3-10
Making Time Domain Measurements
Making Reflection Response Measurements
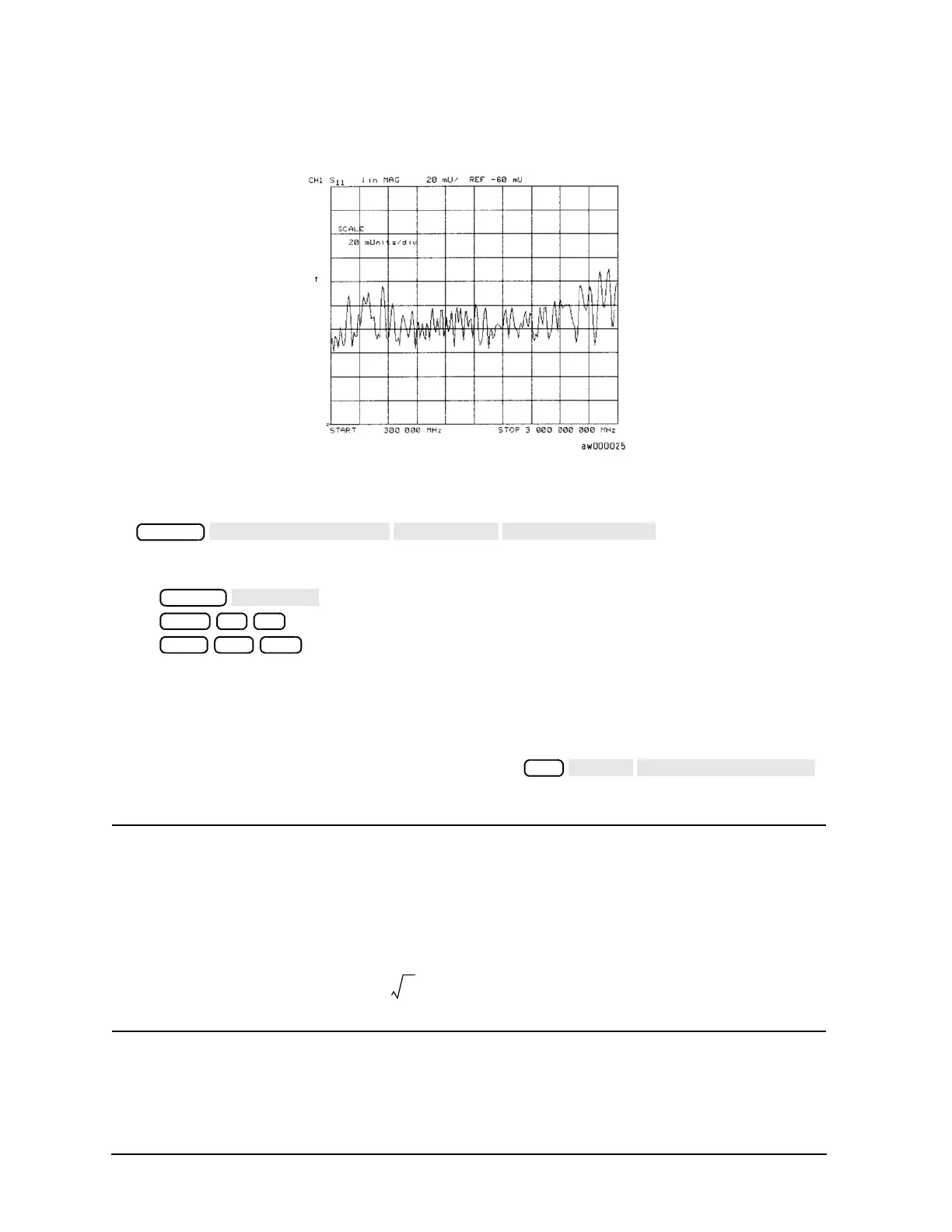
Figure 3-8 Device Response in the Frequency Domain
5. To transform the data from the frequency domain to the time domain, press:
6. To view the time domain over the length (<4 meters) of the cable under test, press:
The stop time corresponds to the length of the cable under test. The energy travels about 1 foot per
nanosecond, or 0.3 meter/ns, in free space. Most cables have a relative velocity of about 0.66 the speed
in free space. Calculate about 3 ns/foot, or 10 ns/meter, for the stop time when you are measuring the
return trip distance to the cable end.
7. To enter the relative velocity of the cable under test, press
and enter a velocity factor for your cable under test.
NOTE Most cables have a relative velocity of 0.66 (for polyethylene dielectrics) or 0.7 (for PTFE
dielectrics). If you would like the markers to read actual one-way distance rather than return
trip distance, enter one-half the actual velocity factor. Then the markers will read the actual
one-way distance to the reflection of interest rather than the "electrical length" that
assumes a relative velocity of 1.
where
r
is the relative permittivity of the cable dielectric.
Velocity Factor
1
r
--------=

 Loading...
Loading...




