Chapter 5 FUNCTION CODES
5.1 Function Code Tables
Function codes enable the FVR-Micro of inverters to be set up to match your system requirements.
Each function code consists of a 3-letter alphanumeric string. The first letter is an alphabet that
identifies its group and the following two letters are numerals that identify each individual code in the
group. The function codes are classified into seven groups: Fundamental Functions (F codes),
Extension Terminal Functions (E codes), Control Functions (C codes), Motor 1 Parameters (P
codes), High Performance Functions (H codes), Application Functions (J codes) and Link
Functions (y codes). To determine the property of each function code, set data to the function code.
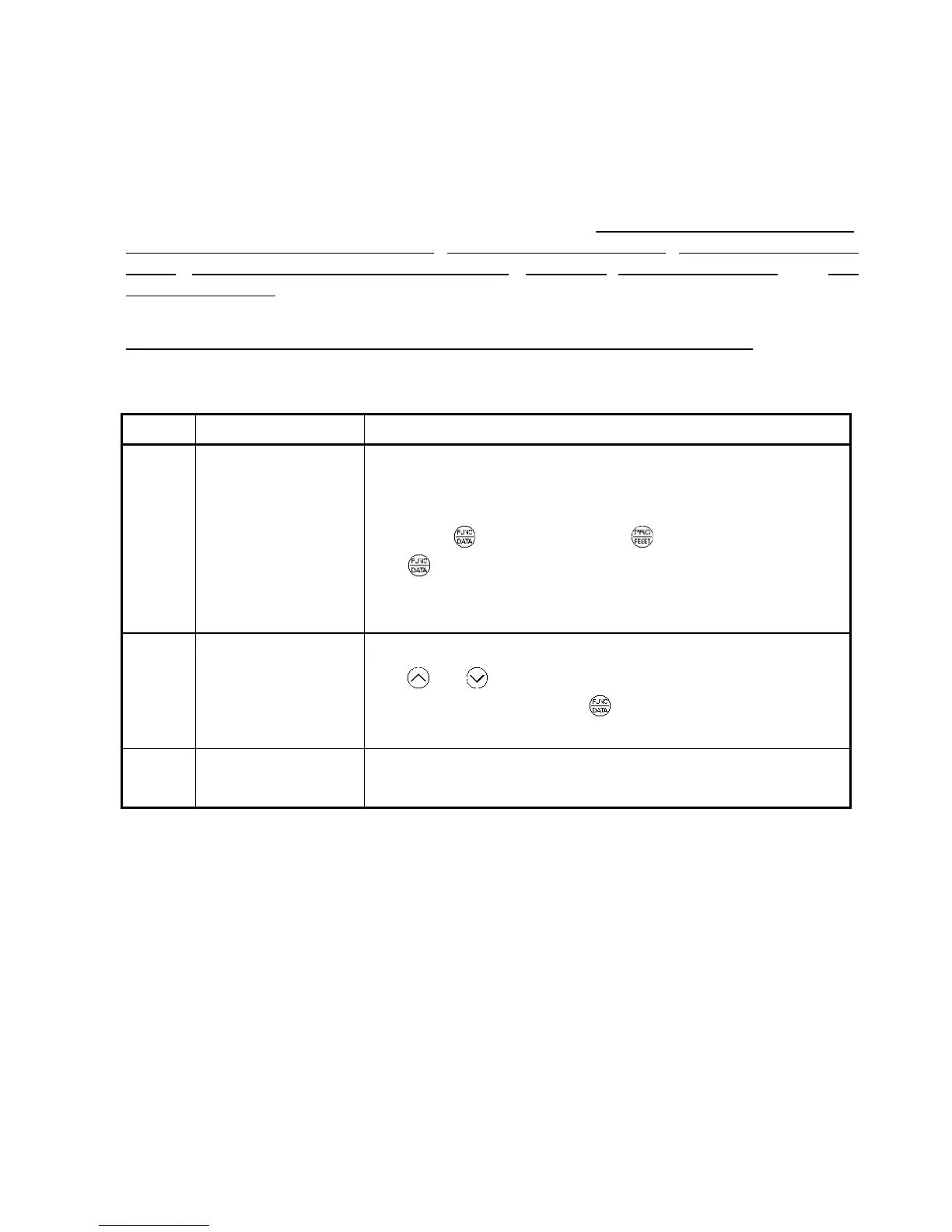
Changing, validating, and saving function code data when the motor is running
Function codes are indicated by the following based on whether they can be changed or not when
the inverter is running:
Notation Change when running Validating and saving function code data
Y*
Possible
If the data of the codes marked with Y* is changed, the
change will immediately take effect; however, the change is
not saved into the inverter's memory. To save the change,
press the key. If you press the key without pressing
the key to exit the current state, then the changed data
will be discarded and the previous data will take effect for the
inverter operation.
Y
Possible
The data of the codes marked with Y can be changed with
the and keys regardless of whether the motor is
running or not. Pressing the key will make the change
effective and save it into the inverter's memory.
N
Impossible
—
 Loading...
Loading...