8-2
Cisco ONS 15454 SONET/SDH ML-Series Multilayer Ethernet Card Software Feature and Configuration Guide, R4.0
78-15224-02
Chapter 8 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
Understanding IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
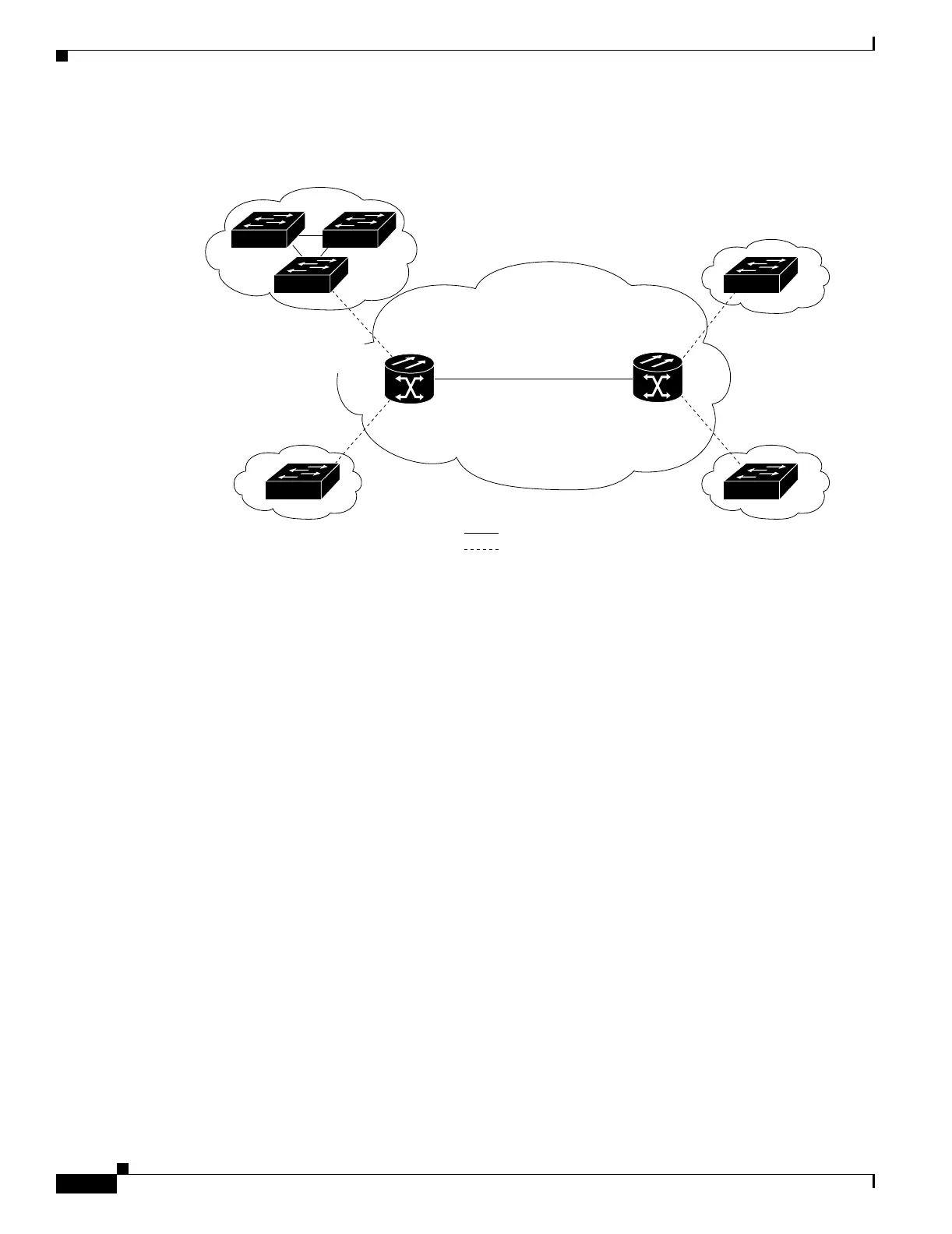
Figure 8-1 IEEE 802.1Q Tunnel Ports in a Service-Provider Network
Packets coming from the customer trunk port into the tunnel port on the ML-Series card are normally
IEEE 802.1Q-tagged with appropriate VLAN ID. The tagged packets remain intact inside the ML-Series
card and, when they exit the trunk port into the service provider network, are encapsulated with another
layer of an IEEE 802.1Q tag (called the metro tag) that contains the VLAN ID unique to the customer.
The original IEEE 802.1Q tag from the customer is preserved in the encapsulated packet. Therefore,
packets entering the service-provider infrastructure are double-tagged, with the outer tag containing the
customer’s access VLAN ID, and the inner VLAN ID being the VLAN of the incoming traffic.
When the double-tagged packet enters another trunk port in a service provider ML-Series card, the outer
tag is stripped as the packet is processed inside the switch. When the packet exits another trunk port on
the same core switch, the same metro tag is again added to the packet. Figure 8-2 on page 8-3 shows the
structure of the double-tagged packet.
Customer A
VLANs 1 to 100
Customer B
VLANs 1 to 200
Customer B
VLANs 1 to 200
Customer A
VLANs 1 to 100
Tunnel port
VLAN 40
Tunnel port
VLAN 40
Trunk
Asymmetric link
Tunnel port
VLAN 30
ONS 15454
with ML100T-12
POS
0
POS
0
Router_A
SONET STS-N
ONS 15454
with ML100T-12
Router_B
Fast Ethernet 1
Fast Ethernet 0
Fast Ethernet 1
Fast Ethernet 0
83233
Tunnel port
VLAN 30

 Loading...
Loading...