PID constant setting is available
*8
. Moreover, PID constant can
have simple adjustment with 21 steps. The simply adjusted PID
constant will change against the detail setting in the rate shown on
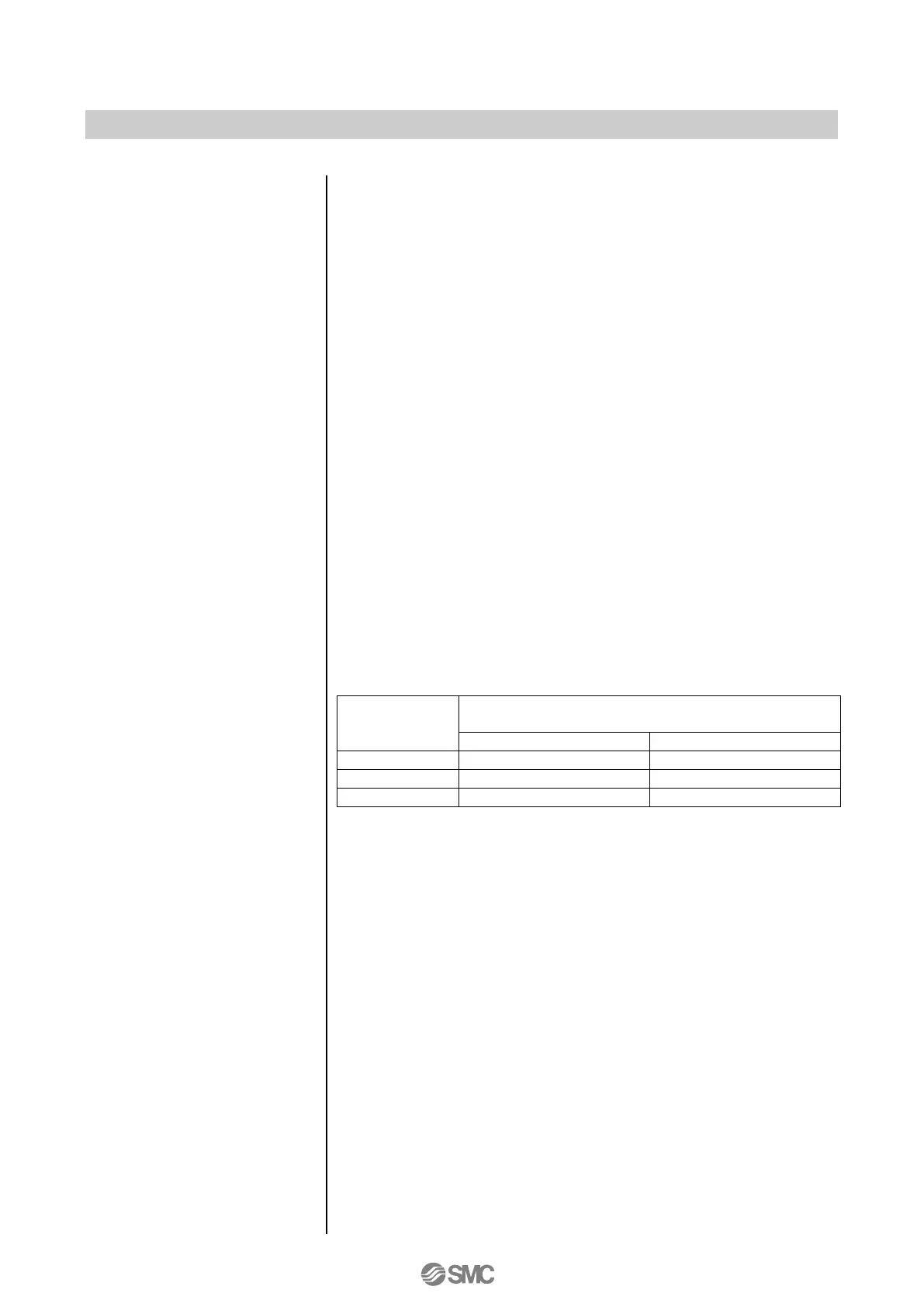
Table 12
*9
. If more detail adjustment is necessary, calculate a PID
constant for simple adjustment based on the ratio on Table 12
*10
.
With the results, change a value of the detail setting. If these set
values are all initialized when calibration is performed.
PID constant for direct (Dir) direction
(811) Proportional gain setting; 0.001 to 9.999
(812) Integrated time setting; 0.000 to 9.999
*11
(813) Differentiation time setting; 0.000 to 9.999
*11
PID constant for reverse (ruS) direction
(821) Proportional gain setting; 0.001 to 9.999
(822) Integrated time setting; 0.000 to 9.999
*11
(823) Differentiation time setting; 0.000 to 9.999
*11
Simple adjustment for PID constant (EASy)
(831) Proportional gain setting; -10 to 10
(832) Integrated time setting; -10 to 10
(833) Differentiation time setting; -10 to 10
8: When automation calibration is performed, PID constant is
automatically set. Change the PID constant if necessary. Although
PID for extraction and retraction can be set independently,
smooth stop may not be available at desired position if they are
different.
9: The indication of the detail setting will not change even if the simple
adjustment is modified.
10: The simple adjustment and the detail setting will interfere with each
other. Set the simple adjustment at 0 if the detail setting is
conducted.
11: The function of integrated operation and differentiation operation is
inactivated when integrated time and differentiation time are set at
“0.000”.
 Loading...
Loading...