64
Fig. 4-13
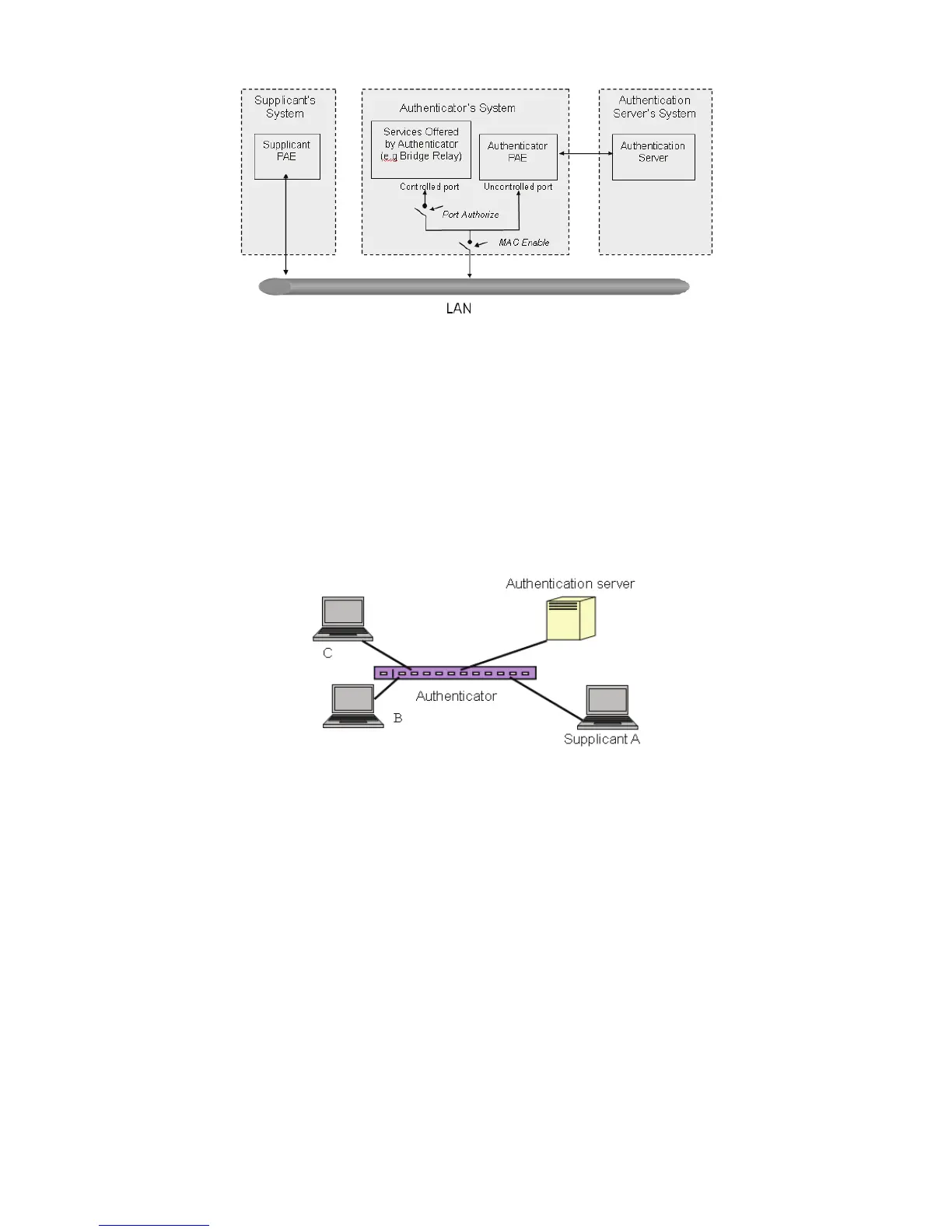
In the Fig. 4-14, this is the typical configuration, a single supplicant, an authenticator and an
authentication server. B and C is in the internal network, D is the Authentication server running RADIUS.
The switch at the central location acts as the Authenticator connecting to PC A and A is a PC outside the
controlled port, running Supplicant PAE. In this case, PC A wants to access the services on device B and
C. First, it must exchange the authentication message with the authenticator on the port it connected via
EAPOL packet. The authenticator transfers the supplicant’s credentials to Authentication server for
verification. If successful, the authentication server will provide the authenticator the grant. PC A, then, is
allowed to access B and C via the switch. If there are two switches directly connected together instead of
single one, for the link connecting two switches, it may have to act two port roles at the end of the link:
authenticator and supplicant, because the traffic is bi-directional.
Fig. 4-14
The Fig. 4-15 shows the procedure of 802.1x authentication. There are steps for the login based
on 802.1x port access control management. The protocol used in the right side is EAPOL and the left side
is EAP.
1. At the initial stage, the supplicant A is unauthenticated and a port on switch acting as an
authenticator is in unauthorized state. So the access is blocked in this stage.
2. Initiating a session. Either authenticator or supplicant can initiate the message exchange.
If supplicant initiates the process, it sends EAPOL-start packet to the authenticator PAE
and authenticator will immediately respond EAP-Request/Identity packet.
3. The authenticator always periodically sends EAP-Request/Identity to the supplicant for
requesting the identity it wants to be authenticated.
4. If the authenticator doesn’t send EAP-Request/Identity, the supplicant will initiate EAPOL-
Start the process by sending to the authenticator.
5. Next, the Supplicant replies an EAP-Response/Identity to the authenticator. The
authenticator will embed the user ID into Radius-Access-Request command and send it
to the authentication server for confirming its identity.
D
 Loading...
Loading...