<Appendix 3 For ISC (Inductive Conductivity)>
App.3-1
IM 12A01A02-01E 8th Edition : Oct. 01, 2015-00
Appendix 3
For ISC (Inductive Conductivity)
n Temperature compensation
The conductivity of a solution is very dependent on temperature. Typically for every 1°C
change in temperature the solution conductivity will change by approximately 2%. The effect of
temperature varies from one solution to another and is determined by several factors like solution
composition, concentration and temperature range. A coefcient (α) is introduced to express the
amount of temperature inuence in % change in conductivity/°C. In almost all applications this
temperature inuence must be compensated before the conductivity reading can be interpreted
as an accurate measure of concentration or purity.
l NaCl (standard temperature compensation)
The FLXA202/FLXA21 has the default temperature compensation function based on a sodium
chloride (NaCl) solution. This function can be used for various applications and is compatible with
the NaCl compensation function of typical laboratory or portable instruments.
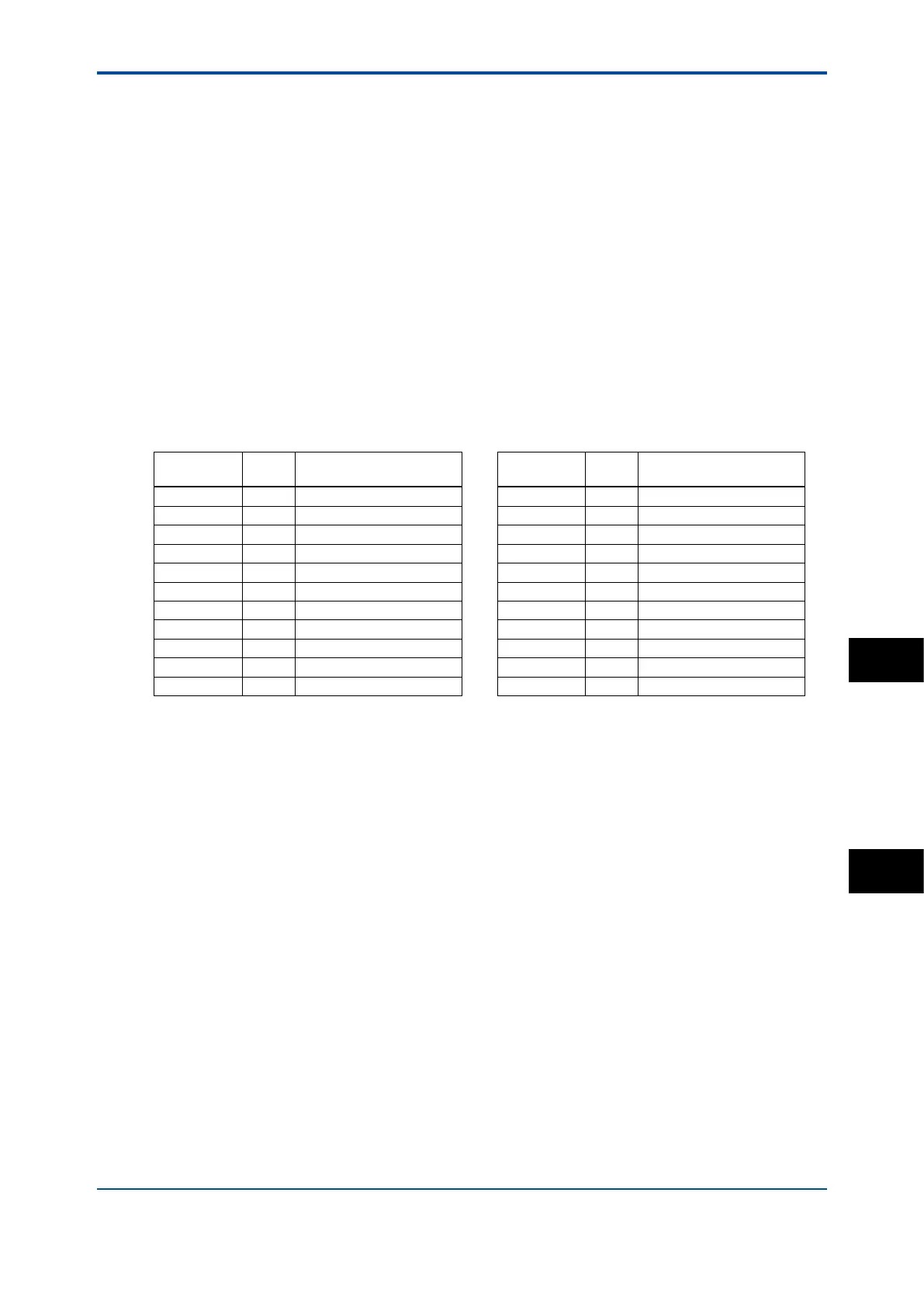
Table 1 NaCl compensation according to IEC 60746-3 with Tref. = 25°C
Temperature
(°C)
Ratio*
Temperature compensa-
tion coefcient (%/°C)
Temperature
(°C)
Ratio*
Temperature compensa-
tion coefcient (%/°C)
0 0.54 1.8 100 2.68 2.2
10 0.72 1.9 110 2.90 2.2
20 0.90 2.0 120 3.12 2.2
25 1.00 — 130 3.34 2.2
30 1.10 2.0 140 3.56 2.2
40 1.31 2.0 150 3.79 2.2
50 1.53 2.1 160 4.03 2.2
60 1.76 2.2 170 4.23 2.2
70 1.99 2.2 180 4.42 2.2
80 2.22 2.2 190 4.61 2.2
90 2.45 2.2 200 4.78 2.2
*: The ratio of the conductivity at respective temperatures to the conductivity at the reference temperature.
l Temperature compensation coefcient (TC)
Set the temperature compensation coefcient based on the degree of inuence of temperature
on the conductivity (%/°C).
If the temperature compensation coefcient of the sample solution is known from laboratory
experiments or has been previously determined, enter the value.
The setting range is between 0.00 and 10.0%. By combining with the reference temperature
setting, a linear compensation function can be obtained. This is applicable to all kinds of chemical
solution.
<Congure calculated temperature coefcient (TC).>
Follow routing
Commissioning >> Measurement setup >> Temp.compensation >> T.C.
Enter the temperature coefcient calculated from the following formula:
App.
ISC
 Loading...
Loading...