Section 2
2.1
OPERATION
Functional Description - Position Sensor
The Position Sensor supplies an output voltage proportional to the applied magnetic field. This magnetic
sensor, based on hall effect, is ideal for sensing linear or rotative position. The mechanical vibrations do
not affect Position Sensor.
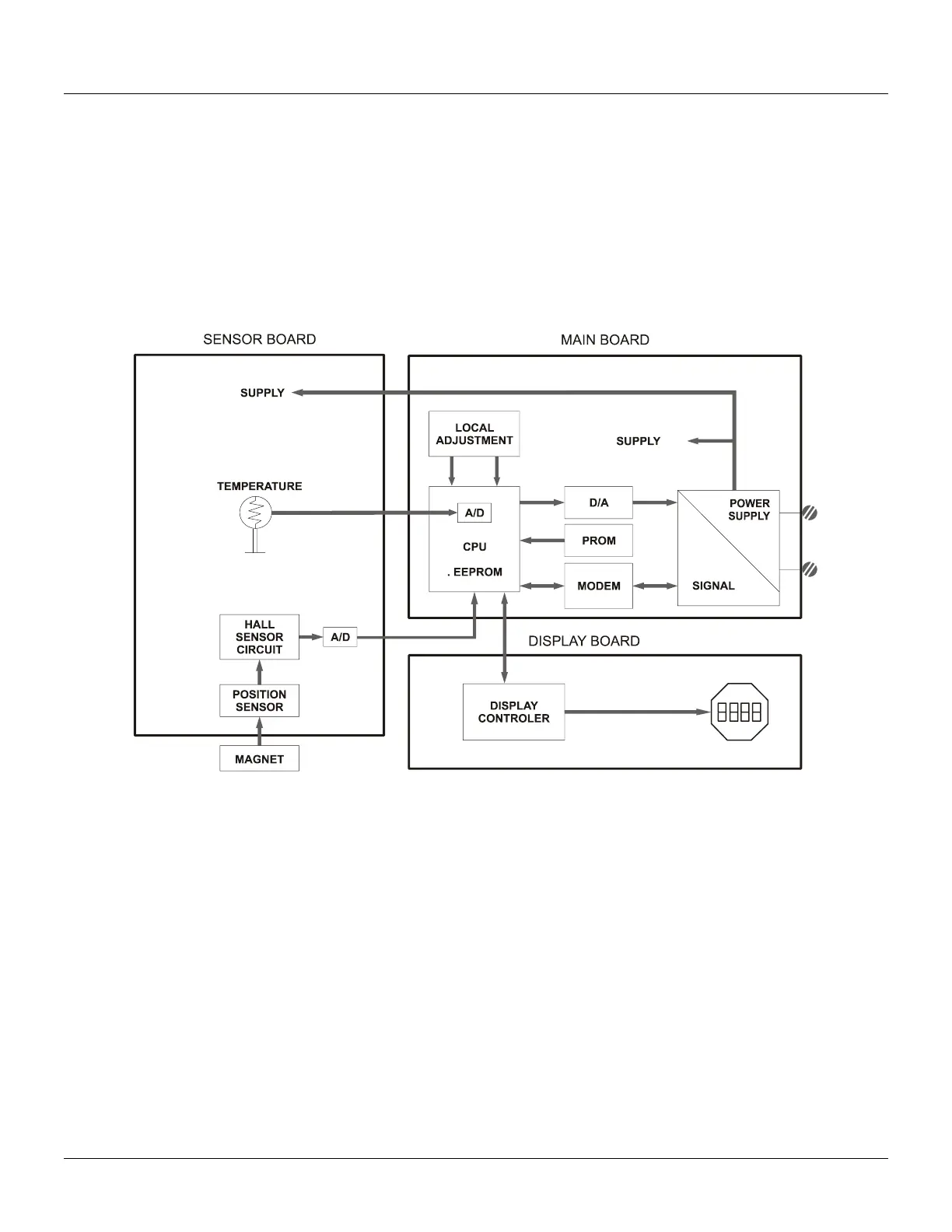
Functional Description - Electronics
The function of each block in the block diagram is described below.
Figure 2.1 - TP301 Block Diagram
Hall Effect Position Sensor
The magnet, installed in the instrument to the position to be measured, moves the of the instrument
movement accordingly. The hall effect position sensor detects the movement and produces a small
voltage change variation proportional to the magnetic field variation due to the magnet movement.
Temperature Sensor
The sensor circuit of hall processes that tension variation, generating a signal for the converter A/D. The
converter A/D produces a set of signals for the transmitter CPU (Central Processing Unit).
Modem HART
Modulates and demodulates communication signals superimposed onto current line. A "1" is
represented by 1200 Hz and a "0" by 2200 Hz. The frequency signal is symmetrical and does not affect
the DC level of the of the 4 - 20 mA signal.
CPU Central Processing Unit, RAM, PROM and EEPROM
The CPU is the transmitter intelligent part, being responsible for the data management and block
execution, operation self-diagnostics and communication. The program is stored in PROM. For
temporary storage of data there is a RAM. The data in the RAM is lost if the power is switched off,
however the device also has a non-volatile EEPROM where key data is stored. Examples of such data
are the calibration and TP301 configuration.

 Loading...
Loading...