Genesis II Select
™
User’s & Installation Manual
16/September/2015
46
responses which are readily identied by a qualied operator. Signs
that a speed is spurious can include the following characteristics:
t "WBMJEUBSHFUNPUPSWFIJDMFTQFFEJOUIFPQFSBUJPOBMSBOHFXJMM
always override the source of interference and will be conrmed
by the audio component.
t 5IF%PQQMFSUPOFXJMMMBDLUIFQJUDIBOEDMBSJUZDPNQPOFOU
t 4QFFETBSFJSSFHVMBS
t 4QFFETBQQFBSUPUSBDLXJUIUIFFOHJOFTQFFET
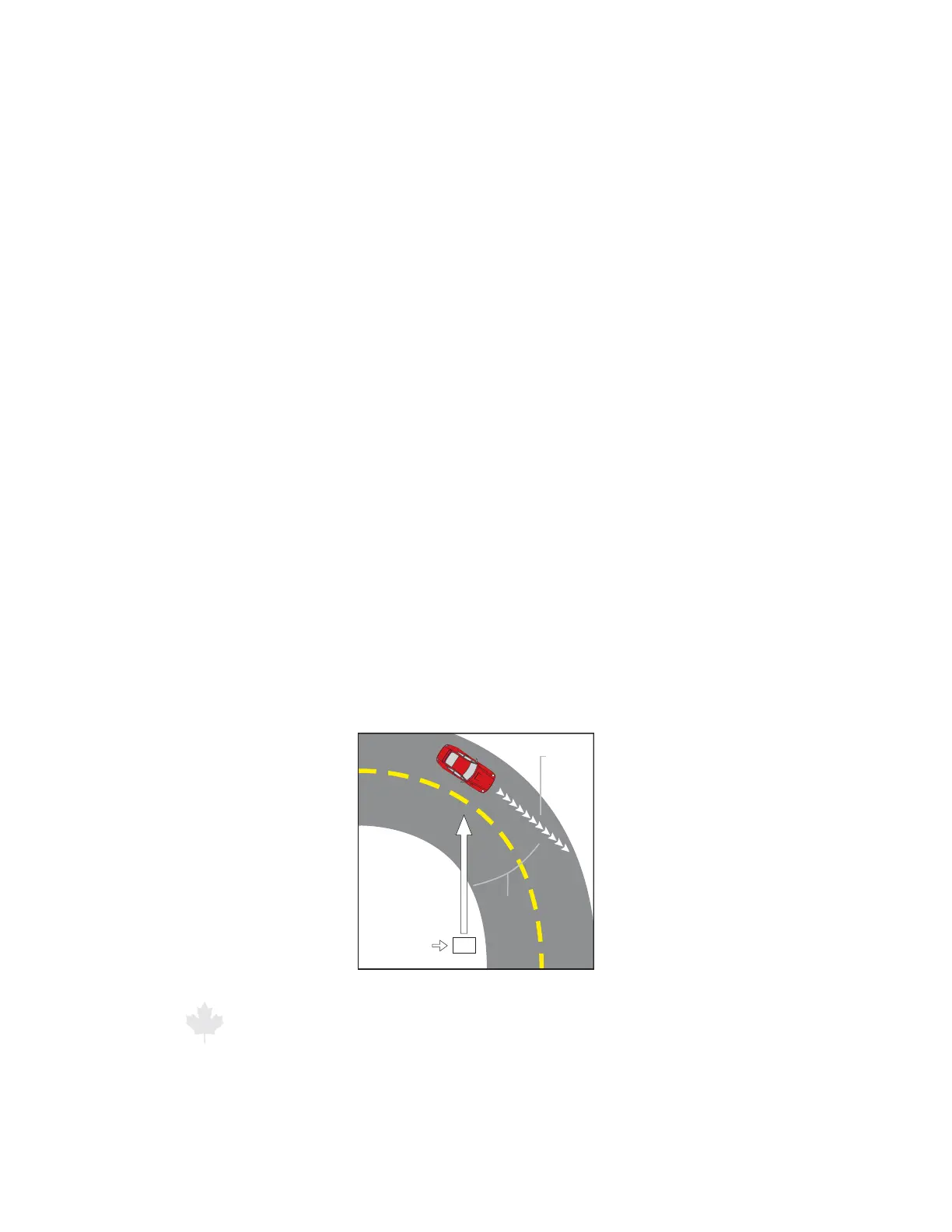
7.2.1 Angular Interference (Cosine Eect)
The cosine eect causes the radar unit to display a speed, which
is always lower than the actual target motor vehicle speed. This
condition exists when the target motor vehicle’s path is not parallel
to the antenna, including conditions such as the motor vehicle
traveling on a curve or a hill.
As the angle between the beam of the antenna and the target
motor vehicle increases, the displayed speed decreases. Ideally,
an angle of zero (0) degrees is preferable, because the displayed
speed is the actual target motor vehicle speed. However, in all uses
of police radar, the radar device is always at a slight angle to the
target motor vehicle to avoid collisions.
Velocity
Vector
Angle
Radar
Figure 7.2.1
An angle between the antenna and the target motor vehicle
causes the cosine eect.

 Loading...
Loading...