42-16
Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide
OL-10088-01
Chapter 42 Monitoring the Security Appliance
Configuring and Managing Logs
Sending All Messages in a Class to a Specified Output Destination
When you configure all messages in a class to go to a type of output destination, this configuration
overrides the configuration in the specific output destination command. For example, if you specify that
messages at level 7 should go to the log buffer, and you also specify that ha class messages at level 3
should go to the buffer, then the latter configuration takes precedence.
To configure the security appliance to send an entire system log message class to a configured output
destination, enter the following command:
hostname(config)# logging class message_class {buffered | console | history | mail |
monitor | trap} [severity_level]
Where the message_class argument specifies a class of system log messages to be sent to the specified
output destination. See Table 42-2 for a list of system log message classes.
The buffered, history, mail, monitor, and trap keywords specify the output destination to which system
log messages in this class should be sent. The history keyword enables SNMP logging. The monitor
keyword enables Telnet and SSH logging. The trap keyword enables syslog server logging. Select one
destination per command line entry. If you want to specify that a class should go to more than one
destination, enter a new command for each output destination.
The severity_level argument further restricts the system log messages to be sent to the output destination
by specifying a severity level. For more information about message severity levels, see the “Severity
Levels” section on page 42-23.
The following example specifies that all system log messages related to the class ha (high availability,
also known as failover) with a severity level of 1 (alerts) should be sent to the internal logging buffer.
hostname(config)# logging class ha buffered alerts
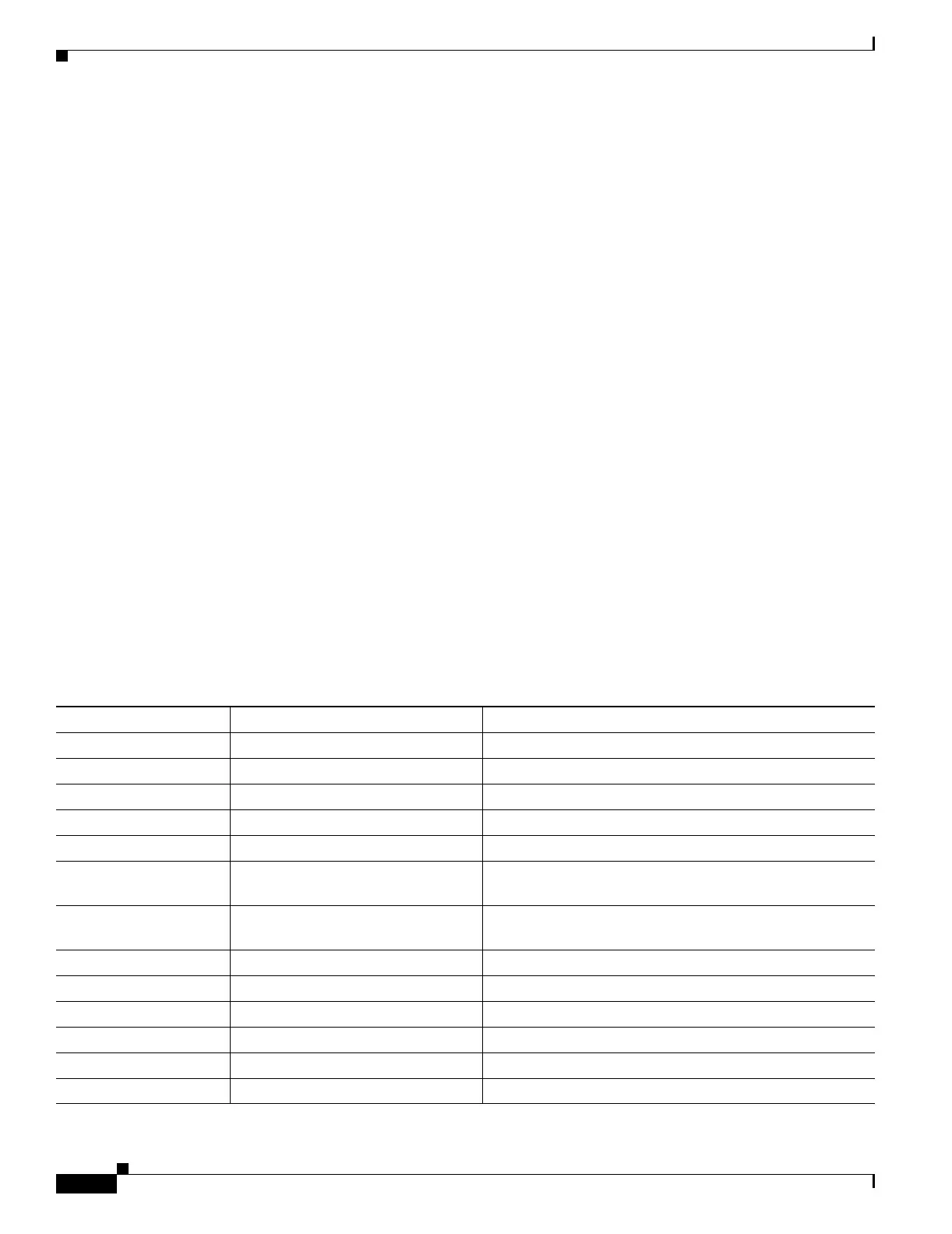
Table 42-2 lists the system log message classes and the ranges of system log message IDs associated with
each class.
Table 42-2 System Log Message Classes and Associated Message ID Numbers
Class Definition System Log Message ID Numbers
ha Failover (High Availability) 101, 102, 103, 104, 210, 311, 709
rip RIP Routing 107, 312
auth User Authentication 109, 113
bridge Transparent Firewall 110, 220
config Command interface 111, 112, 208, 308
sys System 199, 211, 214, 216, 306, 307, 315, 414, 604, 605, 606, 610,
612, 614, 615,701, 711
session User Session 106, 108, 201, 202, 204, 302, 303, 304, 305, 314, 405, 406,
407, 500, 502, 607, 608, 609, 616, 620, 703, 710
ip IP Stack 209, 215, 313, 317, 408
snmp SNMP 212
vpdn PPTP and L2TP Sessions 213, 403, 603
vpn IKE and IPSec 316, 320, 402, 404, 501, 602, 702, 713, 714, 715
ospf OSPF Routing 318, 409, 503, 613
np Network Processor 319

 Loading...
Loading...











