Trace Engineering DR Series Owner’s Manual - Version 3.2 - 9/7/98 - Page 14
Generator Requirements
The maximum charge rate of the battery charger is dependent upon the peak AC voltage available.
Since the battery charger uses only the top portion of the input sine wave, small variations in peak
voltage result in large variations in the amount of energy to the charger*. This charger’s output is rated
on the basis of public power input which has a peak voltage of 164V (230V AC power has a peak
voltage of 330).
It takes a powerful AC generator set to maintain the full 164 volt peak while delivering the current
necessary to operate the charger at its maximum rate (typically 5KW for 2500VA models and 2.5KW
for 1500VAt models). Smaller generators will have the tops of their waveform clipped under such
loads. Running at these reduced peak voltages will not harm the charger, but it will limit the maximum
charge rate. Large auxiliary AC loads may exacerbate this problem.
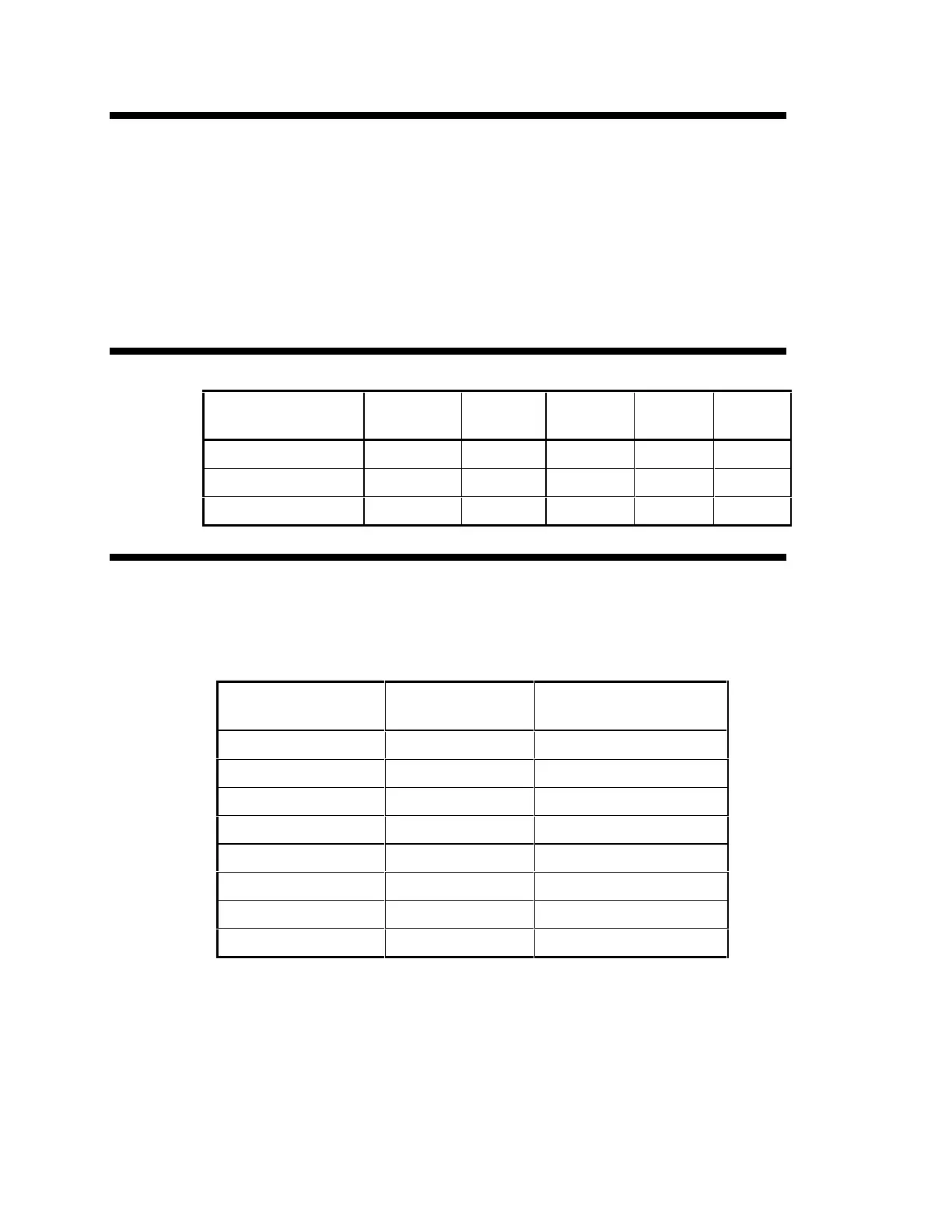
Peak Voltage Available vs. Charge Rate Amps
PEAK VOLTAGE
AVAILABLE
DR1512 DR2412 DR1524 DR2424 DR3624
170 VOLTS 70Amps 120Amps 35Amps 70Amps 70Amps
160 VOLTS 35Amps 60Amps 17.5Amps 35Amps 35Amps
145 VOLTS 15Amps 25Amps 7Amps 15Amps 15Amps
Table 3, Peak Voltage vs. Charge Rate Amps
Generator Examples: Typical Maximum Charge Rate
Amps
Table 4, Maximum Charge Rate with some Typical Generator Models
GENERATOR TYPE INVERTER TYPE TYPICAL MAX CHARGE
RATE AMPS
Honda 800 Trace DR1512 43 Amps
Honda 2200 Trace DR1512 57 Amps
Homelite 2500 Trace DR1512 11 Amps
Honda 3500 Trace DR1512 39 Amps
Honda 6000 Trace DR1512 70 Amps
Honda 1600 Trace DR1524 25 Amps
Westerbeke 7.0KW Trace DR1512 About 45 Amps
Westerbeke 12.5KW Trace DR1512 About 65 Amps
*This characteristic is due to the fact that the battery charger’s DC output is the dividend of the transformer turns ratio. In
example, if a transformer has a 10:1 turns ratio, a 164 volt AC input voltage shows up as approximately 16.4 volts at the
low DC side of the charger after rectification and filtering (164/10), 140 volts AC becomes approximately 14.0 volts DC,
etc. Any peak AC voltage below about 130 volt AC is pretty much useless for charging as it only provides roughly 13.0
volts DC.

 Loading...
Loading...