4 Output Specifications
Data output from Xsens DOT is represented in different coordinate systems. Each data
output is explained below.
4.1 Coordinate systems
4.1.1 Sensor coordinate system
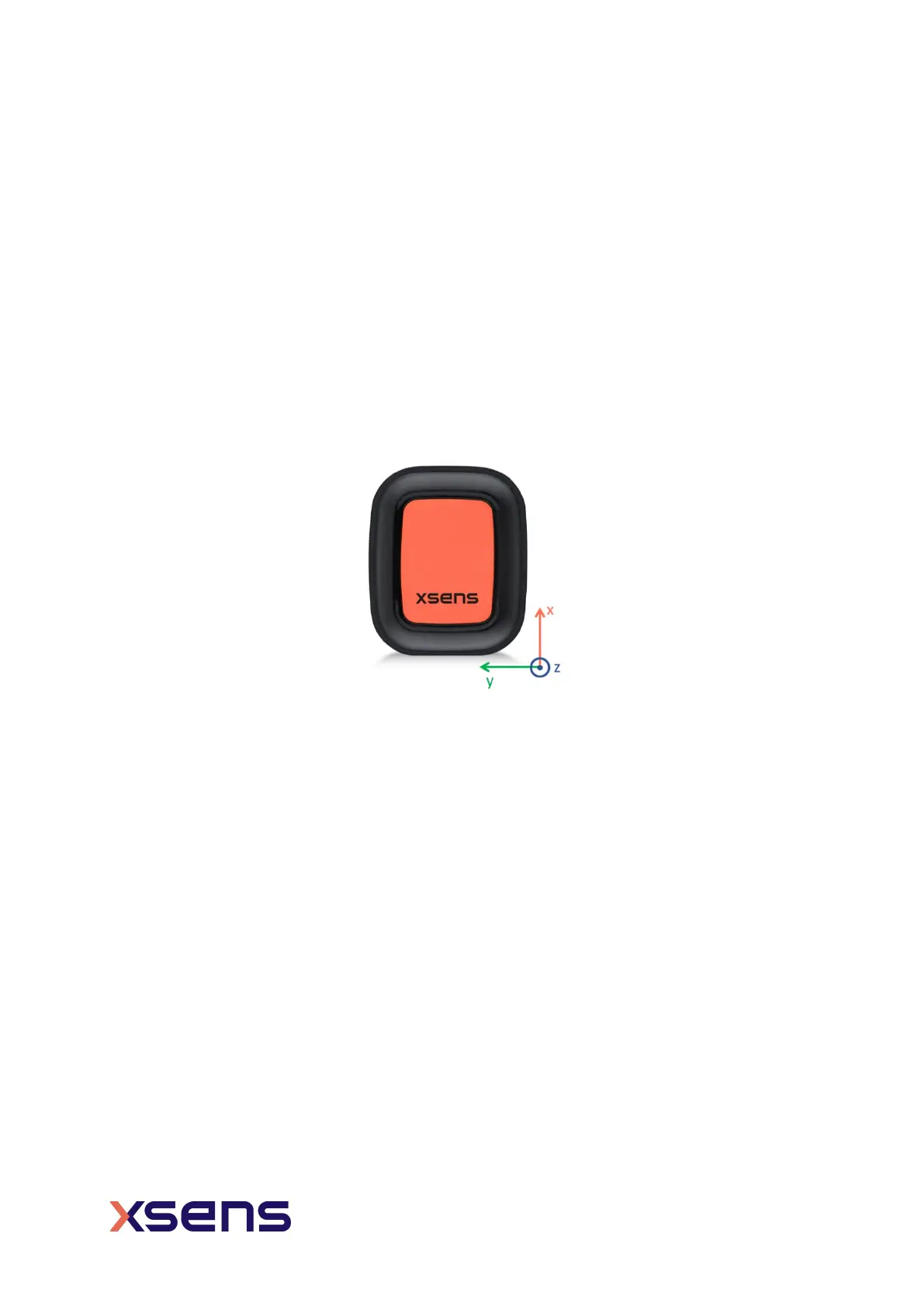
The sensor coordinate system (S) is a right-handed coordinate Cartesian system that
is body-fixed to the sensor. Depicted below is the sensor coordinate system on DOT, using
small x, y and z.
Figure 12: Xsens DOT sensor coordinate system
4.1.2 Orientation coordinate system
By default, the local earth-fixed reference coordinate system (L) used is defined as
a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system with:
• X positive to the East (E).
• Y positive to the North (N).
• Z positive when pointing up (U).
This coordinate system is known as East-North-Up (ENU) and is the standard in inertial
navigation for aviation and geodetic applications. With the default ENU (L) coordinate
system, Xsens yaw output is defined as the angle between East (X) and the horizontal
projection of the sensor x-axis, positive about the local vertical axis (Z) following the right-
hand rule. The origin of the reference frame is located in correspondence of the location of
the accelerometer. For additional information on the position of the accelerometer, check
out the Xsens DOT technical drawing at chapter 5.4.
The orientation calculated by Xsens DOT is the orientation of the sensor coordinate system
(S) with respect to the local earth coordinate system (L). Xsens DOT can output a North
referenced Yaw, also referred to as Heading. By default, the orientation output is in the
 Loading...
Loading...