2.12 Line differential protection
LdI> (87L)
VAMP 24h support phone +358 (0)20 753 3264
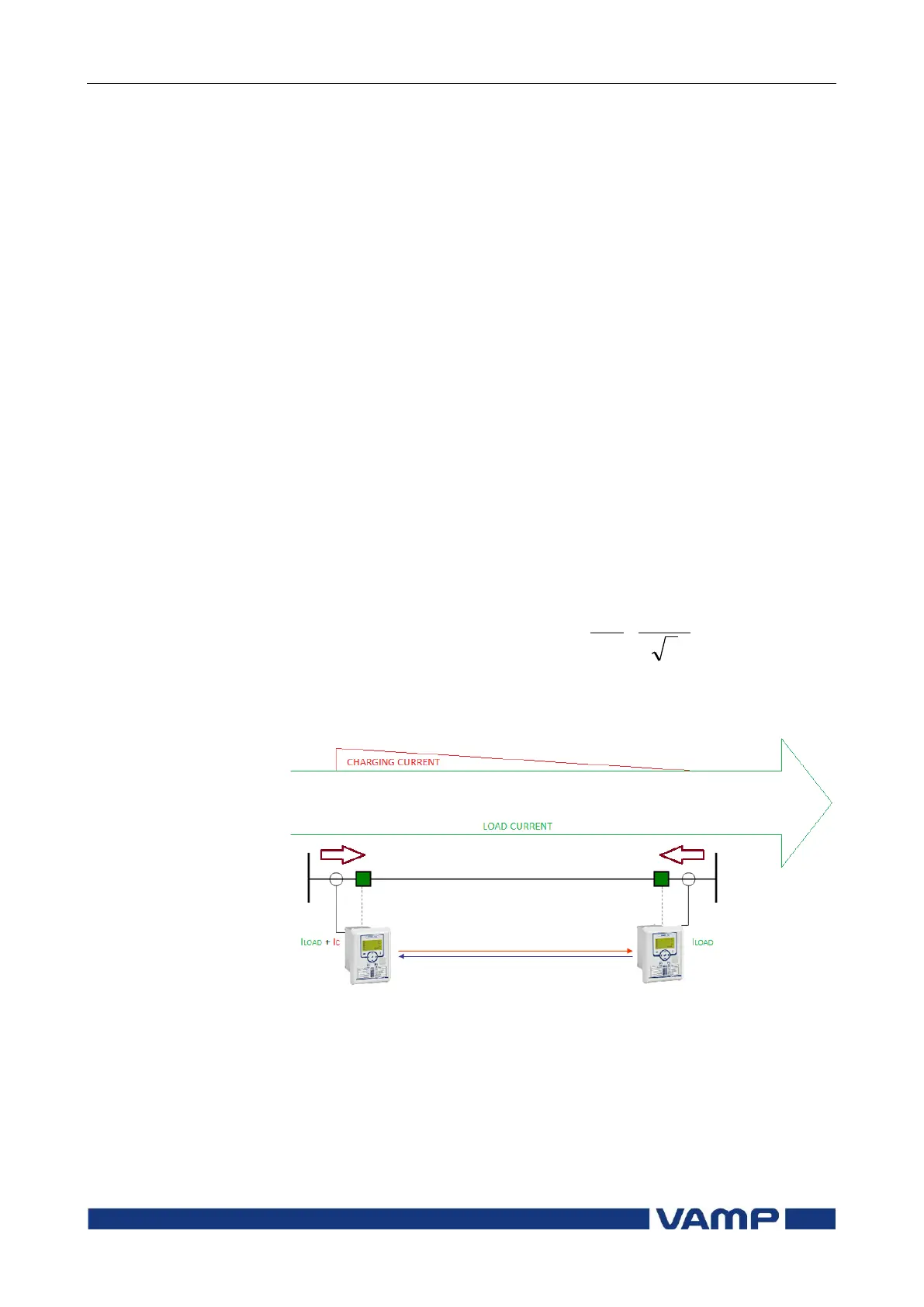
2.12.1. Capacitive charging current
Major charging currents can be expected on cable or hybrid
feeders. The charging current of the cable will increase
according the lengt of the circuit. The capacitive charging
current leads the feeder load current and therefore is causing
differential (phase and magnitude) to the protected feeder.
Steady state difference in currents will have an impact on the
minimum differential settings that may be used.
Equation 2.12.1-1: Capacitive charging current
Where:
l = Cable length (km)
I
C
= Charging current (amperes)
f = Frequency
C = Cable capacitance ( µF / km)
U = Voltage to neutral (kV)
Example: 32km of certain 15kV cable:
3
10
3
15
23.05014.3232
kV
km
F
HzkmI
C
will cause about 20A of constant charging current. In this case
differential stage should be set above 20A.
Figure 2.12.1-1 Behaviour of constant charging current
NOTE! When cable feeder is energized there will be significant transient
charging current. The frequency of this transient is above basic
component and does not effect to the differential calculation.
 Loading...
Loading...