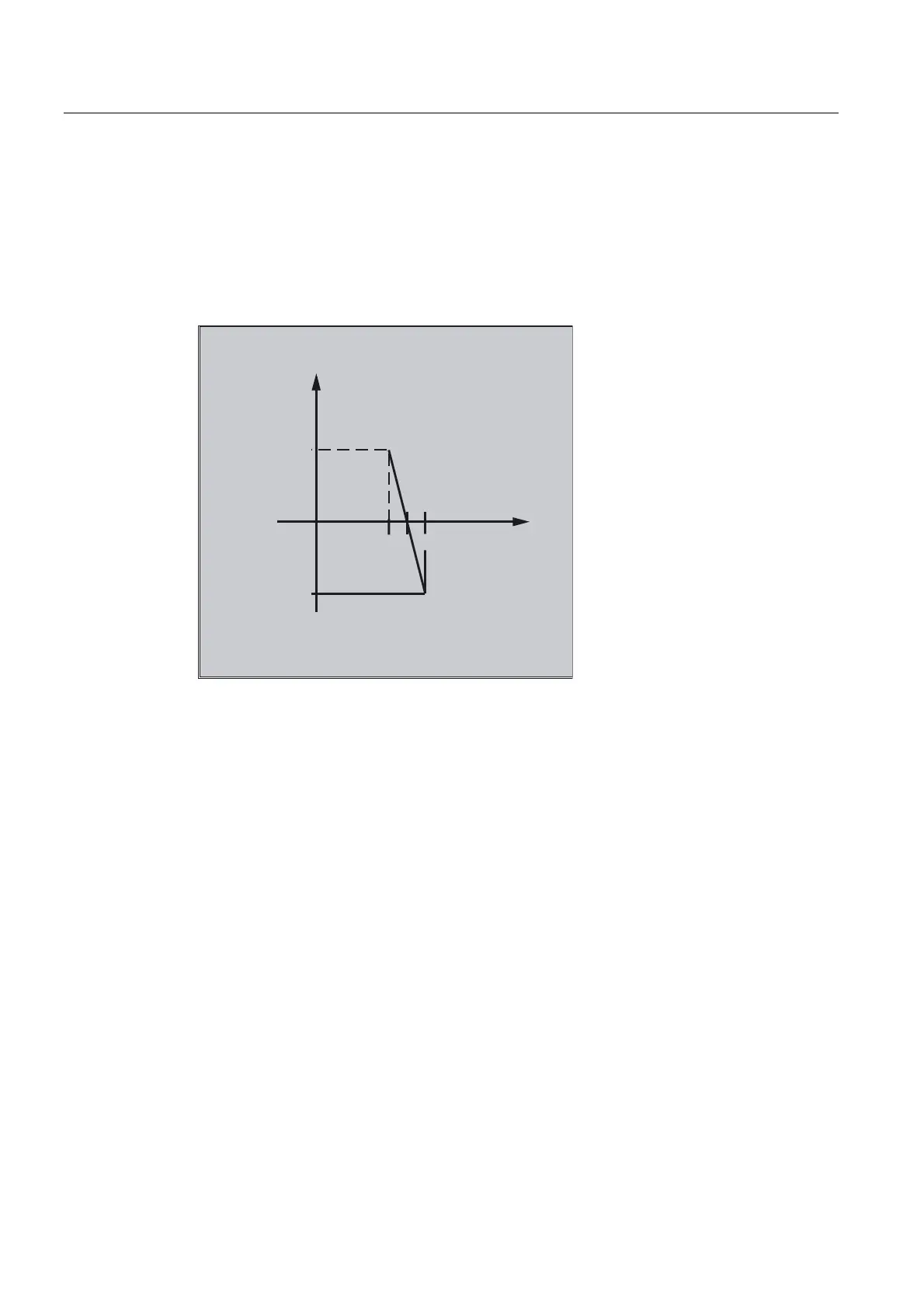
Example of adaptive control (additive)
Additive influence on the programmed feedrate
A programmed feedrate is to be controlled additive using the current of the X axis (infeed
axis):
The feedrate should only vary by +/- 100 mm/min and the current fluctuates by +/-1A around
the working point of 5A.
,
$
)
>@
>@
PPPLQ
YROWDJHOLPLW
8SSHUOLPLW
1. Polynomial definition
Determination of the coefficients
y = f(x) = a
0
+ a
1
x + a
2
x
2
+ a
3
x
3
a
1
= -100mm/1 min A
a
0
= -(-100)*5 =500
a
2
= a
3
= 0 (no square and cubic component)
Upper limit = 100
Lower limit = -100
This means:
FCTDEF(1,-100,100,500,-100,0,0)
2. Activate AC control
ID=1 DO SYNFCT(1,$AC_VC,$AA_LOAD[x])
;Read the current axis load (% of the max. drive current) via $AA_LOAD[x],
;calculate the path feedrate override with the polynomial defined above.

 Loading...
Loading...






















