7- 36
Operating Concepts
Noise Reduction Techniques
Noise Reduction Techniques
The key is used to access three different noise reduction techniques: sweep-to-sweep averaging,
display smoothing, and variable IF bandwidth. All of these can be used simultaneously. Averaging and
smoothing can be set independently for each channel, and the IF bandwidth can be set independently if the
stimulus is uncoupled.
Averaging
Averaging computes each data point based on an exponential average of consecutive sweeps weighted by a
user-specified averaging factor. Each new sweep is averaged into the trace until the total number of sweeps
is equal to the averaging factor, for a fully averaged trace. Each point on the trace is the vector sum of the
current trace data and the data from the previous sweep. A high averaging factor gives the best
signal-to-noise ratio, but slows the trace update time. Doubling the averaging factor reduces the noise by 3
dB. Averaging is used for ratioed measurements: if it is attempted for a single-input measurement (e.g. A or
B), the message CAUTION: AVERAGING INVALID ON NON-RATIO MEASURE is displayed. The effect
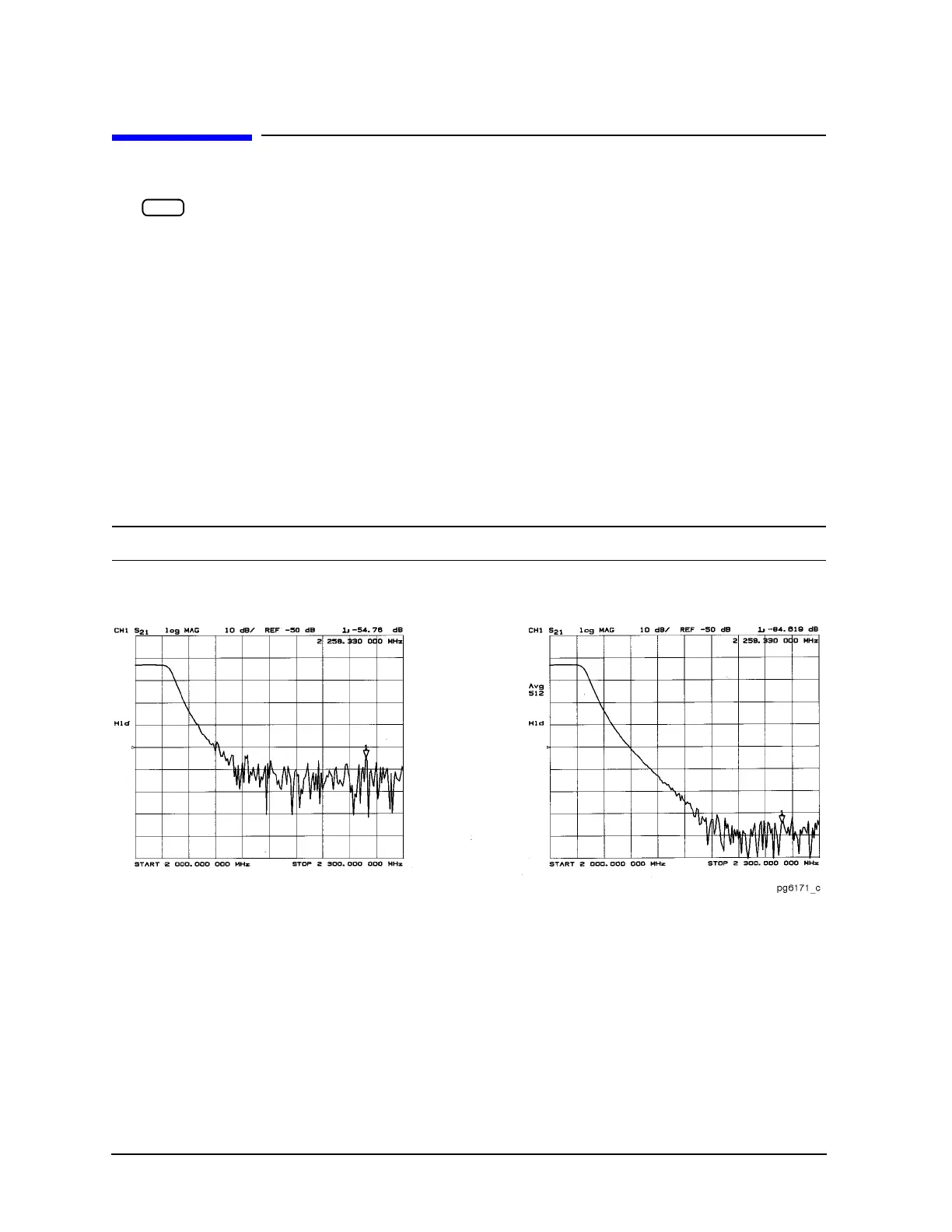
of averaging on a log magnitude format trace is shown in
Figure 7-18.
NOTE If you switch power ranges with averaging on, the average will restart.
Figure 7-18 Effect of Averaging on a Trace
 Loading...
Loading...
















