IM 12D08B02-01E
Parameter setting 5-5
5-2-4. Temperature compensation
1. Why temperature compensation?
The conductivity of a solution is very dependent on temperature. Typically for every 1 °C change in
temperature the solution conductivity will change by approximately 2 %. The effect of temperature varies
from one solution to another and is determined by several factors like solution composition, concentra-
tion and temperature range. A coefficient () is introduced to express the amount of temperature influ-
ence in % change in conductivity/°C. In almost all applications this temperature influence must be com-
pensated before the conductivity reading can be interpreted as an accurate measure of concentration or
purity.
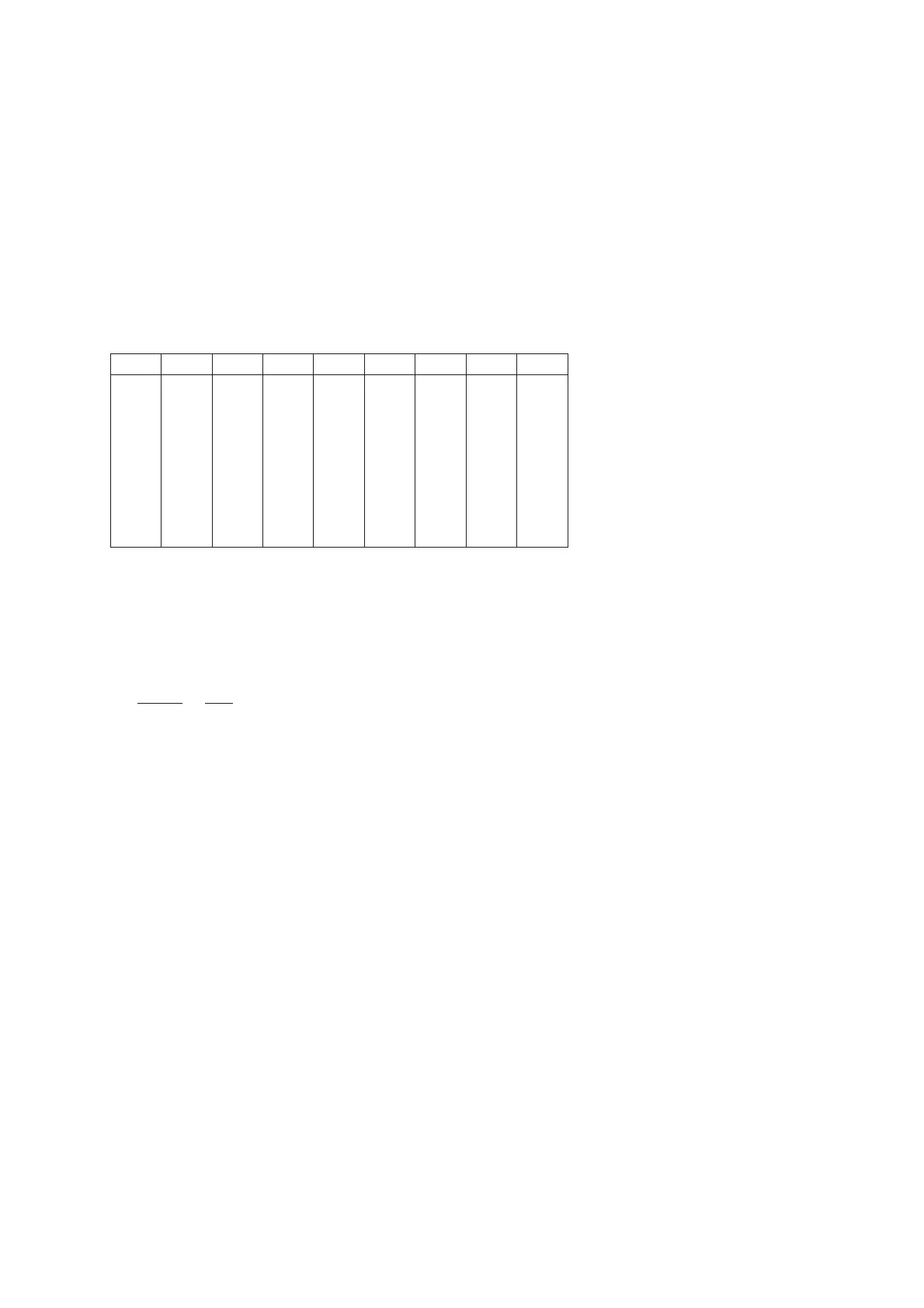
Table 5-1. NaCl-compensation according to IEC 60746-3 with Tref = 25 °C
TKtα TKtα TKtα
0 0.54 1.8 60 1.76 2.2 130 3.34 2.2
10 0.72 1.9 70 1.99 2.2 140 3.56 2.2
20 0.90 2.0 80 2.22 2.2 150 3.79 2.2
25 1.0 --- 90 2.45 2.2 160 4.03 2.2
30 1.10 2.0 100 2.68 2.2 170 4.23 2.2
40 1.31 2.0 110 2.90 2.2 180 4.42 2.2
50 1.53 2.1 120 3.12 2.2 190 4.61 2.2
200 4.78 2.2
2. Standard temperature compensation
From the factory the EXA is calibrated with a general temperature compensation function based on a
sodium chloride salt solution. This is suitable for many applications and is compatible with the compen-
sation functions of typical laboratory or portable instruments.
A temperature compensation factor is derived from the following equation:
=
K
t
- K
ref
x
100
T - T
ref
K
ref
In which:
= Temperature compensation factor
(in %/ °C)
T = Measured temperature (°C)
K
t
= Conductivity at T
T
ref
= Reference temperature (°C)
K
ref
= Conductivity at T
ref
3. Manual temperature compensation
If the standard compensation function is found to be inaccurate for the sample to be measured, the
transmitter can be set manually for a linear factor on site to match the application.
The procedure is as follows:
1. Take a representative sample of the process liquid to be measured.
2. Heat or cool this sample to the reference temperature of the transmitter (usually 25 °C).
3. Measure the conductivity of the sample with the EXA and note the value.
4. Bring the sample to the typical process temperature (to be measured with the EXA).
5. Adjust the display indication to the noted value at the reference temperature.
6. Check that the temperature compensation factor has been changed.
7. Insert the conductivity cell into the process again.
4. Other possibilities (section 5-4)
1. Enter calculated coefficient.
2. Enter matrix temperature compensation.

 Loading...
Loading...










