| Traditional Deployment Methods | 60
• Configuring Route Traversal
Port Forwarding
The most common scenario is deploying the VCS in an intranet (behind a firewall). You must assign a static
private IP address to the VCS. In the meantime, do port forwarding on the firewall.
Port forwarding is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication
request from one address and port number combination to another while the packets are traversing a
network gateway, such as a router or firewall.
To receive a public-to-private call, you must forward the following ports to the public network on your router
or firewall.
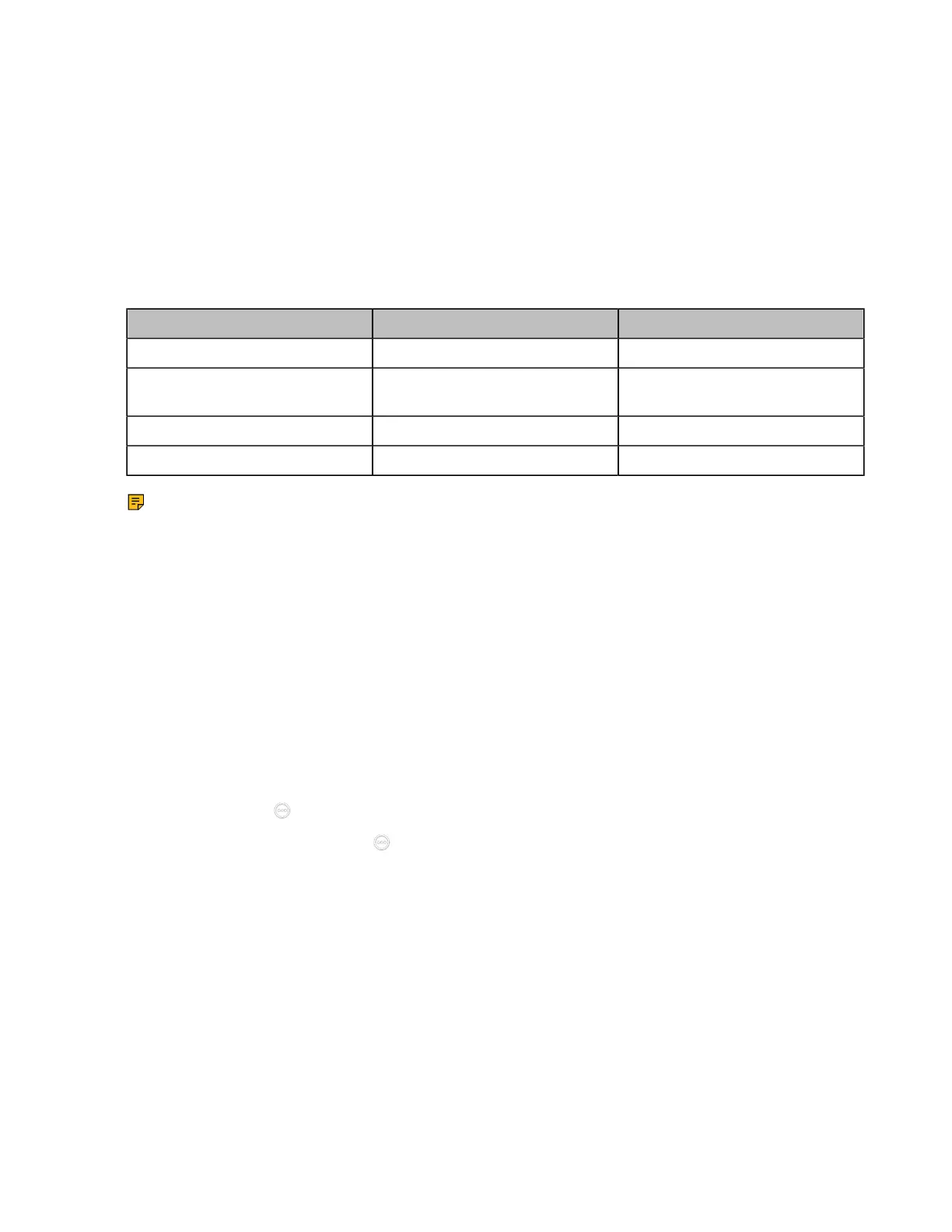
Port Port Static NAT/Type
H.323 1719-1720 UDP/TCP
Control and media for audio,
video, content, and data/FECC
50000-51000 TCP/UDP
Web management port (optional) 443 TCP
SIP (optional) 5060-5061 TCP/UDP
Note: Forwarding the ports to the public network may cause security problems and you can
prevent the endpoint from being attacked by adding a blacklist.
Related tasks
Adding Meeting Blocklists
Configuring NAT
You can use H.323 protocol to make private-to-public calls after you configure the port forwarding and
enable the static NAT feature. If you want to use SIP protocol to make private-to-public calls, you also need
to enable the static NAT settings for the SIP protocol.
Procedure
1. Do one of the following:
• On your web user interface, go to Network > NAT/Firewall > NAT Configuration.
• On your VCS: go to More > Settings > Network Setting > Wired Network > NAT/Firewall > NAT.
For VP59, tap > Settings > Network Setting > Wired Network > NAT/Firewall > NAT.
•
On your CTP20/CTP18 , tap > Settings > Network Setting > Host Network > NAT/Firewall >
NAT.

 Loading...
Loading...