SoftwareDescription
FlexibleAutomation
5−11
5.3 Program Execution
Program execution is defined in the organizational modules. The user
can influence the system performance, e.g. start−up, by means of the
available OMs. Events like error detection, interrupt inputs and time−
outs during program execution result in the automatic call of the respec
tive organizational module.
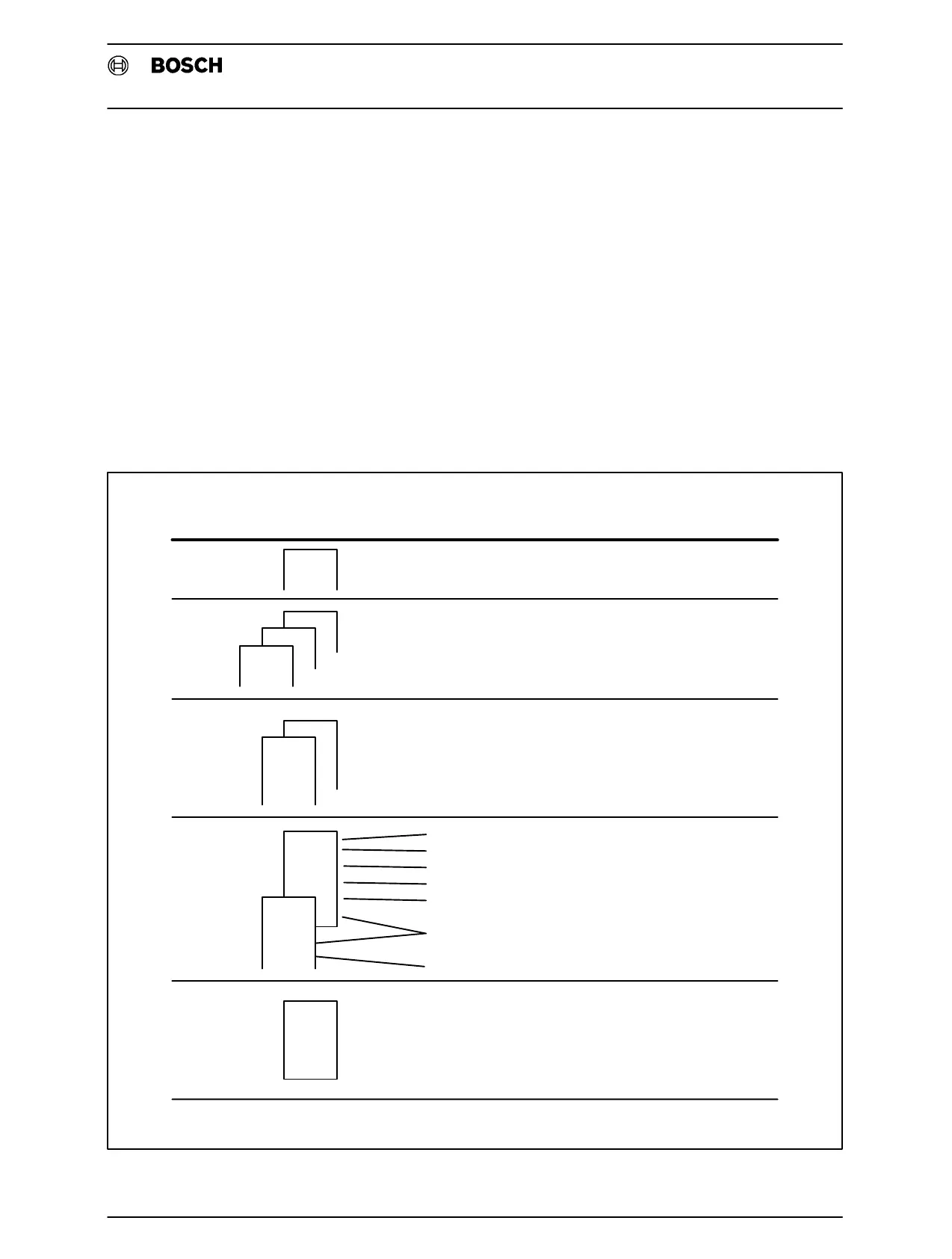
The following table gives a summary of the criteria which define the or
ganizational modules for a given type of program execution. The user
program can be executed in cyclic, interrupt−controlled and time−con
trolled manner.
OMNo. Execution
1
OM1
Cyclic
Interrupt−controlled,InterruptInputs
OM4
OM3
OM2
2
3
4
EI1.0
EI1.1
1stPriority
2ndPriority
3rdPriorityEI1.2
OM6
OM55
6
OM8
OM77
8
OM9
9
Time−controlledExecution
TimeBaseprogrammableinOM7
TimeBase2forOM6
−
−
−
−
−
Start−upfollowing"poweron"
Defineremanencyrange(T,C,M)
Allocationlistgeneration
Definewatchdog
Definetimebasesfortime−controlled
execution(OM5,6)
Copyanydatamoduletothedata
bufferrange
Start−upfromthestopstate
−
−
ErrorDetection
−
−
−
−
Cycletimeexceeded
Modulenestingdepth>32
Invalidcommand
Callofanon−existingmodule
TimeBase1forOM5withpriority
Fig.5−6Organizational Modules
 Loading...
Loading...